|
Rothia Mucilaginosa
''Rothia mucilaginosa'' is a Gram-positive, coagulase-negative, encapsulated, non-spore-forming and non-motile coccus, present in clusters, tetrads or pairs that is a part of the normal oropharyngeal flora. Belonging to the family ''Micrococcaceae'', it was first isolated from the mucous membrane of the cheek and gingiva. It is an oral commensal, that has been linked to causing severe bacteremia in immunocompromised patients. This bacterium has also been shown to form biofilms, similar to that of '' Pseudomonas aeruginosa''. ''R. mucilaginosa'' is a cohabitant in the lower airways of patient with bronchiectasis Morphology ''Rothia mucilaginosa'' is a Gram-positive, coagulase-negative, encapsulated, non-spore-forming and non-motile coccus, present in clusters, tetrads or pairs. ''R. mucilaginosa'' can easily be confused for the bacteria from the genera '' Micrococcus'' and ''Staphylococcus''. One way that it can be distinguished from those two is by its strong adherence to the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter Migula
Emil Friedrich August Walter (or Walther) Migula (born 1863 in Żyrowa, Poland; died 1938 in Eisenach, Germany) was a Poland-born German botanist. In 1890, he was habilitated for botany at Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, where he spent several years as a professor. At Karlsruhe, he also worked in the bacteriology department of the Food Research Institute. He was Professor of Botany at the research academy at Eisenach. He published many articles on the subjects of cryptogamic botany, bacteriology, and plant physiology. He is remembered for describing the bacterial genus ''Pseudomonas'', and for publication of ''Kryptogamen-Flora von Deutschland, Deutsch-Österreich und der Schweiz'' ryptogamic Flora of Germany, Austria, and Switzerland">Austria">ryptogamic Flora of Germany, Austria, and Switzerland">Austria.html" ;"title="ryptogamic Flora of Germany, Austria">ryptogamic Flora of Germany, Austria, and Switzerland a work connected with Otto Wilhelm Thomé's ''Flora von Deut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
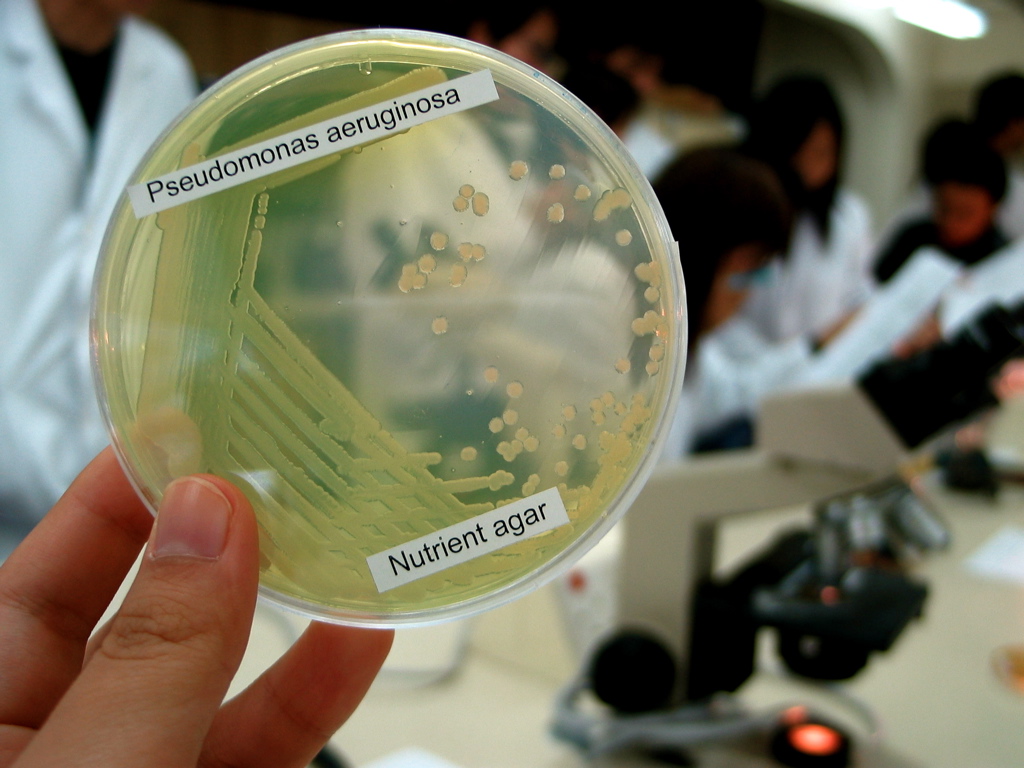
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa
''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is a common encapsulated, gram-negative, aerobic– facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium that can cause disease in plants and animals, including humans. A species of considerable medical importance, ''P. aeruginosa'' is a multidrug resistant pathogen recognized for its ubiquity, its intrinsically advanced antibiotic resistance mechanisms, and its association with serious illnesses – hospital-acquired infections such as ventilator-associated pneumonia and various sepsis syndromes. The organism is considered opportunistic insofar as serious infection often occurs during existing diseases or conditions – most notably cystic fibrosis and traumatic burns. It generally affects the immunocompromised but can also infect the immunocompetent as in hot tub folliculitis. Treatment of ''P. aeruginosa'' infections can be difficult due to its natural resistance to antibiotics. When more advanced antibiotic drug regimens are needed adverse eff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrococcus
''Micrococcus'' (mi’ krō kŏk’ Əs) is a genus of bacteria in the Micrococcaceae family. ''Micrococcus'' occurs in a wide range of environments, including water, dust, and soil. Micrococci have Gram-positive spherical cells ranging from about 0.5 to 3 micrometers in diameter and typically appear in tetrads. They are catalase positive, oxidase positive, indole negative and citrate negative. ''Micrococcus'' has a substantial cell wall, which may comprise as much as 50% of the cell mass. The genome of ''Micrococcus'' is rich in guanine and cytosine (GC), typically exhibiting 65 to 75% GC-content. Micrococci often carry plasmids (ranging from 1 to 100 MDa in size) that provide the organism with useful traits. Some species of ''Micrococcus'', such as ''M. luteus'' (yellow) and ''M. roseus'' (red) produce yellow or pink colonies when grown on mannitol salt agar. Isolates of ''M. luteus'' have been found to overproduce riboflavin when grown on toxic organic pollutants like pyridi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staphylococcus
''Staphylococcus'' is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria in the family Staphylococcaceae from the order Bacillales. Under the microscope, they appear spherical ( cocci), and form in grape-like clusters. ''Staphylococcus'' species are facultative anaerobic organisms (capable of growth both aerobically and anaerobically). The name was coined in 1880 by Scottish surgeon and bacteriologist Alexander Ogston (1844–1929), following the pattern established five years earlier with the naming of '' Streptococcus''. It combines the prefix "staphylo-" (from grc, σταφυλή, staphylē, bunch of grapes), and suffixed by the Modern (from ). Staphylococcus was one of the leading infections in hospitals and many strains of this bacterium have become antibiotic resistant. Despite strong attempts to get rid of them, staph bacteria stay present in hospitals, where they can infect people who are most at risk of infection. Staphylococcus includes at least 43 species. Of these, nine have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronchiectasis
Bronchiectasis is a disease in which there is permanent enlargement of parts of the airways of the lung. Symptoms typically include a chronic cough with mucus production. Other symptoms include shortness of breath, coughing up blood, and chest pain. Wheezing and nail clubbing may also occur. Those with the disease often get lung infections. Bronchiectasis may result from a number of infectious and acquired causes, including measles, pneumonia, tuberculosis, immune system problems, as well as the genetic disorder cystic fibrosis. Cystic fibrosis eventually results in severe bronchiectasis in nearly all cases. The cause in 10–50% of those without cystic fibrosis is unknown. The mechanism of disease is breakdown of the airways due to an excessive inflammatory response. Involved airways ( bronchi) become enlarged and thus less able to clear secretions. These secretions increase the amount of bacteria in the lungs, resulting in airway blockage and further breakdown of the airw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
COX-2 Inhibitor
COX-2 inhibitors are a type of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that directly targets cyclooxygenase-2, COX-2, an enzyme responsible for inflammation and pain. Targeting selectivity for COX-2 reduces the risk of peptic ulceration and is the main feature of celecoxib, rofecoxib, and other members of this drug class. After several COX-2-inhibiting drugs were approved for marketing, data from clinical trials revealed that COX-2 inhibitors caused a significant increase in heart attacks and strokes, with some drugs in the class having worse risks than others. Rofecoxib (sold under the brand name Vioxx) was taken off the market in 2004 because of these concerns, while celecoxib (sold under the brand name Celebrex) and traditional NSAIDs received boxed warnings on their labels. Many COX-2-specific inhibitors have been removed from the US market. As of December 2011, only Celebrex (generic name of celecoxib) is still available for purchase in the United States. In the European ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteremia
Bloodstream infections (BSIs), which include bacteremias when the infections are bacterial and fungemias when the infections are fungal, are infections present in the blood. Blood is normally a sterile environment, so the detection of microbes in the blood (most commonly accomplished by blood cultures) is always abnormal. A bloodstream infection is different from sepsis, which is the host response to bacteria. Bacteria can enter the bloodstream as a severe complication of infections (like pneumonia or meningitis), during surgery (especially when involving mucous membranes such as the gastrointestinal tract), or due to catheters and other foreign bodies entering the arteries or veins (including during intravenous drug abuse). Transient bacteremia can result after dental procedures or brushing of teeth. Bacteremia can have several important health consequences. The immune response to the bacteria can cause sepsis and septic shock, which has a high mortality rate. Bacteria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sepsis
Sepsis, formerly known as septicemia (septicaemia in British English) or blood poisoning, is a life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs. This initial stage is followed by suppression of the immune system. Common signs and symptoms include fever, increased heart rate, increased breathing rate, and confusion. There may also be symptoms related to a specific infection, such as a cough with pneumonia, or painful urination with a kidney infection. The very young, old, and people with a weakened immune system may have no symptoms of a specific infection, and the body temperature may be low or normal instead of having a fever. Severe sepsis causes poor organ function or blood flow. The presence of low blood pressure, high blood lactate, or low urine output may suggest poor blood flow. Septic shock is low blood pressure due to sepsis that does not improve after fluid replacement. Sepsis is caus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocarditis
Endocarditis is an inflammation of the inner layer of the heart, the endocardium. It usually involves the heart valves. Other structures that may be involved include the interventricular septum, the chordae tendineae, the mural endocardium, or the surfaces of intracardiac devices. Endocarditis is characterized by lesions, known as ''Vegetation (pathology), vegetations'', which is a mass of platelets, fibrin, microcolony, microcolonies of microorganisms, and scant inflammatory cells. In the subacute form of infective endocarditis, the vegetation may also include a center of granuloma, granulomatous tissue, which may fibrose or calcify. There are several ways to classify endocarditis. The simplest classification is based on cause: either ''infective'' or ''non-infective'', depending on whether a microorganism is the source of the inflammation or not. Regardless, the diagnosis of endocarditis is based on clinical features, investigations such as an echocardiogram, and blood cultures d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |