|
Roman Catholic Diocese Of Nepi-Sutri
The diocese of Nepi-Sutri was a Roman Catholic ecclesiastical territory in central Italy, created in 1435 by unifying the diocese of Nepi and the diocese of Sutri. It existed until 1986, when it was united into the current diocese of Cività Castellana."Diocese of Nepi e Sutri" ''''. David M. Cheney. Retrieved February 29, 2016"Titular Episcopal See of Nepi" ''GCatholic.org''. Gabriel Chow. Retrieved March 9, 2016 History In the[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diocese Of Cività Castellana
The Diocese of Civita Castellana () is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or diocese of the Catholic Church in Latium, central Italy. It has existed in the current form since 1986, when the Diocese of Nepi e Sutri was united into the Diocese of Civita Castellana, Orte e Gallese. The Diocese of Gallese had been added to the Dioceses of Civita Castellana and Orte in 1805. The name of the diocese was shortened in 1991, in accordance with Vatican policies. The diocese of Civita Castellana is immediately Exemption (Catholic canon law), exempt to the Holy See."Diocese of Civita Castellana" ''Catholic-Hierarchy.org''. David M. Cheney. Retrieved February 29, 2016 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Boniface I
Pope Boniface I () was the bishop of Rome from 28 December 418 to his death on 4 September 422. His election was disputed by the supporters of Eulalius until the dispute was settled by Emperor Honorius. Boniface was active in maintaining church discipline, and he restored certain privileges to the metropolitical sees of Narbonne and Vienne, exempting them from any subjection to the primacy of Arles. He was a contemporary of Augustine of Hippo, who dedicated to him some of his works. Early life Little is known of his life antecedent to his election. He was married and his wife died before he became pope. The ''Liber Pontificalis'' calls him a Roman and the son of the presbyter Iocundus or Jocundus. He is believed to have been ordained by Pope Damasus I (366–384) and to have served as representative of Innocent I at Constantinople (c. 405). Election On the day of Pope Zosimus's funeral, which was held at San Lorenzo fuori le Mura, partisans of Eulalius occupied the Late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop Of Piacenza
A bishop is an ordained member of the clergy who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution. In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance and administration of dioceses. The role or office of the bishop is called episcopacy or the episcopate. Organisationally, several Christian denominations utilise ecclesiastical structures that call for the position of bishops, while other denominations have dispensed with this office, seeing it as a symbol of power. Bishops have also exercised political authority within their dioceses. Traditionally, bishops claim apostolic succession, a direct historical lineage dating back to the original Twelve Apostles or Saint Paul. The bishops are by doctrine understood as those who possess the full priesthood given by Jesus Christ, and therefore may ordain other clergy, including other bishops. A person ordained as a deacon, priest (i.e. presbyter), and then bishop is understood to hold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bonitho
Bonizo of Sutri or Bonitho (c.1045–c.1095) was a Bishop of Sutri and then of Piacenza in central Italy, in the last quarter of the 11th century. He was an adherent of Gregory VII and an advocate of the reforming principles of that pope. He wrote three works of polemical history, including '' Liber ad amicum'', which detailed the struggles between civil and religious authorities. He was driven out of both of his dioceses, once by the emperor and once by opponents of Gregorian-style reform. Life Bonizo was born about 1045, though there is no documentary material referring to the date of his birth, or the place, or of his family. It is argued that he was a native of Milan in Northern Italy. Early in his life he associated himself with the reform group known as the Pataria. Bonizo took part in several councils held in Rome. He was present in Rome at a synod of Pope Alexander II, probably the one held in February or March 1073. On 27 November 1074, Pope Gregory wrote a letter to B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Benedict VII
Pope Benedict VII (; died 10 July 983) was the bishop of Rome and ruler of the Papal States from October 974 to his death on 10 July 983. Family and early career Benedict was born in Rome, the son of David or Deodatus and nephew of Alberic II of Spoleto. He was also connected to the Conti family.De Montor, Artaud. ''The Lives and Times of the Popes'', The Catholic Publication Society of New York, 1911 Before his accession to the papacy, he served as bishop of Sutri. Pontificate Benedict VII was elected pope by the Roman clergy and people in October 974 under the influence of Sicco, envoy of Emperor Otto II. He ascended as a compromise candidate to replace Boniface VII, who had caused the death of Pope Benedict VI, usurped the pontificate, and in a month plundered the Vatican of its most valuable contents. He then escaped to Constantinople. The new pope's authority was opposed by Boniface VII and his supporters, and although the antipope himself was forced to flee, his party ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gian Lorenzo Bernini
Gian Lorenzo (or Gianlorenzo) Bernini (, ; ; Italian Giovanni Lorenzo; 7 December 1598 – 28 November 1680) was an Italians, Italian sculptor and Italian architect, architect. While a major figure in the world of architecture, he was more prominently the leading sculptor of his age, credited with creating the Baroque sculpture, Baroque style of sculpture. As one scholar has commented, "What Shakespeare is to drama, Bernini may be to sculpture: the first pan-European sculptor whose name is instantaneously identifiable with a particular manner and vision, and whose influence was inordinately powerful ..." In addition, he was a painter (mostly small canvases in oil) and a man of the theatre: he wrote, directed and acted in plays (mostly Carnival satires), for which he designed stage sets and theatrical machinery. He produced designs as well for a wide variety of decorative art objects including lamps, tables, mirrors, and even coaches. As an architect and city planner, he de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanus Of Caesarea
Romanus of Caesarea (Greek: Ρωμανός), also known as Romanus of Antioch, is venerated as a martyr. A deacon of Caesarea, he was martyred at Antioch. Life In 303 or 304, at the beginning of the Diocletianic Persecution, a deacon called Romanus, served in Caesarea in Palestine. He was living in Antioch where in the midst of the persecutions, he encouraged the Christians to stand firm. During a pagan festival, he upbraided the participants for worshiping idols. Taken prisoner, he was condemned to death by fire, and was bound to the stake. When rain extinguished the flames, Romanus was brought before Emperor Galerius who was then in Antioch. At the emperor's command Romanus' tongue was cut out. Tortured in various ways in prison he was finally strangled.Kirsch, Johann Peter. "Sts. Romanus." The Cath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synod Of Sutri
The Council of Sutri (or Synod of Sutri) was called by the Holy Roman Emperor Henry III and opened on December 20, 1046, in the hilltown of Sutri, at the edge of the Duchy of Rome. The Catholic Church does not list this as an ecumenical council. Record in the ''Annales Romani'' The ''Annales Romani'' record the events thus: Reasons for calling the council The council was called to resolve disorder over the papacy. A faction in the church encouraged Henry III to intervene, both to resolve the conflict and to receive his crown from the pope in an official ceremony. In the autumn of 1046 Henry III, already King of the Germans, crossed the Alps at the head of a large army and accompanied by a retinue of the secular and ecclesiastical princes of the empire, all of whom were his sworn vassals. Henry had two intentions, to be crowned Holy Roman emperor by the pope at Rome and, in order that the pontiff concerned have an unassailable title—one that would not cast doubts upon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papal Legate
300px, A woodcut showing Henry II of England greeting the Pope's legate. A papal legate or apostolic legate (from the ancient Roman title '' legatus'') is a personal representative of the Pope to foreign nations, to some other part of the Catholic Church, or to representatives of a state or monarchy. A legate is empowered in matters of Catholic faith and for the settlement of ecclesiastical matters. The legate is appointed directly by the Pope—the Bishop of Rome and head of the Catholic Church. Hence a legate is usually sent to a government, to a sovereign, to a large body of believers (such as a national church), or to take charge of a major religious effort, such as an ecumenical council, a crusade to the Holy Land, or even against a heresy such as the Cathars. The term ''legation'' is applied both to a legate's mandate and to the territory concerned (such as a state, or an ecclesiastical province). The relevant adjective is ''legatine''. History 200px, Cardinal Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liutprand, King Of The Lombards
Liutprand was the List of kings of the Lombards, king of the Lombards from 712 to 744 and is chiefly remembered for his multiple phases of law-giving, in fifteen separate sessions from 713 to 735 inclusive, and his long reign, which brought him into a series of conflicts, mostly successful, with most of Italian peninsula, Italy. He is often regarded as the most successful Lombard monarch, notable for the Donation of Sutri in 728, which was the first accolade of sovereign territory to the Papacy. Early life Liutprand's life began inauspiciously. His father was driven to exile among the Bavarians, his older brother Sigipert was blinded by Aripert II, king of the Lombards, and his mother Theodarada and sister Aurona were mutilated (their noses and ears were cut off). Liutprand was spared only because his youth made him appear harmless, described as adolescens in Paul the Deacon's ''Historia Langobardorum'' (Book VI, xxii), suggesting that he was 'probably older than 19 but still in h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exarch
An exarch (; from Ancient Greek ἔξαρχος ''exarchos'') was the holder of any of various historical offices, some of them being political or military and others being ecclesiastical. In the late Roman Empire and early Byzantine Empire, an ''exarch'' was a governor of a particular territory. From the end of the 3rd century or early 4th, every Roman diocese was governed by a vicarius, who was titled "exarch" in eastern parts of the Empire, where the Greek language and the use of Greek terminology dominated, even though Latin was the language of the imperial administration from the provincial level up until the 440s (Greek translations were sent out with the official Latin text). In Greek texts, the Latin title is spelled βικάριος (). The office of exarch as a governor with extended political and military authority was later created in the Byzantine Empire, with jurisdiction over a particular territory, usually a frontier region at some distance from the capital Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
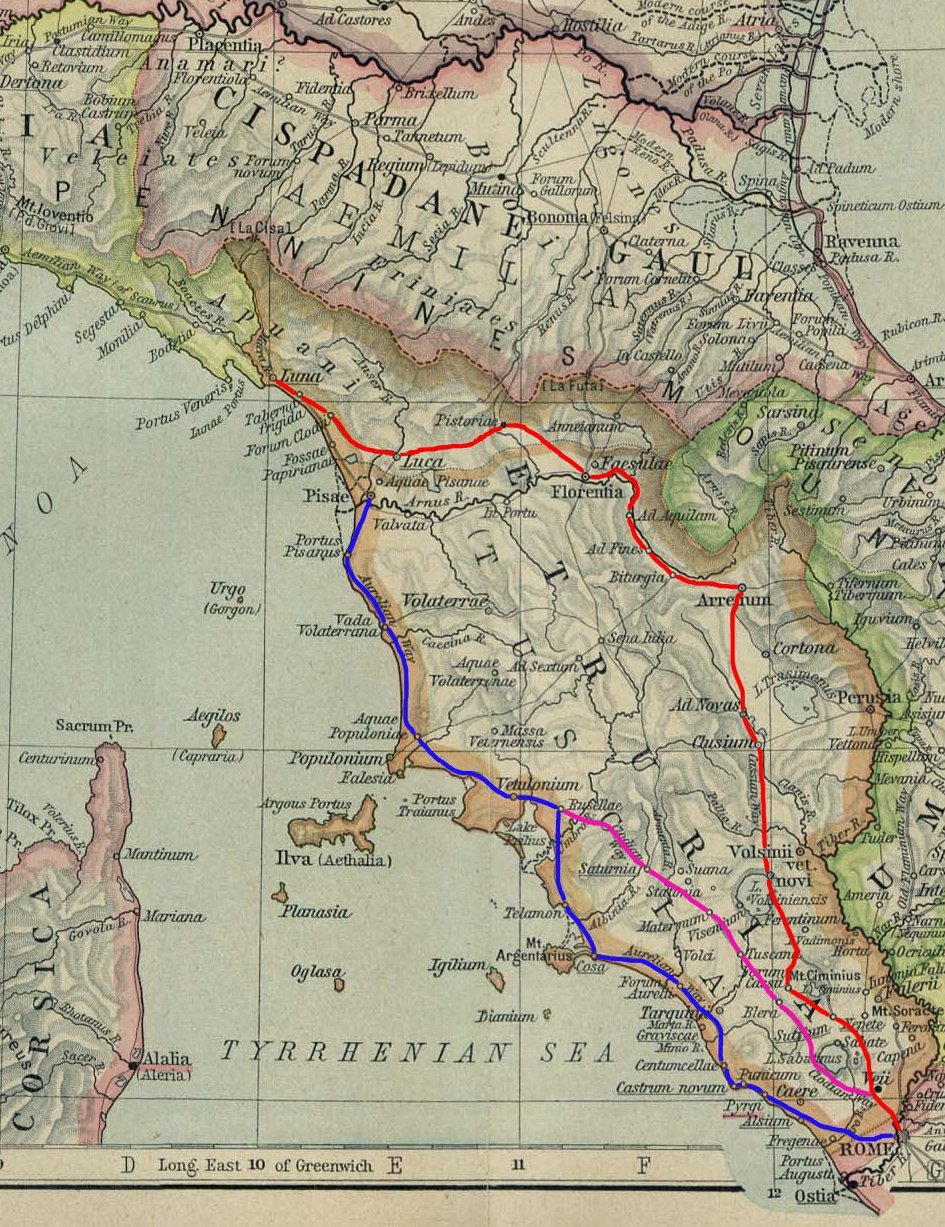
Cassian Way
The Via Cassia () was an important Roman road striking out of the Via Flaminia near the Milvian Bridge in the immediate vicinity of Rome and, passing not far from Veii, traversed Etruria. The ''Via Cassia'' passed through Baccanae, Sutrium, Volsinii, Clusium, Arretium, Florentia, Pistoria, and Luca, joining the Via Aurelia at Luna. The Via Cassia intersected other important roads. At mile 11 the Via Clodia diverged north-north-west. At Sette Vene, another road, probably the Via Annia, branched off to Falerii. In Sutrium, the ''Via Ciminia'' split off and later rejoined. The date of its construction is uncertain: it cannot have been earlier than 187 BC, when the consul Gaius Flaminius constructed a road from Bononia to Arretium, which must have coincided with a portion of the later Via Cassia. It is not mentioned by any ancient authorities before the time of Cicero, who in 45 BC speaks of the existence of three roads from Rome to Mutina: the Flaminia, the Aurelia and the Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |