|
Roberto De' Nobili
Roberto de Nobili (1577 ŌĆō 16 January 1656) was an Italian priest, a member of the Society of Jesus (Jesuits), who worked as a missionary in Southern India. He used novel methods to preach Christianity, adopting many local customs of India which were, in his view, not contrary to Christian principles, and he won papal approval for a policy of accommodation that allowed coverts to Christianity to continue to engage in Hindu practices deemed social practices rather than expressions of Hinduism. Biography Born in Montepulciano, Tuscany, in September 1577, Roberto de Nobili arrived at the ports of the Portuguese in Goa and Bombay in western India on 20 May 1605. It is probable that he met here Fr Thomas Stephens, a Jesuit who had arrived in Goa in 1579, and was probably then in the process of composing his '' Khristapurana'', an epic poem using Hindu literary forms to tell Christ's life story. Roberto de Nobili, nicknamed the White Brahmin, embodied the missionary fervor of Chri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Roberto De' Nobili (1541ŌĆō1559)
Roberto de' Nobili (1541ŌĆō1559) was a grand-nephew of Pope Julius III, who made him a Cardinal (Catholic Church), cardinal of the Catholic Church at the age of twelve. Biography Roberto de' Nobili was born in Montepulciano on 17 September 1541, the son of Vincenzo de' Nobili, count of Civitella, and Maddalena Barbolani, the niece of Pope Julius III, from the family of the counts of Montauto. His paternal ancestry was that of the De Nobili family of Montepulciano. His family moved to Rome in 1550 when Pope Julius III was elected. As a boy he was tutored by Giulio Poggiano, Ottavio Pantagato, and Girolamo Ponzio, and by age ten was fluent in Latin and Ancient Greek. He also studied philosophy, literature, and the Bible, Scriptures. Pope Julius III made him a cardinal deacon in the Papal consistory, consistory of 22 December 1553, when he was twelve years old. He was assigned the Titular church#Cardinal-deaconries, deaconry of Santa Maria in Domnica on 6 February 1555. He participa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Telugu Language
Telugu (; , ) is a Dravidian languages, Dravidian language native to the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, where it is also the official language. Spoken by about 96 million people (2022), Telugu is the most widely spoken member of the Dravidian language family, and one of the twenty-two Languages with legal status in India, scheduled languages of the Republic of India. It is one of the few languages that has primary official status in more than one States and union territories of India, Indian state, alongside Hindi and Bengali language, Bengali. Telugu is one of the languages designated as a Classical Languages of India, classical language by the Government of India. It is the 14th most spoken native language in the world.Statistics in Modern Standard Telugu is based on the dialect of erstwhile Krishna, Guntur, East Godavari and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ezourvedam
The ''Ezourvedam'' is a forgery "consisting of certain 'Vedic' materials translated by Jesuits with the intention of isolating elements most in harmony with Christianity". Rather than being an original Sanskrit work, the ''Ezourvedam'' turned out to be a French text that was written by French Jesuits and meant to be translated into Sanskrit. History and authorship A manuscript called ''Ezourvedam'' was given to Voltaire in 1760 by Louis Laurent de F├®derbe, Count of Modave. The text was in French, and said to be a French translation of a Sanskrit original. Voltaire was enthusiastic about the work, had it copied and brought it to the attention of others. However, by 1761, Voltaire regarded the text to be a mere commentary on the Vedas. It was first published in 1778 (Voltaire died that same year). The genuineness of the ''Ezourvedam'' was questioned in 1782; the doubts were confirmed in 1822. Rather than an original Sanskrit work, the ''Ezourvedam'' turned out to be a French tex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Chennai
Chennai, also known as Madras (List of renamed places in India#Tamil Nadu, its official name until 1996), is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Tamil Nadu by population, largest city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost states and territories of India, state of India. It is located on the Coromandel Coast of the Bay of Bengal. According to the 2011 Census of India, 2011 Indian census, Chennai is the List of most populous cities in India, sixth-most-populous city in India and forms the List of million-plus urban agglomerations in India, fourth-most-populous urban agglomeration. Incorporated in 1688, the Greater Chennai Corporation is the oldest municipal corporation in India and the second oldest in the world after City of London Corporation, London. Historically, the region was part of the Chola dynasty, Chola, Pandya dynasty, Pandya, Pallava dynasty, Pallava and Vijayanagara Empire, Vijayanagara kingdoms during various eras. The coastal land which then contained th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mylapore
Mylapore (also spelt Mayilapur), or Thirumayilai, is a neighbourhood in the central part of the city of Chennai, India. It is one of the oldest residential parts of the city. The locality is claimed to be the birthplace of the celebrated Tamil philosopher Valluvar, and the Hindu saint and philosopher, Peyalvar. It is also believed by Christians to be the place of martyrdom of St. Thomas the Apostle, who preached along the Malabar Coast, and established the Malankara Nasrani community. Mylapore is known for its tree-lined avenues, Kapaleeshwarar Temple, Katcheri seasons, and Ramakrishna Matha among many others. St. Thomas Cathedral Basilica, Chennai which is believed to house the tomb of Thomas the Apostle, is in Mylapore. Etymology The word ''Mylapore'' is the anglicized form of the Dravidian word ''Mayilāppūr''. It is derived from the Tamil phrase , which means 'land of the peacock scream'.Saints, Goddesses and Kings By Susan Bayly Historically, peacocks have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
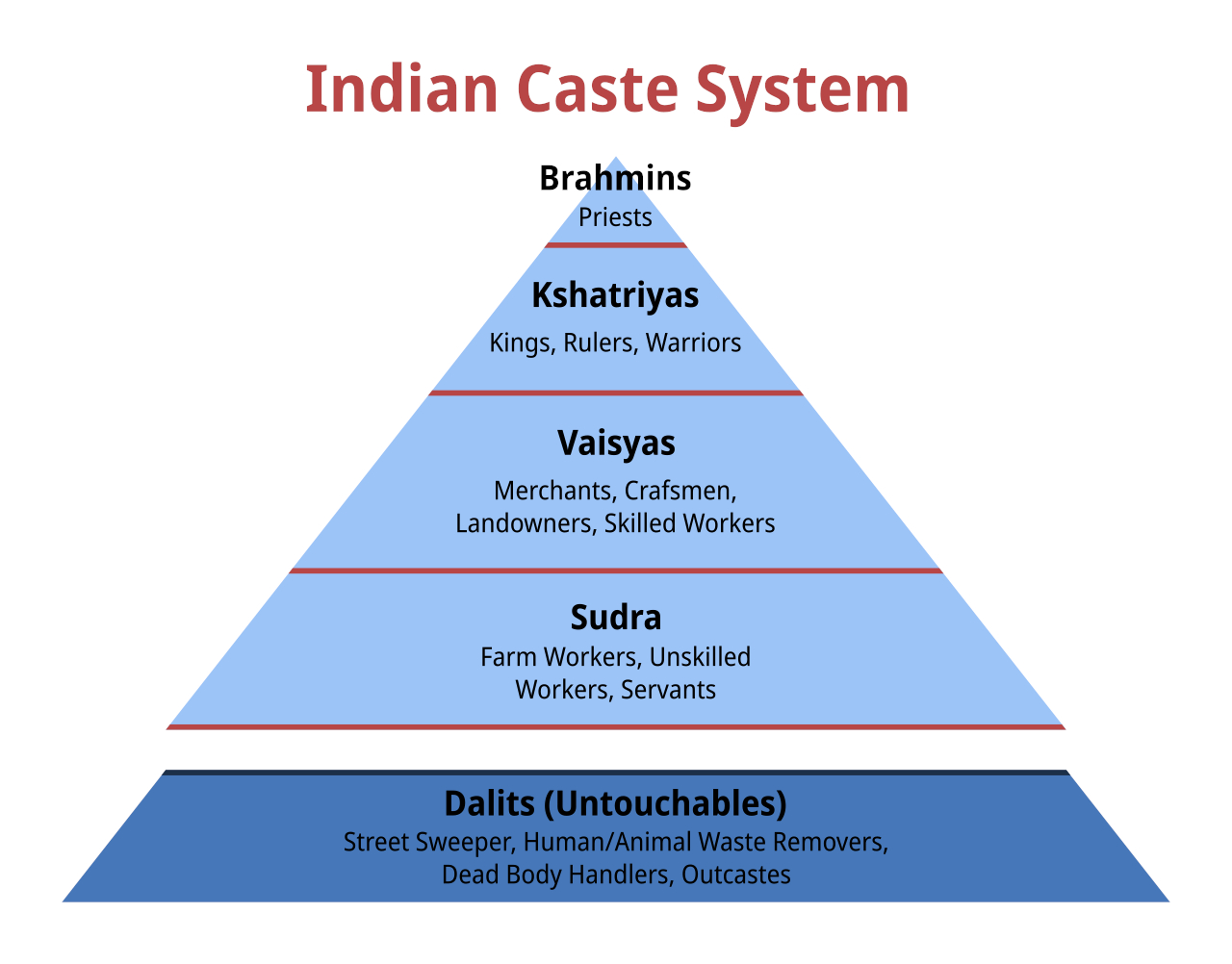
Dalit
Dalit ( from meaning "broken/scattered") is a term used for untouchables and outcasts, who represented the lowest stratum of the castes in the Indian subcontinent. They are also called Harijans. Dalits were excluded from the fourfold varna of the caste hierarchy and were seen as forming a fifth varna, also known by the name of ''Panchama''. Several scholars have drawn parallels between Dalits and the '' Burakumin'' of Japan, the '' Baekjeong'' of Korea and the peasant class of the medieval European feudal system. Dalits predominantly follow Hinduism with significant populations following Buddhism, Sikhism, Christianity, and Islam. The constitution of India includes Dalits as one of the Scheduled Castes; this gives Dalits the right to protection, positive discrimination (known as reservation in India), and official development resources. Terminology The term ''Dalit'' is for those called the "untouchables" and others that were outside of the traditional Hindu caste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pope Gregory XV
Pope Gregory XV (; ; 9 January 1554 ŌĆō 8 July 1623), born Alessandro Ludovisi, was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 9 February 1621 until his death in 1623. He is notable for founding the Congregation for the Propagation of the Faith, an organization tasked with overseeing the spread of Catholicism and missionary work. Gregory XV was also responsible for the canonization of Saints Ignatius of Loyola, Francis Xavier, Teresa of ├üvila, and Philip Neri, which solidified his commitment to the Counter-Reformation. Biography Early life Alessandro Ludovisi was born in Bologna on 9 January 1554 to Pompeo Ludovisi, Count of Samoggia (now Savigno in the Province of Bologna) and Camilla Bianchini. He was the third of seven children. He was educated at the Collegio Romano, Roman College run by the Society of Jesus in Rome, and also at the German College in Rome. He later attended the University of Bologna to obtain degrees in Canon law (Catholic Church) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Catechism
A catechism (; from , "to teach orally") is a summary or exposition of Catholic theology, doctrine and serves as a learning introduction to the Sacraments traditionally used in catechesis, or Christian religious teaching of children and adult converts. Catechisms are doctrinal manuals ŌĆō often in the form of questions followed by answers to be memorised ŌĆō a format #Secular catechisms, that has been used in non-religious or secular contexts as well. The term ''catechumen'' refers to the designated recipient of the catechetical work or instruction. In the Catholic Church, catechumens are those who are preparing to receive the Sacraments of the Catholic Church, Sacrament of Baptism. Traditionally, they would be placed separately during Holy Mass from those who had been baptized, and would be dismissed from the liturgical assembly before the Profession of Faith (Nicene Creed) and General Intercessions (Prayers of the Faithful). Catechisms are characteristic of Western Christiani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Guru
Guru ( ; International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration, IAST: ''guru'') is a Sanskrit term for a "mentor, guide, expert, or master" of certain knowledge or field. In pan-Indian religions, Indian traditions, a guru is more than a teacher: traditionally, the guru is a reverential figure to the disciple (or ''wikt:ÓżČÓż┐ÓżĘÓźŹÓż», shisya'' in Sanskrit, literally ''seeker [of knowledge or truth'']) or student, with the guru serving as a "counsellor, who helps mould values, shares experiential knowledge as much as Knowledge#Hinduism, literal knowledge, an Role model, exemplar in life, an inspirational source and who helps in the spiritual evolution of a student". Whatever language it is written in, Judith Simmer-Brown says that a tantra, tantric spiritual text is often codified in an obscure twilight language so that it cannot be understood by anyone without the verbal explanation of a qualified teacher, the guru. A guru is also one's spiritual guide, who helps one to discover the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Prasadam
200px, ''Naivedya'' offered to Sri Maya Chandrodaya Mandir in Mayapur, India">Mayapur.html" ;"title="Sri Maya Chandrodaya Mandir, Mayapur">Sri Maya Chandrodaya Mandir in Mayapur">Sri Maya Chandrodaya Mandir, Mayapur">Sri Maya Chandrodaya Mandir in Mayapur, India Pras─üda (, Sanskrit: Óż¬ÓźŹÓż░ÓżĖÓżŠÓż”), prasad or prasadam is a religious offering in Hinduism. Most often ''Prasada'' is vegetarian food especially cooked for devotees after praise and thanksgiving to a god. ''Mahaprasada'' (also called ''bhandar─ü''),Pashaura Singh, Louis E. Fenech, 2014The Oxford Handbook of Sikh Studies/ref> is the consecrated food offered to the deity in a Hindu temple which is then distributed and partaken by all the devotees regardless of any orientation.Chitrita Banerji, 2010Eating India: Exploring the Food and Culture of the Land of SpicesSubhakanta Behera, 2002Construction of an identity discourse: Oriya literature and the Jagannath lovers (1866ŌĆō1936) pp. 140ŌĆō177.Susan Pattinson, 2011Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kovil
Kovil or koyil (meaning: residence of god)The modern Tamil word for Hindu temple is ''k┼Źvil'' () meaning "the residence of God". In ancient Tamil Nadu, the king (, ''K┼Ź'') was considered to be a ŌĆśrepresentative of God on earth' and lived in a ''k┼Źvil'', which also means "kingŌĆÖs house". Old words for king like ''K┼Ź'' ( "King"), ''Iß╣¤ai'' ( "Emperor") and ''─Ćß╣ćß╣Łavan'' ( "Conqueror") are now primarily used to refer to God. is the Tamil term for a distinct style of Hindu temple with Dravidian architecture. Etymology Both the terms ''koyil'' (, ''k┼Źyil'') and ''kovil'' (, ''k┼Źvil'') are used interchangeably. In Tamil, ( wikt:ta:Ó«ĢÓ»ŗÓ«ĄÓ«┐Ó«▓Ó»Ź) is the word derived, according to the rules of Tamil grammar."Ó«ēÓ«¤Ó««Ó»ŹÓ«¬Ó«¤Ó»üÓ««Ó»åÓ«»Ó»ŹÓ«¬Ó»Ź Ó«¬Ó»üÓ«ŻÓ«░Ó»ŹÓ«ÜÓ»ŹÓ«ÜÓ«┐" Ó«ÄÓ«®Ó»ŹÓ«▒ Ó«żÓ««Ó«┐Ó«┤Ó»Ź Ó«ćÓ«▓Ó«ĢÓ»ŹÓ«ĢÓ«Ż Ó«ĄÓ«┐Ó«żÓ«┐Ó«¬Ó»ŹÓ«¬Ó«¤Ó«┐, "Ó«ĄÓ»Ź" Ó«ĄÓ«░Ó»üÓ««Ó»Ź, Ó«ĢÓ»ŗ + Ó«ćÓ«▓Ó»Ź = Ó«ĢÓ»ŗÓ«ĄÓ«┐Ó«▓Ó»Ź. Ó«ēÓ«¤Ó««Ó»ŹÓ«¬Ó«¤Ó»ü Ó««Ó»åÓ«»Ó»Ź: Ó«©Ó«┐Ó«▓Ó» ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |