|
Ro (dubious Danish King)
Hrothgar ( ; ) was a semi-legendary Danish king living around the early sixth century AD. Hrothgar appears in the Anglo-Saxon epics ''Beowulf'' and ''Widsith'', in Norse sagas and poems, and in medieval Danish chronicles. In both Anglo-Saxon and Scandinavian tradition, Hrothgar is a Scylding, the son of Halfdan, the brother of Halga, and the uncle of Hrólfr Kraki. Moreover, in both traditions, the mentioned characters were the contemporaries of the Swedish king Eadgils; and both traditions also mention a feud with men named Fróði and Ingeld. The consensus view is that Anglo-Saxon and Scandinavian traditions describe the same person. Names Hrothgar, also rendered ''Hrōðgār'', is an Old English form attested in ''Beowulf'' and ''Widsith'', the earliest sources to mention the character. In non-English sources, the name appears in more or less corresponding Old Icelandic, Old Danish, and Latinized versions. He appears as ''Hróarr'', ''Hroar'', etc., in sagas and poetry, and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wealhþeow
Wealhtheow (also rendered Wealhþēow or Wealthow; ) is a queen of the Danes in the Old English poem ''Beowulf'', first introduced in line 612. Character overview Wealhtheow is of the Wulfing clan, Queen of the Danes. She is married to Hrothgar (Hrōðgār), the Danish king and is the mother of sons, Hreðric and Hroðmund, and a daughter Freawaru. In her marriage to Hrothgar she is described as ''friðusibb folca'' (l. 2017), 'the kindred pledge of peace between peoples', signifying interdynastic allegiance between Wulfing and Scylding achieved with her marriage to Hrothgar. She is both 'Lady of the Helmings' (l. 620) (by descent, of the Wulfing clan of Helm) and 'Lady of the Scyldings' (l. 1168), by marriage and maternity. Two northern sources associate the wife of Hrothgar with England. The ''Skjöldunga saga'', in Arngrímur Jónsson's abstract, chapter 3, tells that Hrothgar (''Roas'') married the daughter of an English king. The '' Hrolfs saga kraka'', chapter 5, tel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hrólfr Kraki
Hrólfr Kraki (Old Norse: ), ''Hroðulf'', ''Rolfo'', ''Roluo'', ''Rolf Krage'' (early 6th century) was a semi-legendary Danish king who appears in both Anglo-Saxon and Scandinavian tradition. Both traditions describe him as a Danish Scylding, the nephew of Hroðgar and the grandson of Healfdene. The consensus view is that Anglo-Saxon and Scandinavian traditions describe the same people. Whereas the Anglo-Saxon ''Beowulf'' and ''Widsith'' do not go further than treating his relationship with Hroðgar and their animosity with Froda and Ingeld, the Scandinavian sources expand on his life as the king at Lejre and on his relationship with Halga, Hroðgar's brother. In ''Beowulf'' and ''Widsith'', it is never explained how Hroðgar and Hroðulf are uncle and nephew. ''Beowulf'' The poem ''Beowulf'' introduces Hroðulf as kinsman. Later, the text explains that Hroðulf is Hroðgar's nephew and that "each was true to the other". Hroðgar is given three siblings, brothers Heorog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beowulf - Hrothgar
''Beowulf'' (; ) is an Old English poem, an epic in the tradition of Germanic heroic legend consisting of 3,182 alliterative lines. It is one of the most important and most often translated works of Old English literature. The date of composition is a matter of contention among scholars; the only certain dating is for the manuscript, which was produced between 975 and 1025 AD. Scholars call the anonymous author the "''Beowulf'' poet". The story is set in pagan Scandinavia in the 5th and 6th centuries. Beowulf, a hero of the Geats, comes to the aid of Hrothgar, the king of the Danes, whose mead hall Heorot has been under attack by the monster Grendel for twelve years. After Beowulf slays him, Grendel's mother takes revenge and is in turn defeated. Victorious, Beowulf goes home to Geatland and becomes king of the Geats. Fifty years later, Beowulf defeats a dragon, but is mortally wounded in the battle. After his death, his attendants cremate his body and erect a barrow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heorot
Heorot (Old English 'hart, stag') is a mead-hall and major point of focus in the Anglo-Saxon poem ''Beowulf''. The hall serves as a seat of rule for King Hrothgar, a legendary Danish king. After the monster Grendel slaughters the inhabitants of the hall, the Geatish hero Beowulf defends the royal hall before subsequently defeating him. Later Grendel's mother attacks the inhabitants of the hall, and she too is subsequently defeated by Beowulf. Name The name ''Heorot'' is the Old English word for a stag. Its use may stem from an association between royalty and stags in Germanic paganism. Archaeologists have unearthed a variety of Anglo-Saxon finds associating stags with royalty. For example, a sceptre or whetstone discovered in mound I of the Anglo-Saxon burial site Sutton Hoo prominently features a standing stag at its top.For general discussion, see Fulk, Bjork, & Niles (2008:119–120). For images and details regarding the sceptre or whetstone, see the British Museum'coll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
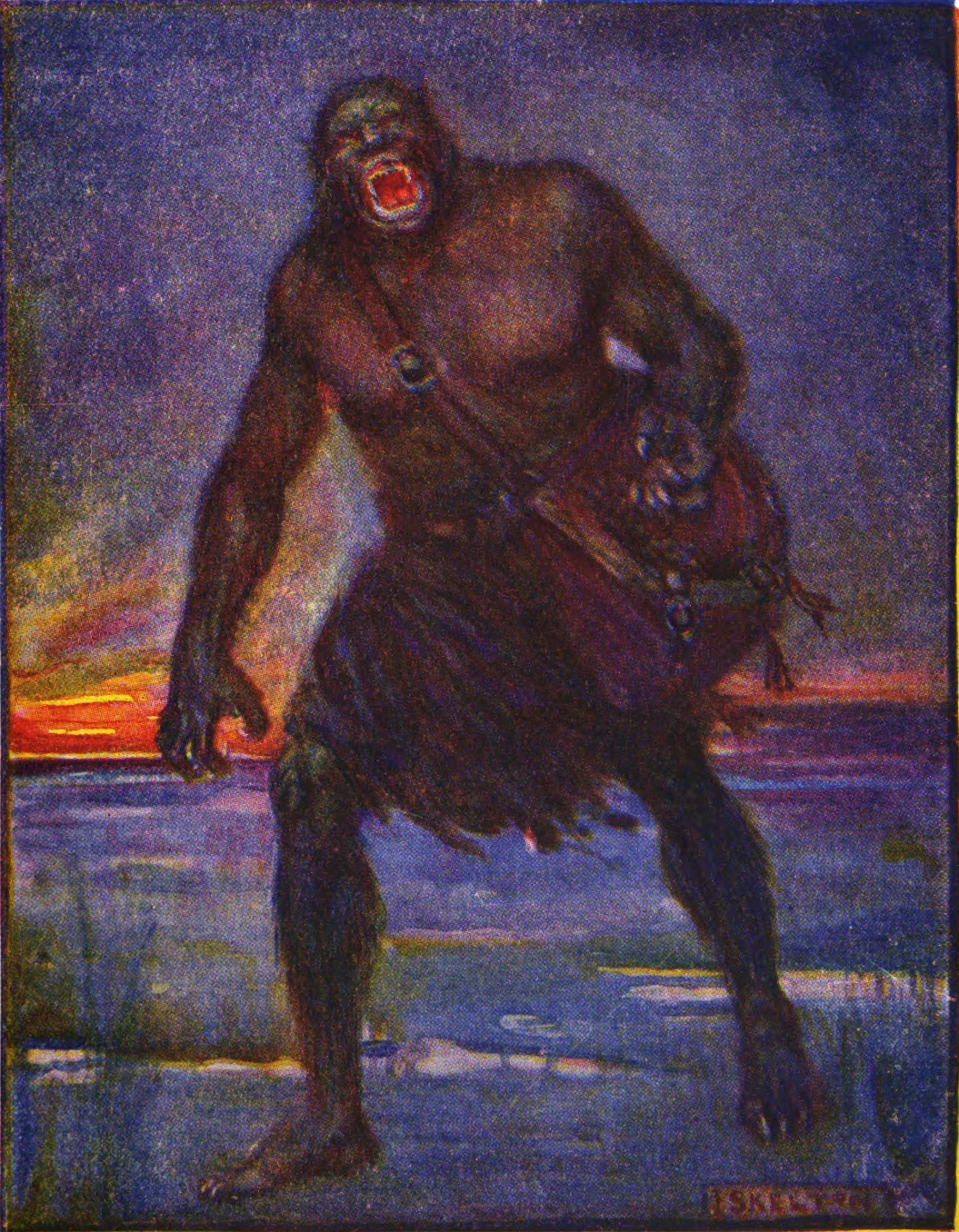
Grendel
Grendel is a character in the Anglo-Saxon epic poem ''Beowulf'' (700–1000 AD). He is one of the poem's three antagonists (along with his mother and the dragon), all aligned in opposition against the protagonist Beowulf. He is referred to as both an , types of beings from wider Germanic mythology. He is also described as a descendant of the Biblical Cain and "a creature of darkness, exiled from happiness and accursed of God, the destroyer and devourer of our human kind." He is usually depicted as a monster or a giant, although his status as a monster, giant, or other form of supernatural being is not clearly described in the poem and thus remains the subject of scholarly debate. The character of Grendel and his role in the story of ''Beowulf'' have been subject to numerous reinterpretations and re-imaginings. Grendel is feared by all in Heorot but Beowulf, who kills both him and his mother. Story Grendel is a figure in the poem ''Beowulf'', preserved in the ''Nowell Codex''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beowulf (hero)
Beowulf (; ) is a legendary Geatish hero in the eponymous epic poem, one of the oldest surviving pieces of English literature. Etymology and origins of the character A number of origins have been proposed for the name ''Beowulf''. Beowulf Henry Sweet, a philologist and linguist specializing in Germanic languages, proposed that the name ''Bēowulf'' literally means in Old English "bee-wolf" or "bee-hunter" and that it is a kenning for "bear".Sweet, Henry. (1884) ''Anglo-Saxon Reader in Prose and Verse'' The Clarendon Press, p. 202. Recorded instances of similar names mirror this etymology. The 1031 AD ''Liber Vitae'' records the name ''Biuuuwulf''. The name is attested to a monk from Durham and means ''bee wolf'' in the Old Northumbrian dialect.Chadwick, Hector Munro (1983) ''The Origin of the English Nation'', p. 294. The 11th century English ''Domesday Book'' contains a recorded instance of the name ''Beulf''. The scholar suggested that the name ''Beowulf'' derived from a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
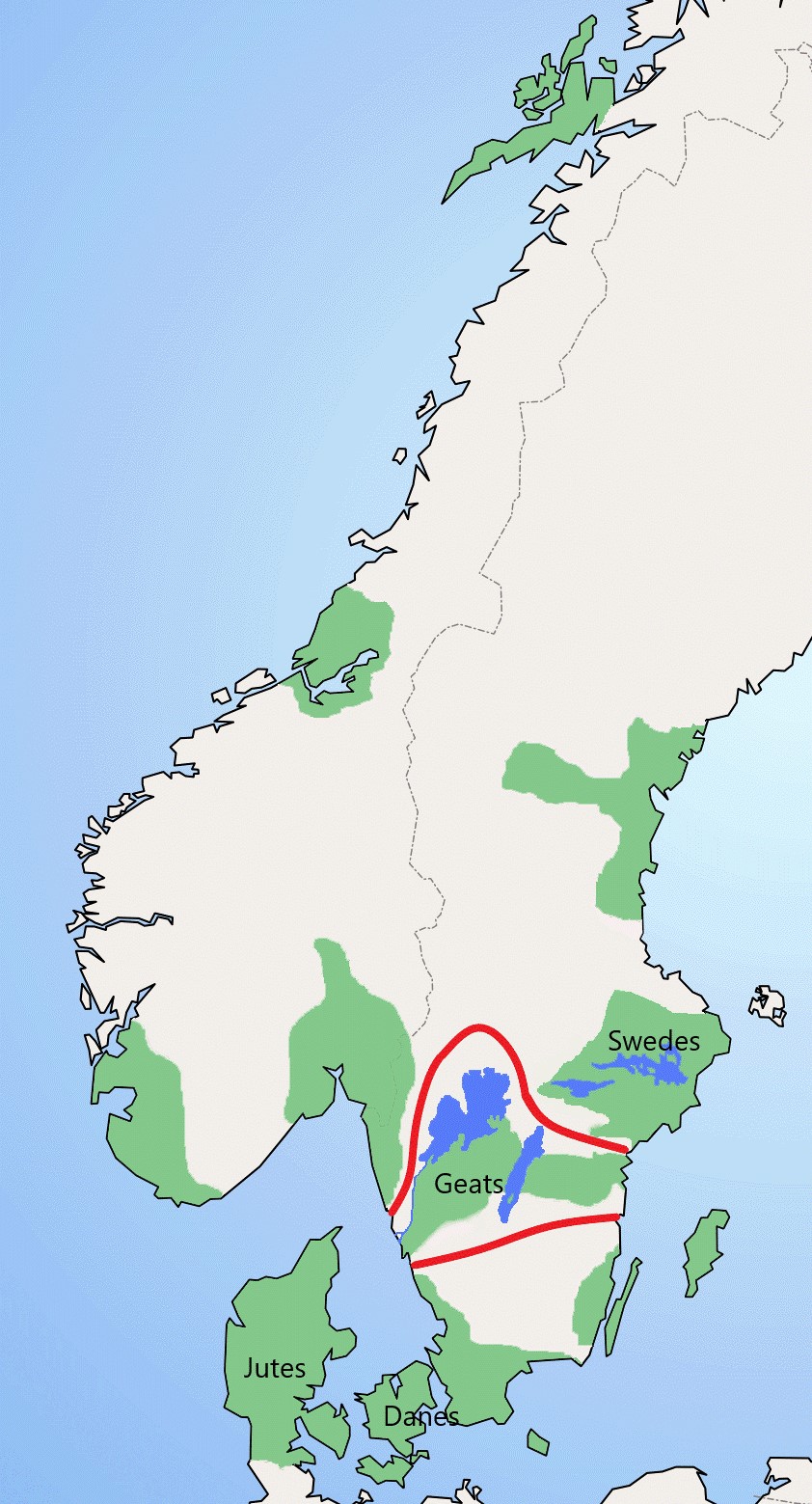
Geat
The Geats ( ; ; ; ), sometimes called ''Goths'', were a large North Germanic tribe who inhabited ("land of the Geats") in modern southern Sweden from antiquity until the Late Middle Ages. They are one of the progenitor groups of modern Swedes, along with the tribes of Swedes and Gutes. The name of the Geats also lives on in the Swedish provinces of and , the western and eastern lands of the Geats, and in many other toponyms. The Swedish dialects spoken in the areas that used to be inhabited by Geats form a distinct group, '' Götamål''. Etymology The etymology of the name ''Geat'' (Old English ', from a Proto-Germanic *''Gautaz'', plural *''Gautōz'') is similar to that of ''Goths'' and '' Gutes'' (*''Gutô'', plural *''Gutaniz''). The names derive from ablaut grades of the Proto-Germanic word *''geutaną'', meaning "to pour". They have the literal meaning "they who pour their seed". (For more information see Goths § Etymology.) The names could also allude to waterc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Saxon Literature
Old English literature refers to poetry (alliterative verse) and prose written in Old English in early medieval England, from the 7th century to the decades after the Norman Conquest of 1066, a period often termed Anglo-Saxon England. The 7th-century work '' Cædmon's Hymn'' is often considered as the oldest surviving poem in English, as it appears in an 8th-century copy of Bede's text, the ''Ecclesiastical History of the English People''. Poetry written in the mid 12th century represents some of the latest post-Norman examples of Old English. Adherence to the grammatical rules of Old English is largely inconsistent in 12th-century work, and by the 13th century the grammar and syntax of Old English had almost completely deteriorated, giving way to the much larger Middle English corpus of literature. In descending order of quantity, Old English literature consists of: sermons and saints' lives; biblical translations; translated Latin works of the early Church Fathers; chronicle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roger
Roger is a masculine given name, and a surname. The given name is derived from the Old French personal names ' and '. These names are of Germanic languages">Germanic origin, derived from the elements ', ''χrōþi'' ("fame", "renown", "honour") and ', ' ("spear", "lance") (Hrōþigēraz). The name was introduced into England by the Normans. In Normandy, the Franks, Frankish name had been reinforced by the Old Norse cognate '. The name introduced into England replaced the Old English cognate '. ''Roger'' became a very common given name during the Middle Ages. A variant form of the given name ''Roger'' that is closer to the name's origin is '' Rodger''. Slang and other uses From up to , Roger was slang for the word "penis". In '' Under Milk Wood'', Dylan Thomas writes "jolly, rodgered" suggesting both the sexual double entendre and the pirate term "Jolly Roger". In 19th-century England, Roger was slang for another term, the cloud of toxic green gas that swept through the chlor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Norse Language
Proto-Norse (also called Ancient Nordic; Danish and ; ; ; ) was an Indo-European language spoken in Scandinavia that is thought to have evolved as a northern dialect of Proto-Germanic in the first centuries CE. It is the earliest stage of a characteristically North Germanic language, and the language attested in the oldest Scandinavian Elder Futhark inscriptions, spoken from around the 2nd to the 8th centuries CE (corresponding to the late Roman Iron Age and the Germanic Iron Age). It evolved into the dialects of Old Norse at the beginning of the Viking Age around 800 CE, which later themselves evolved into the modern North Germanic languages ( Faroese, Icelandic, the Continental Scandinavian languages, and their dialects). Phonology Proto-Norse phonology probably did not differ substantially from that of Proto-Germanic. Although the phonetic realisation of several phonemes had probably changed over time, the overall system of phonemes and their distribution remained la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Norse
Old Norse, also referred to as Old Nordic or Old Scandinavian, was a stage of development of North Germanic languages, North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and their Viking expansion, overseas settlements and chronologically coincides with the Viking Age, the Christianization of Scandinavia, and the consolidation of Scandinavian kingdoms from about the 8th to the 15th centuries. The Proto-Norse language developed into Old Norse by the 8th century, and Old Norse began to develop into the modern North Germanic languages in the mid- to late 14th century, ending the language phase known as Old Norse. These dates, however, are not precise, since written Old Norse is found well into the 15th century. Old Norse was divided into three dialects: Old West Norse (Old West Nordic, often referred to as ''Old Norse''), Old East Norse (Old East Nordic), and Old Gutnish. Old West Norse and O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |