|
Right Of Issuance
Monetary sovereignty is the power of the state to exercise exclusive legal control over its currency, broadly defined, by exercise of the following powers: * Legal tender – the exclusive authority to designate the legal tender forms of payment. * Issuance and retirement – the exclusive authority to control the issuance and retirement of the legal tender."The Legal Aspect of Money" by F.A. Mann, 5th edition, Oxford, 1992, pp. 460-78 Incidence of monetary sovereignty Currently, nations such as the USA and Japan, which have autonomous central banks exercise monetary sovereignty. On the other hand, the European Union nations within the Eurozone, have ceded much of their monetary sovereignty to the European Central Bank The European Central Bank (ECB) is the central component of the Eurosystem and the European System of Central Banks (ESCB) as well as one of seven institutions of the European Union. It is one of the world's Big Four (banking)#International .... Referen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State (polity)
A state is a politics, political entity that regulates society and the population within a definite territory. Government is considered to form the fundamental apparatus of contemporary states. A country often has a single state, with various administrative divisions. A state may be a unitary state or some type of federation, federal union; in the latter type, the term "state" is sometimes used to refer to the federated state, federated polities that make up the federation, and they may have some of the attributes of a sovereign state, except being under their federation and without the same capacity to act internationally. (Other terms that are used in such federal systems may include "province", "Region#Administrative regions, region" or other terms.) For most of prehistory, people lived in stateless societies. The earliest forms of states arose about 5,500 years ago. Over time societies became more Social stratification, stratified and developed institutions leading to Centra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
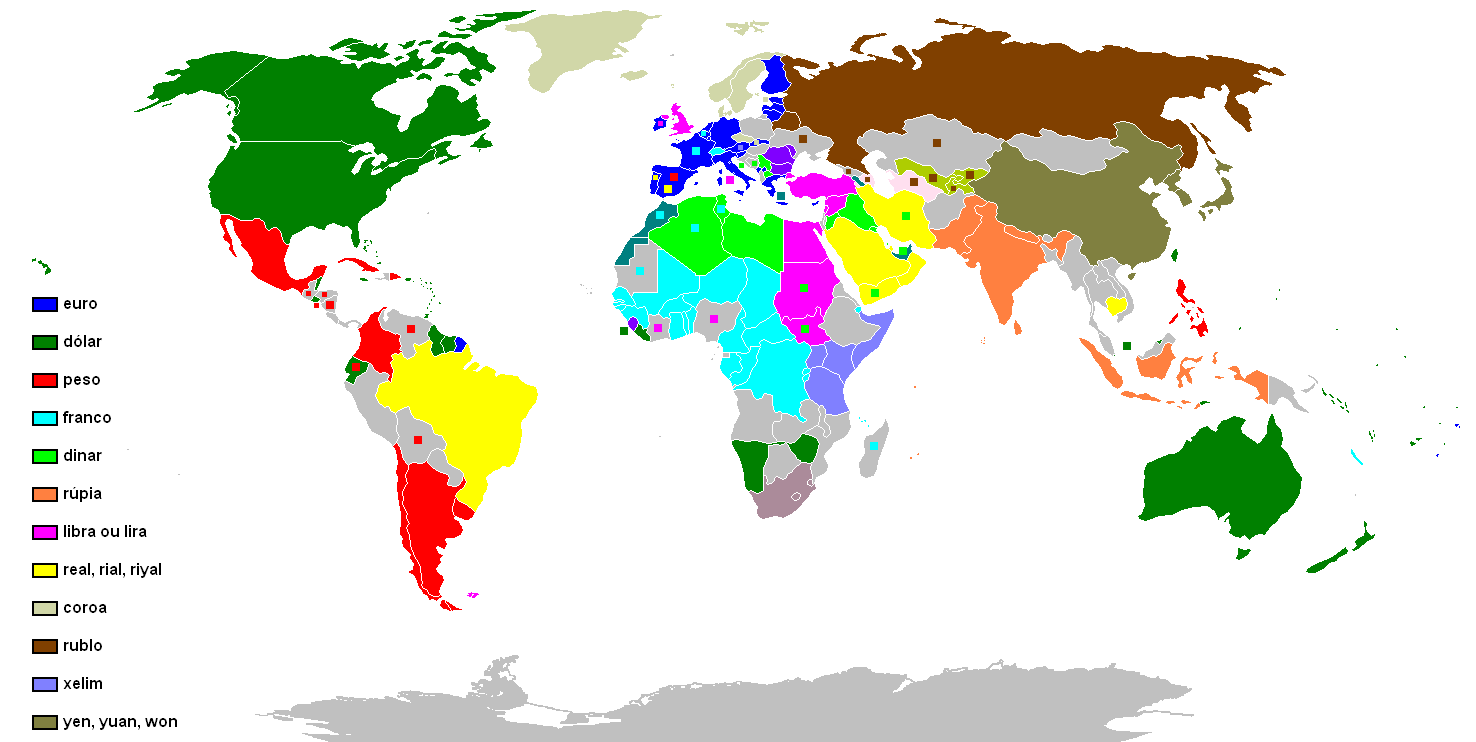
Currency
A currency is a standardization of money in any form, in use or circulation as a medium of exchange, for example banknotes and coins. A more general definition is that a currency is a ''system of money'' in common use within a specific environment over time, especially for people in a nation state. Under this definition, the British Pound sterling (£), euros (€), Japanese yen (¥), and U.S. dollars (US$) are examples of (government-issued) fiat currencies. Currencies may act as stores of value and be traded between nations in foreign exchange markets, which determine the relative values of the different currencies. Currencies in this sense are either chosen by users or decreed by governments, and each type has limited boundaries of acceptance; i.e., legal tender laws may require a particular unit of account for payments to government agencies. Other definitions of the term ''currency'' appear in the respective synonymous articles: banknote, coin, and money. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legal Tender
Legal tender is a form of money that Standard of deferred payment, courts of law are required to recognize as satisfactory payment in court for any monetary debt. Each jurisdiction determines what is legal tender, but essentially it is anything which, when offered ("tendered") in payment of a debt, extinguishes the debt. There is no obligation on the creditor to accept the tendered payment, but the act of tendering the payment in legal tender discharges the debt. It is generally only mandatory to recognize the payment of legal tender in the discharge of a monetary debt from a debtor to a creditor. Sellers offering to enter into contractual relationship, such as a contract for the sale of goods, do not need to accept legal tender and may instead contractually require payment using electronic methods, foreign currencies or any other legally recognized object of value. Coins and banknotes are usually defined as legal tender in many countries, but personal cheque, checks, credit c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated population of over 449million as of 2024. The EU is often described as a ''sui generis'' political entity combining characteristics of both a federation and a confederation. Containing 5.5% of the world population in 2023, EU member states generated a nominal gross domestic product (GDP) of around €17.935 trillion in 2024, accounting for approximately one sixth of global economic output. Its cornerstone, the European Union Customs Union, Customs Union, paved the way to establishing European Single Market, an internal single market based on standardised European Union law, legal framework and legislation that applies in all member states in those matters, and only those matters, where the states ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurozone
The euro area, commonly called the eurozone (EZ), is a Monetary union, currency union of 20 Member state of the European Union, member states of the European Union (EU) that have adopted the euro (Euro sign, €) as their primary currency and sole legal tender, and have thus fully implemented Economic and Monetary Union of the European Union, EMU policies. The 20 eurozone members are: : Austria, Belgium, Croatia, Cyprus, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, the Netherlands, Portugal, Slovakia, Slovenia, and Spain. The seven non-eurozone members of the EU are Bulgaria, the Czech Republic, Denmark, Hungary, Poland, Romania, and Sweden. They continue to use their own national currencies, although all but Denmark are obliged to join once they meet the euro convergence criteria. Bulgaria is targeting to join the eurozone on 1 January 2026. Bulgaria is expected to become the 21st eurozone member from January 1, 2026. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Central Bank
The European Central Bank (ECB) is the central component of the Eurosystem and the European System of Central Banks (ESCB) as well as one of seven institutions of the European Union. It is one of the world's Big Four (banking)#International use, most important central banks with a balance sheet total of around 7 trillion. The Governing Council of the European Central Bank, ECB Governing Council makes monetary policy for the Eurozone and the European Union, administers the foreign exchange reserves of EU member states, engages in foreign exchange operations, and defines the intermediate monetary objectives and key interest rate of the EU. The Executive Board of the European Central Bank, ECB Executive Board enforces the policies and decisions of the Governing Council, and may direct the national central banks when doing so. The ECB has the exclusive right to authorise the issuance of euro banknotes. Member states can issue euro coins, but the volume must be approved by the EC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Currency
A currency is a standardization of money in any form, in use or circulation as a medium of exchange, for example banknotes and coins. A more general definition is that a currency is a ''system of money'' in common use within a specific environment over time, especially for people in a nation state. Under this definition, the British Pound sterling (£), euros (€), Japanese yen (¥), and U.S. dollars (US$) are examples of (government-issued) fiat currencies. Currencies may act as stores of value and be traded between nations in foreign exchange markets, which determine the relative values of the different currencies. Currencies in this sense are either chosen by users or decreed by governments, and each type has limited boundaries of acceptance; i.e., legal tender laws may require a particular unit of account for payments to government agencies. Other definitions of the term ''currency'' appear in the respective synonymous articles: banknote, coin, and money. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monetary Reform
Monetary reform is any movement or theory that proposes a system of supplying money and financing the economy that is different from the current system. Monetary reformers may advocate any of the following, among other proposals: * A return to the gold standard (or silver standard or bimetallism). * Abolition of central bank support of the banking system during periods of crisis and/or the enforcement of full reserve banking for the privately owned banking system to remove the possibility of bank runs, possibly combined with sovereign money issued and controlled by the government or a central bank under the direction of the government. There is an associated debate within Austrian School whether free banking or full reserve banking should be advocated but regardless Austrian School economists such as Murray Rothbard support ending central bank bail outs ("End the Fed, ending the Fed"). * The issuance of interest-free credit (finance), credit by a government-controlled and fully ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sovereignty
Sovereignty can generally be defined as supreme authority. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within a state as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the person, body or institution that has the ultimate authority over other people and to change existing laws. In political theory, sovereignty is a substantive term designating supreme legitimate authority over some polity. In international law, sovereignty is the exercise of power by a state. ''De jure'' sovereignty refers to the legal right to do so; '' de facto'' sovereignty refers to the factual ability to do so. This can become an issue of special concern upon the failure of the usual expectation that ''de jure'' and ''de facto'' sovereignty exist at the place and time of concern, and reside within the same organization. Etymology The term arises from the unattested Vulgar Latin *''superanus'' (itself a derived form of Latin ''super'' – "over") meaning "chief", "ruler". Its spellin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |