|
Rhea Letter
The "Rhea letter" was an early 19th-century political controversy of the United States stemming from the First Seminole War and the contingent annexation of Florida. The controversy involves four (or rather three) key documents: * the "Jackson January letter" sent by U.S. Army general Andrew Jackson to President James Monroe on January 6, 1818, with its later annotation that the "Rhea letter" had been burned * the presumably fictitious "Rhea letter" purportedly sent to Andrew Jackson by Tennessee congressman John Rhea at the behest of James Monroe in February 1818. * the vaguely threatening letter sent to former U.S. president James Monroe on his deathbed in June 1831 by John Rhea at the behest of Andrew Jackson * the "Denunciation of the Insinuations of John Rhea" written by James Monroe as the last document he ever signed This chain of evidence relates to Andrew Jackson's after-the-fact rationalization and defense of his unauthorized invasion of Florida in 1818, a campaign t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homathlemico
Homathlemico (d. April 8, 1818) was a chief of the Muscogee people who once lived at Battle of Autossee, Autussee in what is now Alabama in North America. Along with Josiah Francis (Hillis Hadjo), Hillis Hadjo (Francis the Prophet), he was decoyed to shore and captured near St. Marks, Florida, St. Marks, East Florida by an American naval ship flying a British flag during what is now known as the First Seminole War. Five days later, Homathlemico was summarily executed by order of U.S. Army major-general and future president Andrew Jackson. Jackson claimed that Homathlemico had led the party responsible for the Scott massacre, although there was no due process or trial on these charges before he was executed for his alleged crimes. References Sources * * Pre-statehood history of Florida Native American history of Florida Spanish Florida 19th-century Native American leaders 19th-century Seminole people 1818 deaths Executed Native American people Native Americans of the Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Stenberg
Richard R. Stenberg (b. ) was an American historian. During the 1930s and early 1940s he wrote several influential papers on the U.S. politics and events of the second quarter of the 19th century, sometimes known as the Jacksonian era. He also worked as regional administrator of Federal One's Historical Records Survey. He then largely disappeared from the public record himself, apparently having been confined to a hospital in Washington, D.C. Life and work Stenberg was born around 1910 in Nebraska. He did his doctorate at the University of Texas. In 1934 he was hired to teach European history at the University of Arkansas. He was a regional director, based in San Antonio, of the New Deal-era Historical Records Survey, serving from inception until August 1936. At the time of his son's birth in 1937, he reported to the registrar that he had worked as a teacher at the University of Texas for the past four years. Stenberg is remembered for consistently attacking what was then conse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
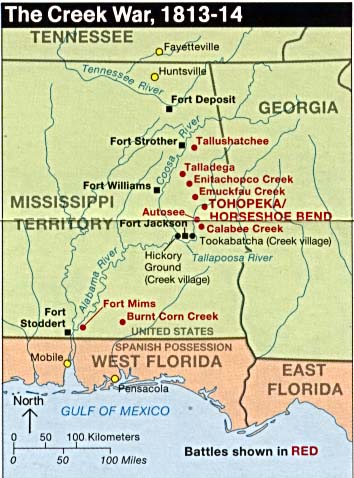
Battle Of Horseshoe Bend
The Battle of Horseshoe Bend (also known as ''Tohopeka'', ''Cholocco Litabixbee'', or ''The Horseshoe''), was fought during the War of 1812 in the Mississippi Territory, now central Alabama. On March 27, 1814, United States forces and Indian allies under Major General Andrew Jackson defeated the Red Sticks, a part of the Creek Indian tribe who opposed American expansion, effectively ending the Creek War. Background The Creek Indians of Georgia and the eastern part of the Mississippi Territory had become divided into two factions: the Upper Creek (or Red Sticks), a majority who opposed American expansion and sided with the British and the colonial authorities of Spanish Florida during the War of 1812; and the Lower Creek, who were more assimilated into the Anglo culture, had a stronger relationship with the U.S. Indian Agent Benjamin Hawkins, and sought to remain on good terms with the Americans. The Shawnee war leader Tecumseh visited Creek and other Southeast Indian towns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Tallushatchee
The Battle of Tallushatchee was fought on November 3, 1813, in northeastern Mississippi Territory (near present-day Alexandria, Alabama) during the Creek War. United States dragoons, commanded by Brigadier General John Coffee, defeated the Red Sticks. Background After the massacre at Fort Mims, General Andrew Jackson assembled an army of 2,500 Tennessee militia. Jackson began marching into Mississippi Territory to combat the Red Stick Creeks. Jackson's troops began to construct Fort Strother along the Coosa River. 15 miles (24 km) away from the fort lay the Creek village of Tallasseehatchee, where a sizeable force of Red Stick warriors were. Jackson ordered his friend and most trusted subordinate, General John Coffee, to attack the village. Battle Coffee took about 900 dragoons and arrived on November 3 at the village, where he divided his brigade into two columns that encircled the town. Two companies ventured into the center of the circle to draw out the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Creek War
The Creek War (also the Red Stick War or the Creek Civil War) was a regional conflict between opposing Native American factions, European powers, and the United States during the early 19th century. The Creek War began as a conflict within the tribes of the Muscogee, but the United States quickly became involved. British traders and Spanish colonial officials in Florida supplied the Red Sticks with weapons and equipment due to their shared interest in preventing the expansion of the United States into regions under their control. The Creek War took place largely in modern-day Alabama and along the Gulf Coast. Major engagements of the war involved the United States military and the Red Sticks (or Upper Creeks), a Muscogee tribal faction who resisted U.S. territorial expansion. The United States formed an alliance with the traditional enemies of the Muscogee, the Choctaw and Cherokee nations, as well as the Lower Creeks faction of the Muscogee. During the hostilities, the Red ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Sticks
Red Sticks (also Redsticks, Batons Rouges, or Red Clubs)—the name deriving from the red-painted war clubs of some Native American Creek—refers to an early 19th century traditionalist faction of Muscogee Creek people in the Southeastern United States. Made up mostly of Creek of the Upper Towns that supported traditional leadership and culture, as well as the preservation of communal land for cultivation and hunting, the Red Sticks arose at a time of increasing pressure on Creek territory by European American settlers. Creek of the Lower Towns were closer to the settlers, had more mixed-race families, and had already been forced to make land cessions to the Americans. In this context, the Red Sticks led a resistance movement against European American encroachment and assimilation, tensions that culminated in the outbreak of the Creek War in 1813. Initially a civil war among the Creek, the conflict drew in United States state forces while the nation was already engaged in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pensacola, Florida
Pensacola ( ) is a city in the Florida panhandle in the United States. It is the county seat and only incorporated city, city in Escambia County, Florida, Escambia County. The population was 54,312 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. It is the principal city of the Pensacola metropolitan area, which had 509,905 residents in the 2020 census. Pensacola was first settled by the Spanish Empire in 1559, antedating the establishment of St. Augustine, Florida, St. Augustine by six years, but was abandoned due to a significant hurricane and not resettled until 1698. Pensacola is a Port of Pensacola, seaport on Pensacola Bay, which is protected by the barrier island of Santa Rosa Island (Florida), Santa Rosa and connects to the Gulf of Mexico. A large Naval Air Station Pensacola, United States Naval Air Station, the first in the United States, is located in Pensacola. It is the base of the Blue Angels flight-demonstration team and the National Naval Aviation Museum. The Univers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maroons
Maroons are descendants of Africans in the Americas and islands of the Indian Ocean who escaped from slavery, through flight or manumission, and formed their own settlements. They often mixed with Indigenous peoples, eventually evolving into separate creole cultures such as the Garifuna and the Mascogos. Etymology ''Maroon'' entered English around the 1590s, from the French adjective , meaning 'feral' or 'fugitive', itself possibly from the American Spanish word , meaning 'wild, unruly' or 'runaway slave'. In the early 1570s, Sir Francis Drake's raids on the Spanish in Panama were aided by "''Symerons''", a likely misspelling of '. The linguist Leo Spitzer, writing in the journal ''Language'', says, "If there is a connection between Eng. ''maroon'', Fr. ', and Sp. ', Spain (or Spanish America) probably gave the word directly to England (or English America)." Alternatively, the Cuban philologist José Juan Arrom has traced the origins of the word ''maroon'' further t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was the armed conflict that comprised the final eight years of the broader American Revolution, in which American Patriot (American Revolution), Patriot forces organized as the Continental Army and commanded by George Washington defeated the British Army during the American Revolutionary War, British Army. The conflict was fought in North America, the Caribbean, and the Atlantic Ocean. The war's outcome seemed uncertain for most of the war. However, Washington and the Continental Army's decisive victory in the Siege of Yorktown in 1781 led King George III and the Kingdom of Great Britain to negotiate an end to the war in the Treaty of Paris (1783), Treaty of Paris two years later, in 1783, in which the British monarchy acknowledged the independence of the Thirteen Colonies, leading to the establishment of the United States as an independent and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire, sometimes referred to as the Hispanic Monarchy (political entity), Hispanic Monarchy or the Catholic Monarchy, was a colonial empire that existed between 1492 and 1976. In conjunction with the Portuguese Empire, it ushered in the European Age of Discovery. It achieved a global scale, controlling vast portions of the Americas, Africa, various islands in Asia and Oceania, as well as territory in other parts of Europe. It was one of the most powerful empires of the early modern period, becoming known as "the empire on which the sun never sets". At its greatest extent in the late 1700s and early 1800s, the Spanish Empire covered , making it one of the List of largest empires, largest empires in history. Beginning with the 1492 arrival of Christopher Columbus and continuing for over three centuries, the Spanish Empire would expand across the Caribbean Islands, half of South America, most of Central America and much of North America. In the beginning, Portugal was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Florida
East Florida () was a colony of Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain from 1763 to 1783 and a province of the Spanish Empire from 1783 to 1821. The British gained control over Spanish Florida in 1763 as part of the Treaty of Paris (1763), Treaty of Paris that ended the Seven Years' War. Deciding that the colony was too large to administer as a single unit, British officials divided Florida into two colonies separated by the Apalachicola River: the colony of East Florida, with its capital located in St. Augustine, Florida, St. Augustine; and West Florida, with its capital located in Pensacola. East Florida was much larger and comprised the bulk of the former Spanish colony and most of the current Florida, state of Florida. It had also been the most populated region of Spanish Florida, but before control was transferred to Britain, most residents – including virtually everyone in St. Augustine – left the territory, with most migrating to Cuba. Britain tried to attract settle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Florida
West Florida () was a region on the northern coast of the Gulf of Mexico that underwent several boundary and sovereignty changes during its history. Great Britain established West and East Florida in 1763 out of land acquired from France and Spain after the Seven Years' War. As its name suggests, it was formed out of the western part of former Spanish Florida (East Florida formed the eastern part, with the Apalachicola River as the border), along with land taken from French Louisiana. Pensacola became West Florida's capital. The colony included about two thirds of what is now the Florida panhandle, as well as parts of the modern U.S. states of Louisiana, Mississippi, and Alabama. As the newly acquired territory was too large to govern from one administrative center, the British divided it into two new colonies separated by the Apalachicola River. British West Florida included the part of former Spanish Florida, which lay west of the Apalachicola, as well as parts of former Fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |