|
Responsibility For The Burning Of Smyrna
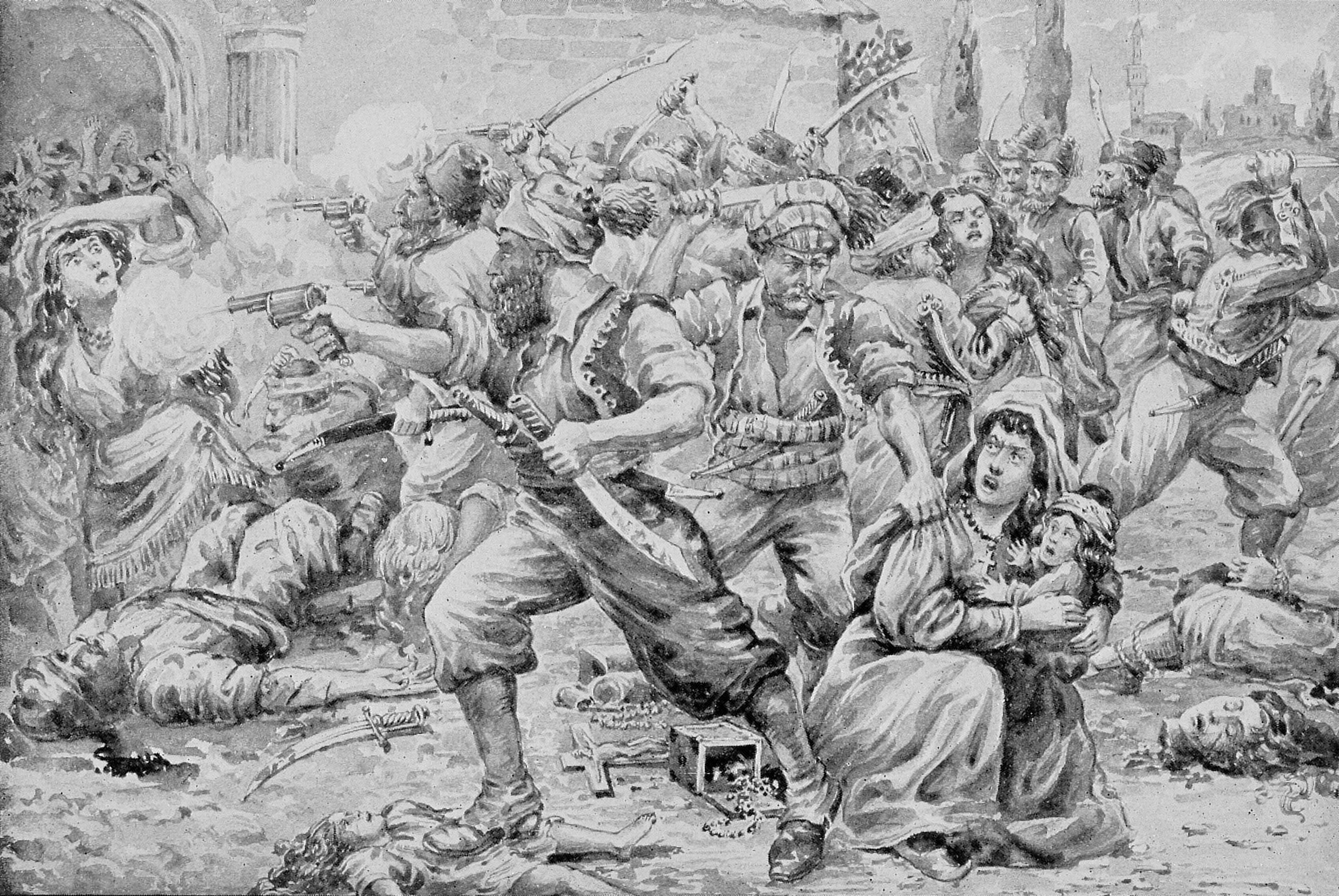
The question of who was responsible for starting the burning of Smyrna continues to be debated, with Turkish sources mostly attributing responsibility to Greeks or Armenians, and vice versa. Other sources, on the other hand, suggest that at the very least, Turkish inactivity played a significant part on the event. Sources claiming Turkish responsibility George Horton's account George Horton was the U.S. Consul General of Smyrna. He was compelled to evacuate Smyrna on 13 September, and arrived in Athens on 14 September. In 1926, he published his own account of what happened in Smyrna, titled ''The Blight of Asia''. He included testimony from a number of eyewitnesses and quoted a number of contemporary scholars. Horton's account states that the last of the Greek soldiers had abandoned Smyrna during the evening of 8 September since it was known in advance that Turkish soldiers would arrive on 9 September. Origins of the Fire Horton said that Turkish soldiers set the fire, on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burning Of Smyrna
The burning of Smyrna ( el, Καταστροφή της Σμύρνης, "Smyrna Catastrophe"; tr, 1922 İzmir Yangını, "1922 Izmir Fire"; hy, Զմիւռնիոյ Մեծ Հրդեհ, ''Zmyuṙno Mets Hrdeh'') destroyed much of the port city of Smyrna (modern İzmir, Turkey) in September 1922. Eyewitness reports state that the fire began on 13 September 1922Horton, George. '' The Blight of Asia''. Indianapolis: The Bobbs-Merrill Company, 1926; repr. London: Gomidas Institute, 2003, p. 96. and lasted until it was largely extinguished on 22 September. It began four days after the Turkish military captured the city on 9 September, effectively ending the Greco-Turkish War, more than three years after the landing of Greek army troops at Smyrna on 15 May 1919. Estimated Greek and Armenian deaths resulting from the fire range from 10,000 to 125,000.Naimark, ''Fires of Hatred'', p. 52. Approximately 80,000 to 400,000 Greek and Armenian refugees crammed the waterfront to escape from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marjorie Housepian Dobkin
Marjorie Anaïs Housepian Dobkin () was an author and an English professor at Barnard College, Columbia University, New York. Her books include the novel ''A Houseful of Love'' (a '' New York Times'' and ''New York Herald Tribune'' bestseller) and the history ''Smyrna 1922: The Destruction of a City''. Biography Housepian Dobkin was born in 1922 to Dr. Moses Housepian and his wife Makrouhie Housepian (née Ashjian), Armenian immigrants in New York City, two and a half months after her grandfather was killed by a Turkish soldier during the burning of Smyrna from which her grandmother fled as a refugee. Her younger brother was the neurosurgeon Edgar Housepian. She attended Barnard College, graduating in 1944. She was a professor of literature and writing from 1957 to 1993, as well as associate dean of studies at Barnard from 1976 until 1993. Her students included the novelist Margaret Cezair-Thompson. Her academic career included: instructor in English at Barnard College (1957� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick Barton Maurice
Major-General Sir Frederick Barton Maurice, (19 January 1871 – 19 May 1951) was a British Army officer, military correspondent, writer and academic. During the First World War he was forced to retire from the army in May 1918 after writing a letter to ''The Times'' criticizing Prime Minister David Lloyd George for making misleading statements about the strength of British forces on the Western Front. He also later founded the British Legion in 1920, and served as its president from 1932 to 1947. Early life and military career Maurice was born in Dublin, the son of John Maurice, a British Army officer and military historian, and his wife Anne Frances "Annie" FitzGerald. He attended St. Paul's School and Sandhurst before joining the Derbyshire Regiment in 1892. His first overseas posting was to British India in 1897–98, during the Tirah Campaign. During this time, he served as aide-de-camp to his father, Major-General John Frederick Maurice. After a promotion to captain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Le Temps (Paris)
''Le Temps'' (, ''The Times'') was one of Paris's most important daily newspapers from 25 April 1861 to 30 November 1942. It was a serious paper of record. Founded in 1861 by Edmund Chojecki (writing under the pen name "Charles Edmond") and Auguste Nefftzer, ''Le Temps'' was under Nefftzer's direction for ten years, when took his place, and for nearly 45 years directed the newspaper with an iron hand until his death in 1914. He was succeeded by his sons Émile (1914), and Adrien Jr. (1925) and by Louis Mills (1929). Soon after Mills' death in 1931, ''Le Temps'' became a public limited company. Adrien Hébrard and his successors left substantial freedom to the editorial room and the newspaper had the reputation of keeping its journalists for a long time. ''Le Temps'' always remained moderate politically. The early issues of the newspaper reflected Nefftzer's liberal philosophy and had considerable trouble achieving readership. He frequently had to turn to friends in Alsace who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William H
William is a masculine given name of Norman French origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of England in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is sometimes abbreviated "Wm." Shortened familiar versions in English include Will, Wills, Willy, Willie, Liam, Bill, and Billy. A common Irish form is Liam. Scottish diminutives include Wull, Willie or Wullie (as in Oor Wullie or the play ''Douglas''). Female forms are Willa, Willemina, Wilma and Wilhelmina. Etymology William is related to the German given name ''Wilhelm''. Both ultimately descend from Proto-Germanic ''*Wiljahelmaz'', with a direct cognate also in the Old Norse name ''Vilhjalmr'' and a West Germanic borrowing into Medieval Latin ''Willelmus''. The Proto-Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-Armenian Sentiment
Anti-Armenian sentiment, also known as anti-Armenianism and Armenophobia, is hostility to, prejudice towards, or discrimination against towards Armenians, Armenia, and Armenian culture. Historically, anti-Armenianism has manifested in several ways, ranging from expressions of hatred of or discrimination against individual Armenians to organized pogroms by mobs or state-sanctioned genocide. Notable instances or persecution include the Hamidean massacres (1894-1897), the Adana massacre (1909), the Armenian genocide (1915), the Stalinist Great Purge (1936-1938), and the Sumgait pogrom (1988). Modern anti-Armenianism is often expressed by opposition to the actions or existence of an Armenian state, aggressive denial of the Armenian genocide or belief in an Armenian conspiracy to fabricate history and manipulate public and political opinion for political gain. Anti-Armenianism has also manifested as extrajudicial killing or intimidation of people of Armenian heritage and destruc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-Greek Sentiment
Anti-Greek sentiment (also known as Hellenophobia ( el, ελληνοφοβία, translit=ellēnophobía), anti-Hellenism, ( el, ανθελληνισμός, translit=anthellinismós), mishellenism ( el, μισελληνισμός, translit=misellēnismós), or Greek- bashing) refers to negative feelings, dislike, hatred, derision, racism, prejudice, and/or discrimination towards Greeks, the Hellenic Republic, and Greek culture. It is the opposite of philhellenism. Historic Ancient Rome In the mid- Republican period Rome phil-Hellenic and anti-Hellenic Roman intellectuals were involved in a conflict over Greek influence. One author explains, "the relationship of Romans to Greek culture was frequently ambiguous: they admired it as superior and adopted its criteria, while they remained skeptical of some aspects; hence they adapted it selectively according to their own purposes." An anti-Hellenic movement emerged in reaction to the primacy of Greek led by the conservative and reactiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkophilia
A Turkophile or Turcophile, ( tr, Türksever) is a person who has a strong positive predisposition or sympathy toward the government, culture, history, or people of Turkey. This could include Turkey itself and its history, the Turkish language, Turkish cuisine, and literature, or in the broader sense, the Turkic peoples in general. The opposite of a Turkophile is a Turkophobe is a person who shows hostility, intolerance, or racism against Turkish or Turkic people, Turkish culture and Turkic countries. Historically, Turkophilia (Turkish: ''Türkseverlik'') has been associated with supporters of the history of the Ottoman Empire, Seljuk Empire and Sultanate of Rûm. Notable Turkophiles * Jean-Étienne Liotard, Swiss painter, art connoisseur and dealer * David Urquhart, Scottish diplomat, writer and politician * Ármin Vámbéry, Hungarian Turkologist and traveller * Ernst Jaeckh, German author * Pierre Loti, French naval officer and novelist * Juanito, French singer * Lev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harcourt, Brace, Jovanovich
Harcourt () was an American publishing firm with a long history of publishing fiction and nonfiction for adults and children. The company was last based in San Diego, California, with editorial/sales/marketing/rights offices in New York City and Orlando, Florida, and was known at different stages in its history as Harcourt Brace, & Co. and Harcourt Brace Jovanovich. From 1919 to 1982, it was based in New York City. Houghton Mifflin acquired Harcourt in 2007. It incorporated the Harcourt name to form Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. As of 2012, all Harcourt books that have been re-released are under the Houghton Mifflin Harcourt name. The Harcourt Children's Books division left the name intact on all of its books under that name as part of HMH. In 2007 the U.S. Schools Education and Trade Publishing parts of Harcourt Education were sold by Reed Elsevier to Houghton Mifflin Riverdeep Group. Harcourt Assessment and Harcourt Education International were acquired by Pearson, the inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark Lambert Bristol
Mark Lambert Bristol (April 17, 1868 – May 13, 1939) was a rear admiral in the United States Navy. Biography He was born on April 17, 1868, in Glassboro, New Jersey. Bristol graduated from the United States Naval Academy in 1887. During the Spanish–American War, he served aboard the battleship USS ''Texas'' and participated in the Battle of Santiago de Cuba. From 1901 to 1903, he served as aide to the Commander-in-Chief North Atlantic Fleet. He commanded the battleship USS ''Oklahoma'' during World War I. He served as the US High Commissioner in Turkey (1919–1927). His correspondence and other documents that he gathered are often cited during discussions on numerous events of that era, including Turkish-Armenian relations in which he played a significant role in his opposition to Armenian aspirations and American involvement in assuming a mandate in Armenia, Bristol was an antisemite who also hated the Greeks and the Armenians. His documents include writings such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rear Admiral
Rear admiral is a senior naval flag officer rank, equivalent to a major general and air vice marshal and above that of a commodore and captain, but below that of a vice admiral. It is regarded as a two star " admiral" rank. It is often regarded as a two-star rank with a NATO code of OF-7. The term originated in the days of naval sailing squadrons and can trace its origins to the Royal Navy. Each naval squadron was assigned an admiral as its head, who commanded from the centre vessel and directed the squadron's activities. The admiral would in turn be assisted by a vice admiral, who commanded the lead ships that bore the brunt of a battle. In the rear of the squadron, a third admiral commanded the remaining ships and, as this section was considered to be in the least danger, the admiral in command of it was typically the most junior. This has continued into the modern age, with rear admiral the most junior admiralty of many navies. In most European navies, the equivalent ran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |