|
Repressor LexA
The LexA repressor or LexA (Locus for X-ray sensitivity A) is a transcriptional repressor () that represses SOS response genes coding primarily for error-prone DNA polymerases, DNA repair enzymes and cell division inhibitors. LexA forms ''de facto'' a two-component regulatory system with RecA, which senses DNA damage at stalled replication forks, forming monofilaments and acquiring an active conformation capable of binding to LexA and causing LexA to cleave itself, in a process called autoproteolysis. LexA polypeptides contains a two domains: a DNA-binding domain and a dimerization domain. The dimerization domain binds to other LexA polypeptides to form dumbbell shaped dimers. The DNA-binding domain is a variant form of the helix-turn-helix DNA binding motif, and is usually located at the N-terminus of the protein. This domain is bound to an SOS box upstream of SOS response genes until DNA damage stimulates autoproteolysis. Clinical significance DNA damage can be inflicted b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Repressor
In molecular genetics, a repressor is a DNA- or RNA-binding protein that inhibits the expression of one or more genes by binding to the operator or associated silencers. A DNA-binding repressor blocks the attachment of RNA polymerase to the promoter, thus preventing transcription of the genes into messenger RNA. An RNA-binding repressor binds to the mRNA and prevents translation of the mRNA into protein. This blocking or reducing of expression is called repression. Function If an inducer, a molecule that initiates the gene expression, is present, then it can interact with the repressor protein and detach it from the operator. RNA polymerase then can transcribe the message (expressing the gene). A co-repressor is a molecule that can bind to the repressor and make it bind to the operator tightly, which decreases transcription. A repressor that binds with a co-repressor is termed an ''aporepressor'' or ''inactive repressor''. One type of aporepressor is the trp repre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UV Light
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of the total electromagnetic radiation output from the Sun. It is also produced by electric arcs, Cherenkov radiation, and specialized lights, such as mercury-vapor lamps, tanning lamps, and black lights. The photons of ultraviolet have greater energy than those of visible light, from about 3.1 to 12 electron volts, around the minimum energy required to ionize atoms. Although long-wavelength ultraviolet is not considered an ionizing radiation because its photons lack sufficient energy, it can induce chemical reactions and cause many substances to glow or fluoresce. Many practical applications, including chemical and biological effects, are derived from the way that UV radiation can interact with organic molecules. These i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Domains
In molecular biology, a protein domain is a region of a protein's polypeptide chain that is self-stabilizing and that folds independently from the rest. Each domain forms a compact folded three-dimensional structure. Many proteins consist of several domains, and a domain may appear in a variety of different proteins. Molecular evolution uses domains as building blocks and these may be recombined in different arrangements to create proteins with different functions. In general, domains vary in length from between about 50 amino acids up to 250 amino acids in length. The shortest domains, such as zinc fingers, are stabilized by metal ions or disulfide bridges. Domains often form functional units, such as the calcium-binding EF hand domain of calmodulin. Because they are independently stable, domains can be "swapped" by genetic engineering between one protein and another to make chimeric proteins. Background The concept of the domain was first proposed in 1973 by Wetlaufer after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quinolone Antibiotic
Quinolone antibiotics constitute a large group of broad-spectrum bacteriocidals that share a bicyclic core structure related to the substance 4-quinolone. They are used in human and veterinary medicine to treat bacterial infections, as well as in animal husbandry, specifically poultry production. Quinolone antibiotics are classified into four generations based on their spectrum of activity and chemical modifications. The first-generation quinolones, such as nalidixic acid, primarily target Gram-negative bacteria and are mainly used for urinary tract infections. Second-generation quinolones introduced fluorine atoms into their structure, creating fluoroquinolones, which significantly expanded their antibacterial activity to include some Gram-positive bacteria. Third-generation fluoroquinolones further improved Gram-positive coverage, while fourth-generation fluoroquinolones offer broad-spectrum activity, including anaerobic bacteria. Only quinolone antibiotics in generat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combination Therapy
In mathematics, a combination is a selection of items from a set that has distinct members, such that the order of selection does not matter (unlike permutations). For example, given three fruits, say an apple, an orange and a pear, there are three combinations of two that can be drawn from this set: an apple and a pear; an apple and an orange; or a pear and an orange. More formally, a ''k''-combination of a set ''S'' is a subset of ''k'' distinct elements of ''S''. So, two combinations are identical if and only if each combination has the same members. (The arrangement of the members in each set does not matter.) If the set has ''n'' elements, the number of ''k''-combinations, denoted by C(n,k) or C^n_k, is equal to the binomial coefficient \binom nk = \frac, which can be written using factorials as \textstyle\frac whenever k\leq n, and which is zero when k>n. This formula can be derived from the fact that each ''k''-combination of a set ''S'' of ''n'' members has k! permu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrase
Retroviral integrase (IN) is an enzyme An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ... produced by a retrovirus (such as HIV) that integrates (forms covalent links between) its genetic information into that of the host cell it infects. Retroviral INs are not to be confused with phage integrases ( recombinases) used in biotechnology, such as λ phage integrase, as discussed in site-specific recombination. The macromolecular complex of an IN macromolecule bound to the ends of the viral DNA ends has been referred to as the '' intasome''; IN is a key component in this and the retroviral pre-integration complex. Structure All retroviral IN proteins contain three canonical domains, connected by flexible linkers: * an N-terminal HH-CC zinc-binding domain (a three-heli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integron
Integrons are genetic mechanisms that allow bacteria to adapt and evolve rapidly through the stockpiling and expression of new genes. These genes are embedded in a specific genetic structure called gene cassette (a term that is lately changing to integron cassette) that generally carries one promoterless open reading frame (ORF) together with a recombination site (''attC''). Integron cassettes are incorporated to the ''attI'' site of the integron platform by site-specific recombination reactions mediated by the integrase. Discovery Integrons were initially discovered on conjugative plasmids through their role in antibiotic resistance. Indeed, these mobile integrons, as they are now known, can carry a variety of cassettes containing genes that are almost exclusively related to antibiotic resistance. Further studies have come to the conclusion that integrons are chromosomal elements, and that their mobilisation onto plasmids has been fostered by transposons and selected by the inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
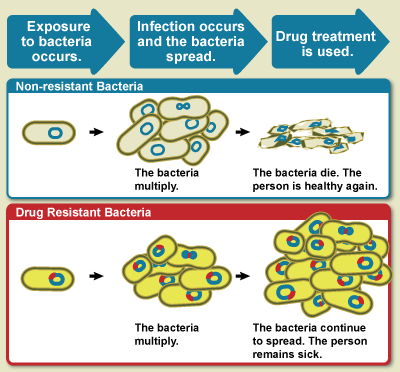
Antibiotic Resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR or AR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from antimicrobials, which are drugs used to treat infections. This resistance affects all classes of microbes, including bacteria (antibiotic resistance), viruses (antiviral resistance), parasites (antiparasitic resistance), and fungi (antifungal resistance). Together, these adaptations fall under the AMR umbrella, posing significant challenges to healthcare worldwide. Misuse and improper management of antimicrobials are primary drivers of this resistance, though it can also occur naturally through genetic mutations and the spread of resistant genes. Antibiotic resistance, a significant AMR subset, enables bacteria to survive antibiotic treatment, complicating infection management and treatment options. Resistance arises through spontaneous mutation, horizontal gene transfer, and increased selective pressure from antibiotic overuse, both in medicine and agriculture, which accelerat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virulence Factor
Virulence factors (preferably known as pathogenicity factors or effectors in botany) are cellular structures, molecules and regulatory systems that enable microbial pathogens (bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa) to achieve the following: * colonization of a niche in the host (this includes movement towards and attachment to host cells) * immunoevasion, evasion of the host's immune response * immunosuppression, inhibition of the host's immune response (this includes leukocidin-mediated cell death) * entry into and exit out of cells (if the pathogen is an intracellular one) * obtain nutrition from the host Specific pathogens possess a wide array of virulence factors. Some are chromosomally encoded and intrinsic to the bacteria (e.g. capsules and endotoxin), whereas others are obtained from mobile genetic elements like plasmids and bacteriophages (e.g. some exotoxins). Virulence factors encoded on mobile genetic elements spread through horizontal gene transfer, and can con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotic Resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR or AR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from antimicrobials, which are drugs used to treat infections. This resistance affects all classes of microbes, including bacteria (antibiotic resistance), viruses (antiviral resistance), parasites (antiparasitic resistance), and fungi (antifungal resistance). Together, these adaptations fall under the AMR umbrella, posing significant challenges to healthcare worldwide. Misuse and improper management of antimicrobials are primary drivers of this resistance, though it can also occur naturally through genetic mutations and the spread of resistant genes. Antibiotic resistance, a significant AMR subset, enables bacteria to survive antibiotic treatment, complicating infection management and treatment options. Resistance arises through spontaneous mutation, horizontal gene transfer, and increased selective pressure from antibiotic overuse, both in medicine and agriculture, which accelerat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Replication
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all life, living organisms, acting as the most essential part of heredity, biological inheritance. This is essential for cell division during growth and repair of damaged tissues, while it also ensures that each of the new cells receives its own copy of the DNA. The cell possesses the distinctive property of division, which makes replication of DNA essential. DNA is made up of a nucleic acid double helix, double helix of two Complementary DNA, complementary DNA strand, strands. DNA is often called double helix. The double helix describes the appearance of a double-stranded DNA which is composed of two linear strands that run opposite to each other and twist together. During replication, these strands are separated. Each strand of the original DNA molecule then serves as a template for the production of its counterpart, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topoisomerase IV
Topoisomerase IV is one of two Type II topoisomerases in bacteria, the other being DNA gyrase. Like gyrase, topoisomerase IV is able to pass one double-strand of DNA through another double-strand of DNA, thereby changing the linking number of DNA by two in each enzymatic step. Both share a hetero-4-mer structure formed by a symmetric homodimer of A/B heterodimers, usually named ''ParC'' and ''ParE''. Functions Topoisomerase IV has two functions in the cell. * First, it is responsible for unlinking, or decatenating, DNA following DNA replication. The double-helical nature of DNA and its semiconservative mode of replication causes the two newly replicated DNA strands to be interlinked. These links must be removed in order for the chromosome (and plasmids) to segregate into daughter cells so that cell division can complete. * Topoisomerase IV's second function in the cell is to relax positive supercoils. It shares this role with DNA gyrase, which is also able to relax positive super ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |