|
Reloncaví Estuary
Reloncaví Estuary (Spanish: Estuario de Reloncaví, archaic: Sin Fondo) is a fjord off Reloncaví Sound, located in the Los Lagos Region of Chile. Several National Parks and Wilderness Areas are situated in the vicinity of this fjord. Among them are: Alerce Andino National Park, Hornopirén National Park, Vicente Pérez Rosales National Park, Llanquihue National Reserve and the Cochamó Valley. The Yate Volcano towers above this fjord. The Puelo River empties into this estuary An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime enviro .... It also receives the outflow of the Todos los Santos Lake through the short tortuous Petrohué River. The Caicura Islets lie where Reloncaví Estuary meet Reloncaví Sound in the southwestern mouth of the fjord. Sources Fjords of Chile Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iglesia Cochamó (37802414655)
Iglesia may refer to: * Iglesia, the Spanish form of church * Iglesia Department * Iglesia ni Cristo * Iglesia Filipina Independiente The Philippine Independent Church (; ), officially referred to by its Philippine Spanish name (IFI) and colloquially called the Aglipayan Church, is an Independent Catholic, independent catholic Christian denomination, in the form of a Religi ... * Iglesia (Metro Madrid), a station on Line 1 {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yate Volcano
Yate Volcano is a large, glaciated stratovolcano located in the southern Andes, in the Los Lagos Region of Chile, south of the Reloncaví Estuary. Yate lies on the major regional Liquiñe-Ofqui Fault, Liquiñe-Ofqui Fault Zone, and is located 10 km north-east of the smaller Hornopiren (volcano), Hornopiren volcano. The last known eruption occurred in 1090 CE. There are no historical records of recent volcanic activity, but there is strategic evidence of smaller eruptions sometime in the Holocene. The volcano is named after Juan Yates, also known as John Yates, a settler of Puerto Americano who played a significant role in the exploration and colonisation of Patagonia. 1965 Landslide and Tsunami On February 19, 1965 a non-eruptive landslide of ice and rock caused by unusually heavy summer rains slid rapidly into a narrow gully, descended around 1500 meters in elevation, and crashed into Lake Cabrera below. This triggered a tsunami that thundered across the lake and swept th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
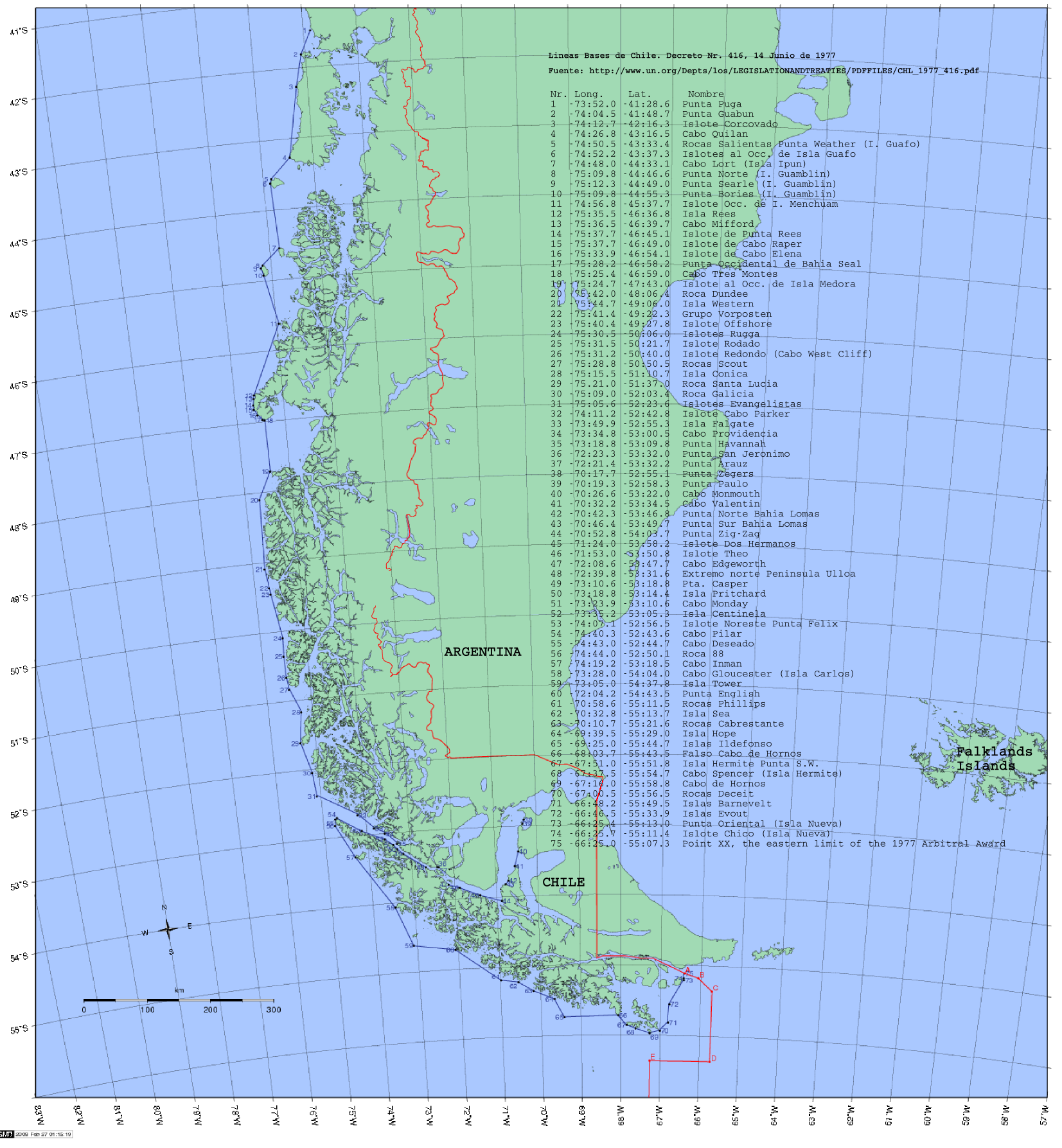
Fjords Of Chile
The southern coast of Chile presents a large number of fjords and fjord-like channels from the latitudes of Cape Horn (55° S) to Reloncaví Estuary (42° S). Some fjords and channels are important navigable channels providing access to ports like Punta Arenas, Puerto Chacabuco, and Puerto Natales. History Indigenous peoples The earliest known inhabitants of the fjords and channels of Chile were, from north to south, the Chono, Alacalufe, and Yaghan, all of whom shared a life style as canoe-faring hunter-gatherers. They also shared physical traits such as being of low stature, long-headed (''Dolichocephalic''), and having a "low face".Trivero Rivera 2005, p. 42. Despite similarities their languages were completely different.Trivero Rivera 2005, p. 33. The Chono moved around in the area from Chiloé Archipelago to 50° S and the Alacalufe from 46° S to the Strait of Magellan. Thus both groups overlapped in Gulf of Penas, Guayaneco Archipelago and other islands. Yaghans inhabit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anales Del Instituto De La Patagonia
The ''Anales del Instituto de la Patagonia'' is a biannual peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the University of Magallanes. It publishes articles on natural science with a focus on Earth science or biology regarding Patagonia, Tierra del Fuego, and Antarctica. The editor-in-chief is Américo Montiel San Martin (University of Magallanes). Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in Biological Abstracts, BIOSIS Previews, CAB Abstracts, and The Zoological Record ''The Zoological Record'' (''ZR'') is an electronic index of zoological literature that also serves as the unofficial register of scientific names in zoology. It was started as a print publication in 1864 by the Zoological Society of London, .... References External links *{{Official website, http://www.analesdelinstitutodelapatagonia.cl/index.php/analespatagonia Spanish-language journals Academic journals published by universities of Chile University of Magallanes Academic journ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caicura Islets
The Caicura Islets (, ''Islotes Caicura'') are a group of small islands located off the Pacific coast of northern Patagonia in Chile. More specifically they lie where the fjord Reloncaví Estuary meet Reloncaví Sound. It is an important breeding site for marine birds and South American sea lions. Prior to the settlement of the islands in the late 20th century there was also a Magellanic penguin colony on them. Southern elephant seal The southern elephant seal (''Mirounga leonina'') is one of two species of elephant seals. It is the largest member of the clade Pinnipedia and the order Carnivora, as well as the largest extant marine mammal that is not a cetacean. It gets its ...s have occasionally been observed at the islets. References {{reflist Islands of Los Lagos Region South American sea lion colonies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petrohué River
Petrohué River () is a List of rivers in Chile, Chilean river located in the Los Lagos Region of Chile. It originates from Todos los Santos Lake in the Vicente Pérez Rosales National Park. At its origin are the Petrohué Waterfalls. Sport fishing The Petrohue River is well known for its recreational fishing; the fishing season begins in November and ends in May. Species found in the river include: * Chinook salmon * Brown trout * Rainbow trout * Atlantic salmon * Coho salmon * Perca trout References Rivers of Los Lagos Region Rivers of Chile {{Chile-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Todos Los Santos Lake
Lake Todos los Santos (Spanish for "All Saints Lake") is a lake located in the Los Lagos Region of southern Chile, 96 km northeast of the regional capital Puerto Montt and 76 km east of Puerto Varas, within the boundaries of the Vicente Pérez Rosales National Park. It has a surface area of 178.5 km² and a maximum depth of 337 m. The Lake's National Park status has ensured protection to its environment. The catchment is largely covered with old-growth Valdivian temperate rain forests. The present form of the lake is the result of glacial and volcanic processes. Hydrology The main tributary of the lake is the Río Peulla/Río Negro, next to the Peulla locality. Its outflow at the Petrohué locality gives rise to the Petrohué River, with an average outflow of 270 m³ per second. Even though the lake has a regulating effect, it is subject to water level variations that may exceed 3 m and reflect in the discharge at the outflow. At a short distance from the Petrohu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estuary
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environments and are an example of an ecotone. Estuaries are subject both to marine influences such as tides, waves, and the influx of saline water, and to fluvial influences such as flows of freshwater and sediment. The mixing of seawater and freshwater provides high levels of nutrients both in the water column and in sediment, making estuaries among the most productive natural habitats in the world. Most existing estuaries formed during the Holocene epoch with the flooding of river-eroded or glacially scoured valleys when the sea level began to rise about 10,000–12,000 years ago. Estuaries are typically classified according to their geomorphological features or to water-circulation patterns. They can have many different names, such as ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puelo River
The Puelo River has its origin in Lake Puelo in Argentine, and flows north-west through the Andes into Chile and the Reloncaví Estuary of the Reloncaví Sound at the northern end of the Gulf of Ancud. Course Just downstream from its source in Puelo Lake, the river enters Inferior Lake. After leaving the lake, the river flows in a generally northwesterly direction, receiving the waters of a chain of lakes, the largest being Azul and Las Rocas. It also receives the waters of Ventisquero and Traidor rivers. A part of the northernmost border of Pumalín Park approximately parallels the course of the Ventisquero River. Traidor River rises in Hornopirén National Park. A large northern tributary of the Puelo, the Manso, has its sources in Mascardi Lake Mascardi Lake (, ) is in the lake region of northern Patagonia in Río Negro Province of Argentina. The lake is near the resort city of Bariloche and is within the Nahuel Huapi National Park. The lake, of glacial origin, is na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cochamó Valley
Cochamó Valley (Spanish pronunciation: Help:IPA/Spanish, [kotʃamo] is a U-shaped valley located in the Andes, in Los Lagos Region of Chile, south of Vicente Pérez Rosales National Park and east of the Reloncaví Estuary. The valley takes its name from the river of Cochamó, and has a striking similarity to Yosemite Valley, due to its granite domes and old-growth forests. Like Yosemite, hikers and rock climbers from around the world come for the valley's several granite walls. A developing eco-tourism location for serious hikers with trails ranging from easy to challenging, and a myriad of rare bird and plant life, and a stunning landscape. Five kilometers from the village of Cochamó is a 6km gravel road that terminates at the hiking trail that leads into this east-west running valley. The trail carries on up through Argentina, traverses some of the most unspoiled areas of northern Patagonia, and rewards travelers with views of granite walls, plunging waterfalls, soaring An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fjord
In physical geography, a fjord (also spelled fiord in New Zealand English; ) is a long, narrow sea inlet with steep sides or cliffs, created by a glacier. Fjords exist on the coasts of Antarctica, the Arctic, and surrounding landmasses of the northern and southern hemispheres. Norway's coastline is estimated to be long with its nearly 1,200 fjords, but only long excluding the fjords. Formation A true fjord is formed when a glacier cuts a U-shaped valley by ice segregation and abrasion of the surrounding bedrock. According to the standard model, glaciers formed in pre-glacial valleys with a gently sloping valley floor. The work of the glacier then left an overdeepened U-shaped valley that ends abruptly at a valley or trough end. Such valleys are fjords when flooded by the ocean. Thresholds above sea level create freshwater lakes. Glacial melting is accompanied by the rebounding of Earth's crust as the ice load and eroded sediment is removed (also called isostasy or gla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Llanquihue National Reserve
Llanquihue National Reserve () is a national reserve in Los Lagos Region of Chile. The reserve lies southeast of Llanquihue Lake, and is bordered by the Petrohué River Petrohué River () is a List of rivers in Chile, Chilean river located in the Los Lagos Region of Chile. It originates from Todos los Santos Lake in the Vicente Pérez Rosales National Park. At its origin are the Petrohué Waterfalls. Sport fis ... on the northeast and by the Reloncaví Estuary on the east. On the south it is bounded by Chapo Lake, which separates the reserve from Alerce Andino National Park. References National reserves of Chile Protected areas of Los Lagos Region Valdivian temperate forests 1912 establishments in Chile Protected areas established in 1912 {{LosLagos-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |