|
Relay Channel
In information theory, a relay channel is a probability model of the communication between a sender and a receiver aided by one or more intermediate relay nodes. General discrete-time memoryless relay channel A discrete memoryless single-relay channel can be modelled as four finite sets, X_1, X_2, Y_1, and Y, and a conditional probability distribution p(y,y_1, x_1,x_2) on these sets. The probability distribution of the choice of symbols selected by the encoder and the relay encoder is represented by p(x_1,x_2). o------------------o , Relay Encoder , o------------------o Λ , , y1 x2 , , V o---------o x1 o------------------o y o---------o , Encoder , --->, p(y,y1, x1,x2) , --->, Decoder , o---------o o------------------o o---------o There exist three main relaying schemes: Decode-and-Forward, Compress-and-Forward and Amplify-a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Theory
Information theory is the mathematical study of the quantification (science), quantification, Data storage, storage, and telecommunications, communication of information. The field was established and formalized by Claude Shannon in the 1940s, though early contributions were made in the 1920s through the works of Harry Nyquist and Ralph Hartley. It is at the intersection of electronic engineering, mathematics, statistics, computer science, Neuroscience, neurobiology, physics, and electrical engineering. A key measure in information theory is information entropy, entropy. Entropy quantifies the amount of uncertainty involved in the value of a random variable or the outcome of a random process. For example, identifying the outcome of a Fair coin, fair coin flip (which has two equally likely outcomes) provides less information (lower entropy, less uncertainty) than identifying the outcome from a roll of a dice, die (which has six equally likely outcomes). Some other important measu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probability
Probability is a branch of mathematics and statistics concerning events and numerical descriptions of how likely they are to occur. The probability of an event is a number between 0 and 1; the larger the probability, the more likely an event is to occur."Kendall's Advanced Theory of Statistics, Volume 1: Distribution Theory", Alan Stuart and Keith Ord, 6th ed., (2009), .William Feller, ''An Introduction to Probability Theory and Its Applications'', vol. 1, 3rd ed., (1968), Wiley, . This number is often expressed as a percentage (%), ranging from 0% to 100%. A simple example is the tossing of a fair (unbiased) coin. Since the coin is fair, the two outcomes ("heads" and "tails") are both equally probable; the probability of "heads" equals the probability of "tails"; and since no other outcomes are possible, the probability of either "heads" or "tails" is 1/2 (which could also be written as 0.5 or 50%). These concepts have been given an axiomatic mathematical formaliza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communication
Communication is commonly defined as the transmission of information. Its precise definition is disputed and there are disagreements about whether Intention, unintentional or failed transmissions are included and whether communication not only transmits semantics, meaning but also creates it. Models of communication are simplified overviews of its main components and their interactions. Many models include the idea that a source uses a code, coding system to express information in the form of a message. The message is sent through a Communication channel, channel to a receiver who has to decode it to understand it. The main field of inquiry investigating communication is called communication studies. A common way to classify communication is by whether information is exchanged between humans, members of other species, or non-living entities such as computers. For human communication, a central contrast is between Verbal communication, verbal and non-verbal communication. Verba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communication Source
A source or sender is one of the basic concepts of communication and information processing. Sources are objects which encode message data and transmit the information, via a channel, to one or more observers (or receivers). In the strictest sense of the word, particularly in information theory, a ''source'' is a process that generates message data that one would like to communicate, or reproduce as exactly as possible elsewhere in space or time. A source may be modelled as memoryless, ergodic, stationary, or stochastic, in order of increasing generality. ''Communication Source'' combines ''Communication and Mass Media Complete'' and ''Communication Abstracts'' to provide full-text access to more than 700 journals, and indexing and abstracting for more than 1,000 core journals. Coverage dating goes back to 1900. Content is derived from academic journals, conference papers, conference proceedings, trade publications, magazines and periodicals. A transmitter can be e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
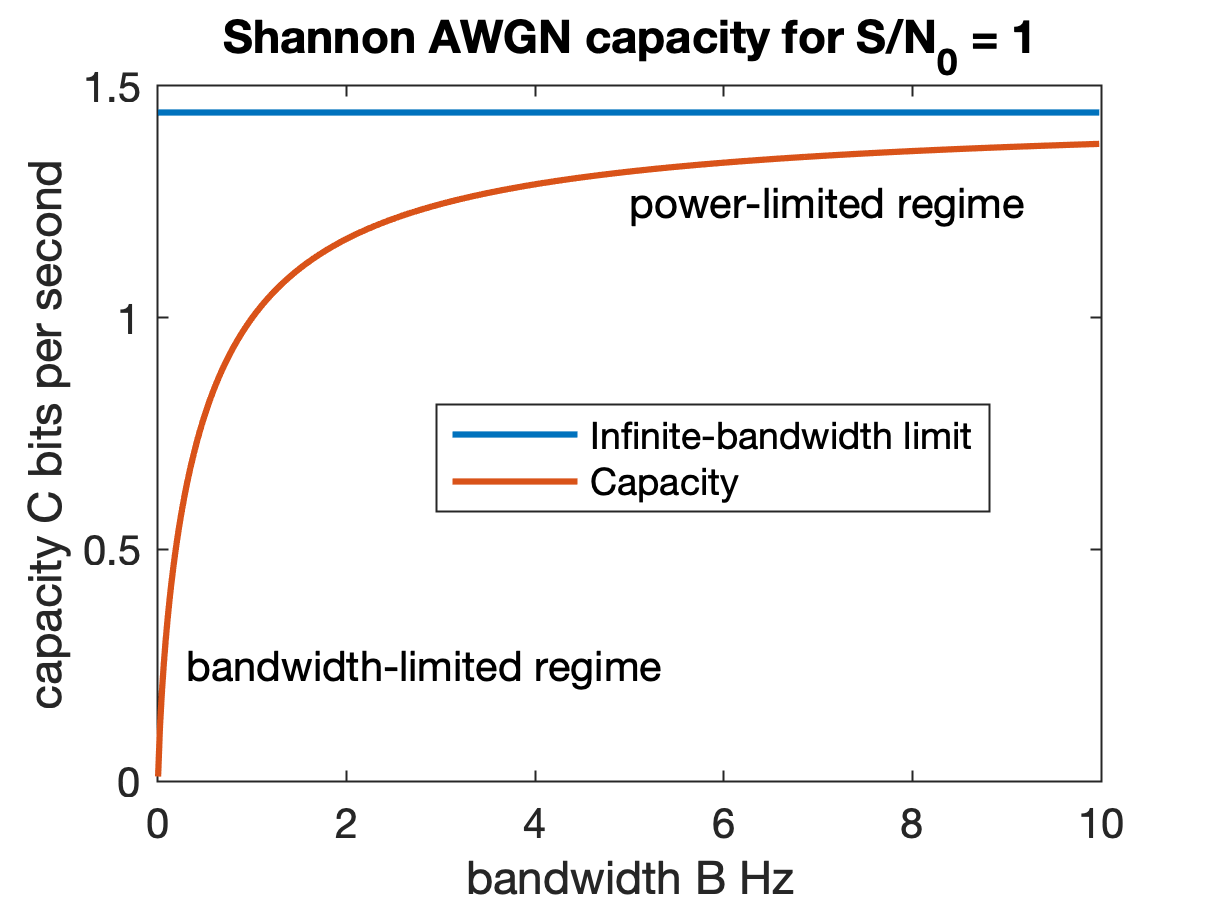
Channel Capacity
Channel capacity, in electrical engineering, computer science, and information theory, is the theoretical maximum rate at which information can be reliably transmitted over a communication channel. Following the terms of the noisy-channel coding theorem, the channel capacity of a given Channel (communications), channel is the highest information rate (in units of information entropy, information per unit time) that can be achieved with arbitrarily small error probability. Information theory, developed by Claude E. Shannon in 1948, defines the notion of channel capacity and provides a mathematical model by which it may be computed. The key result states that the capacity of the channel, as defined above, is given by the maximum of the mutual information between the input and output of the channel, where the maximization is with respect to the input distribution. The notion of channel capacity has been central to the development of modern wireline and wireless communication system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cooperative Diversity
Cooperative diversity is a cooperative multiple antenna technique for improving or maximising total network channel capacities for any given set of bandwidths which exploits user diversity by decoding the combined signal of the relayed signal and the direct signal in wireless multihop networks. A conventional single hop system uses direct transmission where a receiver decodes the information only based on the direct signal while regarding the relayed signal as interference, whereas the cooperative diversity considers the other signal as contribution. That is, cooperative diversity decodes the information from the combination of two signals. Hence, it can be seen that cooperative diversity is an antenna diversity that uses distributed antennas belonging to each node in a wireless network. Note that user cooperation is another definition of cooperative diversity. ''User cooperation'' considers an additional fact that each user relays the other user's signal while cooperative diversi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relay (other)
A relay is an electric switch operated by a signal in one circuit to control another circuit. Relay may also refer to: Electrical engineering * Protective relay, a device designed to trip a circuit breaker when a fault is detected. Historical * Stage station, a place where exhausted horses being used for transport could be exchanged for fresh ones * Cursus publicus, a courier service in the Roman Empire * Relay league, a chain of message-forwarding stations Computer networking * BITNET Relay, a 1980s online chat system * Mail relay, a server used for forwarding e-mail ** Open mail relay, such a server that can be used by anyone Other telecommunication * Relay (satellite) * Broadcast relay station, a transmitter which repeats or transponds the signal of another * Microwave radio relay * Relay channel, in information theory, a communications probability modeling system * Telecommunications Relay Service, a telephone accessibility service for the deaf * Repeater, an electro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Theory
Information theory is the mathematical study of the quantification (science), quantification, Data storage, storage, and telecommunications, communication of information. The field was established and formalized by Claude Shannon in the 1940s, though early contributions were made in the 1920s through the works of Harry Nyquist and Ralph Hartley. It is at the intersection of electronic engineering, mathematics, statistics, computer science, Neuroscience, neurobiology, physics, and electrical engineering. A key measure in information theory is information entropy, entropy. Entropy quantifies the amount of uncertainty involved in the value of a random variable or the outcome of a random process. For example, identifying the outcome of a Fair coin, fair coin flip (which has two equally likely outcomes) provides less information (lower entropy, less uncertainty) than identifying the outcome from a roll of a dice, die (which has six equally likely outcomes). Some other important measu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |