|
Reich Ministry For The Occupied Territories
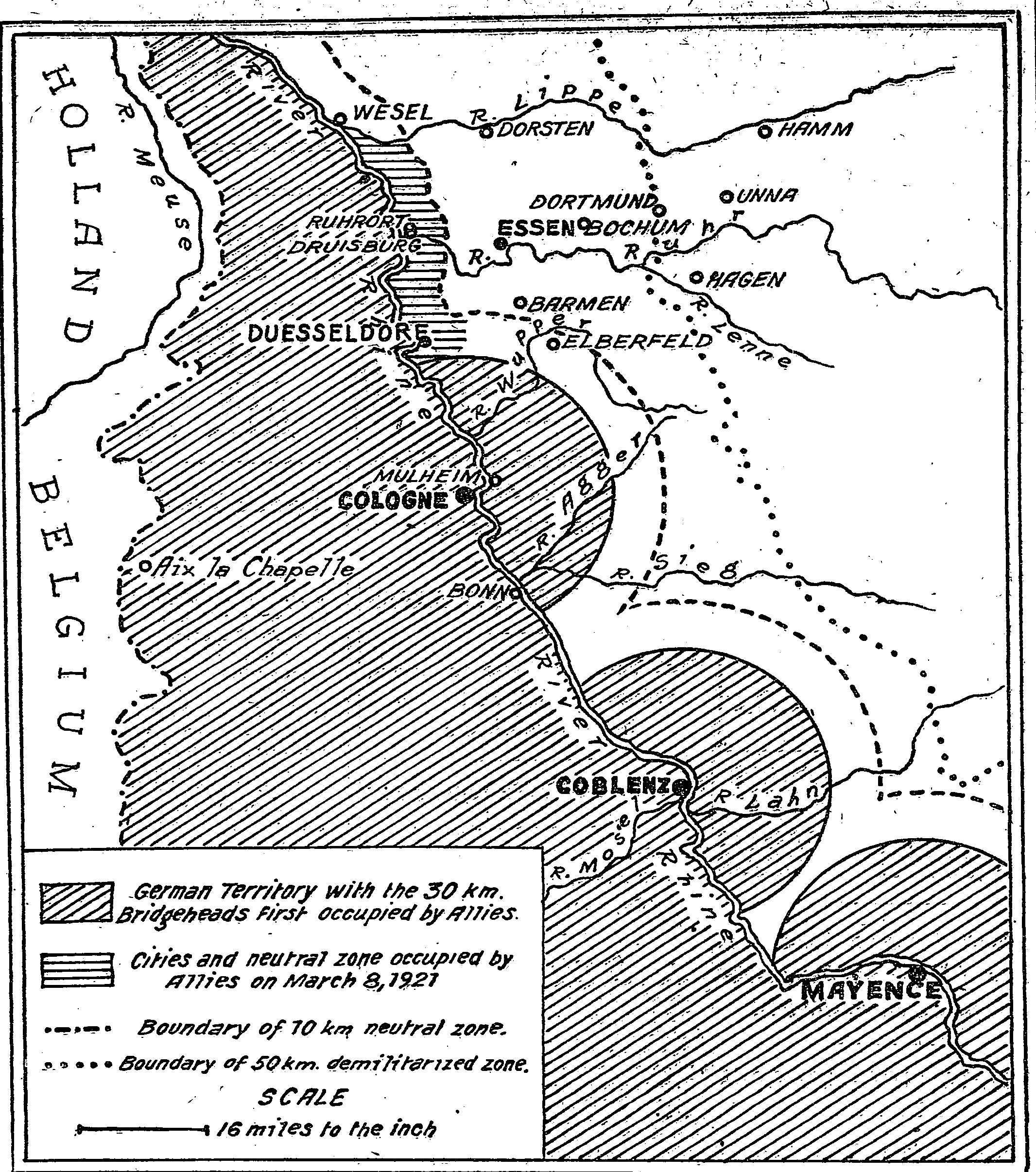
The Reich Ministry for the Occupied Territories () was a cabinet-level ministry of the Weimar Republic from 24 August 1923 to 30 September 1930. It was responsible for the administration of both the Occupation of the Rhineland, Rhineland region occupied by the Allies of World War I, Allies under the terms of the Treaty of Versailles and of the Ruhr after it was Occupation of the Ruhr, occupied by the French and Belgians in January 1923. The Ministry is not to be confused with Reich Ministry for the Occupied Eastern Territories that existed under the National Socialists. Background In December 1918, French, Belgian and British troops Occupation of the Rhineland, occupied parts of the Rhineland and neighboring areas in Hesse, Hesse Nassau, Hesse-Nassau and the Palatinate (region), Palatinate. The Treaty of Versailles, which came into effect on 10 January 1920, defined the left bank of the Rhine and the bridgeheads of Cologne, Koblenz and Mainz as an Allied zone of occupation. As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Territory Of The Saar Basin
The Territory of the Saar Basin (, ; ) was a region occupied and governed by the United Kingdom and France from 1920 to 1935 under a League of Nations mandate. It had its own flag (adopted on 28 July 1920): a blue, white, and black horizontal tricolour. The blue and white stood for Bavaria, and white and black for Prussia, out of whose lands the Saar Territory was formed. Initially, the occupation was under the auspices of the Treaty of Versailles. Its population in 1933 was 812,000, and its capital was Saarbrücken. The territory closely corresponds with the modern German state of Saarland, but was slightly smaller in area. After a plebiscite was held in 1935, it was returned to Germany. Governing Commission Under the Treaty of Versailles, the highly industrialized Saar Basin, including the Saar Coal District (), was to be occupied and governed by the United Kingdom and France under a League of Nations mandate for a period of fifteen years. Its coalfields were also to be cede ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Luther
Hans Luther () (10 March 1879 – 11 May 1962) was a German politician and Chancellor of Germany for 482 days in 1925 to 1926. As Minister of Finance he helped stabilize the Mark during the hyperinflation of 1923. From 1930 to 1933, Luther was head of the Reichsbank and from 1933 to 1937 he served as German Ambassador to the United States. Early life Hans Luther was born in Berlin on 10 March 1879 into a Lutheran family as the son of Otto (1848–1912), a well-off merchant, and Wilhelmine Luther (née Hübner). After attaining the ''Abitur'' at the Leibniz-Gymnasium/Berlin, Luther studied law at Geneva, Kiel and Berlin from 1897 to 1901. His teachers included Otto von Gierke, Franz von Liszt, Heinrich Brunner, Gustav von Schmoller and Hugo Preuss. In 1904, Luther was awarded a Dr.jur. for his dissertation ''Die Zuständigkeit des Bundesrats zur Entscheidung von Thronstreitigkeiten innerhalb des Deutschen Reiches''. He passed the ''Assessor'' exam in 1906 and worked in the Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Marx
Wilhelm Marx (15 January 1863 – 5 August 1946) was a German judge, lawyer, and politician who twice served as chancellor of Germany during the Weimar Republic, from 1923 to 1925 and again from 1926 to 1928. He also briefly held the position of Minister-President of Prussia in 1925. A leading figure in the Centre Party, he served as its chairman from 1922 to 1928. With a total tenure of three years and 73 days, he was the longest-serving chancellor of the Weimar Republic. After being a member of the Reichstag of the German Empire for ten years, Marx was elected in 1919 to the Weimar National Assembly that drafted Germany's new constitution and then in 1920 to the Republic's Reichstag where he served until not long before the Nazi takeover. As chancellor he helped steer Germany through the crisis year of 1923 with its hyperinflation and rebellious state governments. The following year his government worked to end the immediate crisis over Germany's war reparations and then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Brüning Cabinet
The first Brüning cabinet, headed by Heinrich Brüning of the Centre Party (Germany), Centre Party, was the seventeenth democratically elected government during the Weimar Republic. It took office on 30 March 1930 when it replaced the second Müller cabinet, which had resigned on 27 March over the issue of how to fund unemployment compensation. Brüning hoped to be able to work with the Reichstag (Weimar Republic), Reichstag to solve Germany's pressing economic problems, but when it rejected his budget for 1930, he worked with President Paul von Hindenburg to have it converted into an emergency decree. After the Reichstag rejected the decree, Hindenburg, at Brüning's request, dissolved the Reichstag and called new elections. The steps that were taken after the rejection of the 1930 budget marked the beginning of the presidential governments of the Weimar Republic under which the president and chancellor used constitutional emergency powers to bypass the Reichstag. Brüning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Müller Cabinet
The second Müller cabinet, headed by Hermann Müller of the Social Democratic Party (SPD), was the sixteenth democratically elected government during the Weimar Republic. It took office on 28 June 1928 when it replaced the fourth Marx cabinet, which had resigned on 12 June after failing to pass a promised school law. The cabinet was a grand coalition made up of the Social Democratic Party, German Democratic Party (DDP), Centre Party, German People's Party (DVP) and Bavarian People's Party (BVP). Lasting just under one year and 9 months, it was in office longer than any other government of the politically unstable Weimar Republic. The broad range of views it brought together made it difficult to resolve the issues it faced and weakened support for the parliamentary system as a whole. In a vote on military spending for a new armored cruiser, for example, the SPD leadership felt it necessary to go against its own party's overwhelming opposition in order to preser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Stresemann Cabinet
The second Stresemann cabinet, headed by Chancellor Gustav Stresemann of the German People's Party (DVP), was the ninth democratically elected government of the Weimar Republic. It took office on 6 October 1923 when it replaced the first Stresemann cabinet, which had resigned on 3 October over internal disagreements related to increasing working hours in vital industries above the eight-hour per day norm. The new cabinet was a majority coalition of four parties from the moderate left to centre-right. During its brief time in office, the cabinet successfully introduced the new currency that ended the disastrous period of hyperinflation. It was confronted with the resumption of war reparations payments following the end of passive resistance to the occupation of the Ruhr and faced down potentially separatist state governments in Saxony, Thuringia and Bavaria. Stresemann's second cabinet resigned on 23 November 1923 after the Social Democrats (SPD) withdrew from the coaliti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Stresemann Cabinet
The first Stresemann cabinet, headed by Gustav Stresemann of the German People's Party (DVP), was the eighth democratically elected government of the Weimar Republic. The cabinet took office on 13 August 1923 when it replaced the Cuno cabinet under Wilhelm Cuno, which had resigned following a call by the Social Democratic Party for a vote of no confidence which Cuno knew he could not win. The four centre-left to centre parties in Stresemann's coalition did not have a formal coalition agreement, and the Reichstag was not in session during most of the cabinet's short tenure. That led to the use of emergency decrees to handle Germany's economic problems and to fight the move towards a right-wing dictatorship in Bavaria. The cabinet resigned late on 3 October 1923 over a disagreement on increasing working hours for key industrial labourers and was replaced on 6 October by a second Stresemann cabinet. Establishment The Cuno cabinet resigned largely due to dissatisfaction o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reichstag (Weimar Republic)
The Reichstag of the Weimar Republic (1919–1933) was the lower house of Germany's parliament; the upper house was the Reichsrat (Germany), Reichsrat, which represented the states. The Reichstag convened for the first time on 24 June 1920, taking over from the Weimar National Assembly, which had served as an interim parliament following the collapse of the German Empire in November 1918. Under the Weimar Constitution of 1919, the Reichstag was elected every four years by universal, equal, secret and direct suffrage, using a system of party-list proportional representation. All citizens who had reached the age of 20 were allowed to vote, including women for the first time, but excluding soldiers on active duty. The Reichstag voted on the laws of the Reich and was responsible for the budget, questions of war and peace, and confirmation of state treaties. Oversight of the Reich government (the ministers responsible for executing the laws) also resided with the Reichstag. It could f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |