|
Regret-free Mechanism
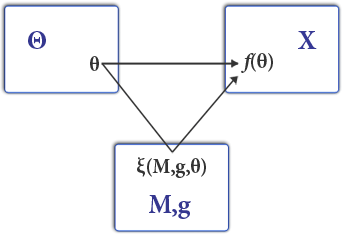
In mechanism design, a regret-free truth-telling mechanism (RFTT, or regret-free mechanism for short) is a mechanism in which each player who reveals his true private information does not feel regret after seeing the mechanism outcome. A regret-free mechanism incentivizes agents who want to avoid regret to report their preferences truthfully. Regret-freeness is a relaxation of ''truthfulness'': every truthful mechanism is regret-free, but there are regret-free mechanisms that are not truthful. As a result, regret-free mechanisms exist even in settings in which strong impossibility results prevent the existence of truthful mechanisms. Formal definition There is a finite set ''X'' of potential outcomes. There is a set ''N'' of agents. Each agent i has a ''preference'' Pi over ''X''. A ''mechanism'' or ''rule'' is a function ''f'' that gets as input the agents' preferences P1,...,Pn, and returns as output an outcome from ''X''. The agents' preferences are their private information ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanism Design
Mechanism design (sometimes implementation theory or institution design) is a branch of economics and game theory. It studies how to construct rules—called Game form, mechanisms or institutions—that produce good outcomes according to Social welfare function, some predefined metric, even when the designer does not know the players' true preferences or what information they have. Mechanism design thus focuses on the study of solution concepts for a class of private-information games. Mechanism design has broad applications, including traditional domains of economics such as market design, but also political science (through voting theory). It is a foundational component in the operation of the internet, being used in networked systems (such as inter-domain routing), e-commerce, and Sponsored search auction, advertisement auctions by Facebook and Google. Because it starts with the end of the game (a particular result), then works backwards to find a game that implements it, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strategyproofness
In mechanism design, a strategyproof (SP) mechanism is a game form in which each player has a weakly- dominant strategy, so that no player can gain by "spying" over the other players to know what they are going to play. When the players have private information (e.g. their type or their value to some item), and the strategy space of each player consists of the possible information values (e.g. possible types or values), a truthful mechanism is a game in which revealing the true information is a weakly-dominant strategy for each player. An SP mechanism is also called dominant-strategy-incentive-compatible (DSIC), to distinguish it from other kinds of incentive compatibility. A SP mechanism is immune to manipulations by individual players (but not by coalitions). In contrast, in a group strategyproof mechanism, no group of people can collude to misreport their preferences in a way that makes every member better off. In a strong group strategyproof mechanism, no group of people can c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cut And Choose
Divide and choose (also cut and choose or I cut, you choose) is a procedure for fair division of a continuous resource between two parties. It involves a heterogeneous good or resource and two partners who have different preferences over parts of the cake (both want as much of it as possible). The procedure proceeds as follows: one person divides the resource into two pieces; the other person selects one of the pieces; the cutter receives the remaining piece. Since ancient times some have used the procedure to divide land, food and other resources between two parties. Currently, there is an entire field of research, called fair cake-cutting, devoted to various extensions and generalizations of cut-and-choose. Divide and choose is envy-free in the following sense: each of the two partners can act in a way that guarantees that, according to their own subjective taste, their allocated share is at least as valuable as the other share, regardless of what the other partner does. Descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Repeated Game
In game theory, a repeated game (or iterated game) is an extensive form game that consists of a number of repetitions of some base game (called a stage game). The stage game is usually one of the well-studied 2-person games. Repeated games capture the idea that a player will have to take into account the impact of their current action on the future actions of other players; this impact is sometimes called their reputation. Single stage game or single shot game are names for non-repeated games. Example Consider two gas stations that are adjacent to one another. They compete by publicly posting pricing, and have the same and constant marginal cost ''c'' (the wholesale price of gasoline). Assume that when they both charge , their joint profit is maximized, resulting in a high profit for everyone. Despite the fact that this is the best outcome for them, they are motivated to deviate. By modestly lowering the price, either can steal all of their competitors' customers, nearly doub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fair Cake-cutting
Fair cake-cutting is a kind of fair division problem. The problem involves a ''heterogeneous'' resource, such as a cake with different toppings, that is assumed to be ''divisible'' – it is possible to cut arbitrarily small pieces of it without destroying their value. The resource has to be divided among several partners who have different preferences over different parts of the cake, i.e., some people prefer the chocolate toppings, some prefer the cherries, some just want as large a piece as possible. The division should be ''unanimously'' fair – each person should receive a piece believed to be a fair share. The "cake" is only a metaphor; procedures for fair cake-cutting can be used to divide various kinds of resources, such as land estates, advertisement space or broadcast time. The prototypical procedure for fair cake-cutting is divide and choose, which is mentioned in the book of Book of Genesis, Genesis to resolve Abraham and Lot's conflict. This procedure solves the fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condorcet-consistent
A Condorcet method (; ) is an election method that elects the candidate who wins a majority of the vote in every head-to-head election against each of the other candidates, whenever there is such a candidate. A candidate with this property, the ''pairwise champion'' or ''beats-all winner'', is formally called the ''Condorcet winner'' or ''Pairwise Majority Rule Winner'' (PMRW). The head-to-head elections need not be done separately; a voter's choice within any given pair can be determined from the ranking. Some elections may not yield a Condorcet winner because voter preferences may be cyclic—that is, it is possible that every candidate has an opponent that defeats them in a two-candidate contest. The possibility of such cyclic preferences is known as the Condorcet paradox. However, a smallest group of candidates that beat all candidates not in the group, known as the Smith set, always exists. The Smith set is guaranteed to have the Condorcet winner in it should one exist. Man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dowdall System
Positional voting is a ranked voting electoral system in which the options or candidates receive points based on their rank position on each ballot and the one with the most points overall wins. The lower-ranked preference in any adjacent pair is generally of less value than the higher-ranked one. Although it may sometimes be weighted the same, it is never worth more. A valid progression of points or weightings may be chosen at will (Eurovision Song Contest) or it may form a mathematical sequence such as an arithmetic progression (Borda count), a geometric one (positional number system) or a harmonic one ( Nauru/Dowdall method). The set of weightings employed in an election heavily influences the rank ordering of the candidates. The steeper the initial decline in preference values with descending rank, the more polarised and less consensual the positional voting system becomes. Positional voting should be distinguished from score voting: in the former, the score that each voter g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borda Voting
The Borda method or order of merit is a positional voting rule that gives each candidate a number of points equal to the number of candidates ranked below them: the lowest-ranked candidate gets 0 points, the second-lowest gets 1 point, and so on. The candidate with the most points wins. The Borda count has been independently reinvented several times, with the first recorded proposal in 1435 being by Nicholas of Cusa (see History below), but is named after the 18th-century French mathematician and naval engineer Jean-Charles de Borda, who re-devised the system in 1770. The Borda count is well-known in social choice theory both for its pleasant theoretical properties and its ease of manipulation. In the absence of strategic voting and strategic nomination, the Borda count tends to elect broadly-acceptable options or candidates (rather than consistently following the preferences of a majority); when both voting and nomination patterns are completely random, the Borda count generally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egalitarian Rule
In social choice and operations research, the egalitarian rule (also called the max-min rule or the Rawlsian rule) is a rule saying that, among all possible alternatives, society should pick the alternative which maximizes the ''minimum utility'' of all individuals in society. It is a formal mathematical representation of the egalitarian philosophy. It also corresponds to John Rawls' principle of maximizing the welfare of the worst-off individual. Definition Let X be a set of possible `states of the world' or `alternatives'. Society wishes to choose a single state from X. For example, in a single-winner election, X may represent the set of candidates; in a resource allocation setting, X may represent all possible allocations. Let I be a finite set, representing a collection of individuals. For each i \in I, let u_i:X\longrightarrow\mathbb be a ''utility function'', describing the amount of happiness an individual ''i'' derives from each possible state. A '' social choice rule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gibbard–Satterthwaite Theorem
The Gibbard–Satterthwaite theorem is a theorem in social choice theory. It was first conjectured by the philosopher Michael Dummett and the mathematician Robin Farquharson in 1961 and then proved independently by the philosopher Allan Gibbard in 1973 and economist Mark Satterthwaite in 1975. It deals with deterministic ordinal electoral systems that choose a single winner, and shows that for every voting rule of this form, at least one of the following three things must hold: # The rule is dictatorial, i.e. there exists a distinguished voter who can choose the winner; or # The rule limits the possible outcomes to two alternatives only; or # The rule is not straightforward, i.e. there is no single always-best strategy (one that does not depend on other voters' preferences or behavior). Gibbard's proof of the theorem is more general and covers processes of collective decision that may not be ordinal, such as cardinal voting. Gibbard's 1978 theorem and Hylland's theorem are e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dictatorship Mechanism
In social choice theory, a dictatorship mechanism is a degenerate voting rule or mechanism where the result depends on one person's. A serial dictatorship is similar, but also designates a series of "backup dictators", who break ties in the original dictator's choices when the dictator is indifferent. Formal definition Non-dictatorship is one of the necessary conditions in Arrow's impossibility theorem.''Game Theory'' Second Edition Guillermo Owen Ch 6 pp124-5 Axiom 5 Academic Press, 1982 In ''Social Choice and Individual Values'', Kenneth Arrow defines non-dictatorship as: :There is no voter i in such that, for every set of orderings in the domain of the constitution, and every pair of social states ''x'' and ''y'', ''x \succeq_i y'' implies x \succeq y. Unsurprisingly, a dictatorship is a rule that does not satisfy non-dictatorship. Anonymous voting rules automatically satisfy non-dictatorship (so long as there is more than one voter). Serial dictatorship When the dictator ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plurality Voting
Plurality voting refers to electoral systems in which the candidates in an electoral district who poll more than any other (that is, receive a plurality) are elected. Under single-winner plurality voting, and in systems based on single-member districts, plurality voting is called single member istrictplurality (SMP), which is widely known as " first-past-the-post". In SMP/FPTP the leading candidate, whether or not they have a majority of votes, is elected. There are several versions of plurality voting for multi-member district. The system that elects multiple winners at once with the plurality rule and where each voter casts as many X votes as the number of seats in a multi-seat district is referred to as plurality block voting. A semi-proportional system that elects multiple winners elected at once with the plurality rule and where each voter casts more than one vote but fewer than the number of seats to fill in a multi-seat district is known as limited voting. A semi-prop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |