|
Razzia (military)
A razzia is a Raid (military), surprise attack against an enemy settlement. Although it primarily sought to obtain booty, historically the objectives of a razzia have been diverse: the capture of Slavery, slaves, Ethnic cleansing, ethnic or Religious persecution, religious cleansing, expansion of territory, and intimidation of the enemy. Over time, its meaning has also been extended to other activities that bear certain similarities to these attacks, such as police raids or certain violent incursions by organized or paramilitary groups, such as those carried out in Brazilian favelas, or in refugee camps during the Second Congo War, war in Central Africa. Etymology The word is from French ''razzia'' 'incursion', and from Algerian Arabic ''ġaziya'' (غزية),'' "algara"'' or 'raid'. ''Ghazwah'' (plural ''ghazawat'') (Arabic: غزوة) is an originally Arabic term meaning "invasion". It comes from the triconsonantal root ''g.z.w.'' ("to attack"). It has the same connotation as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Razzia Of Circassian Guerillas
Razzia (Italian and other languages, 'raid') may refer to: Raids * Ghazw, military expeditions as described in early Islamic literature * Razzia (military), surprise attacks against an enemy settlement * a slave raid conducted by Barbary pirates * a Police raid * a Nazi Roundup (history)#Targeted territories, roundup in World War II ** Raid of the Ghetto of Rome, 1943 Arts and entertainment * Raid (1947 film), ''Raid'' (1947 film) (German: ''Razzia''), a German crime film * Razzia (band), a German punk band * ''Razzia sur la chnouf'', released in the US as ''Razzia'', a 1955 French gangster film * Razzia (2017 film), ''Razzia'' (2017 film), a Moroccan drama film * Razzia Records, a Swedish record label * Razzia (artist) (Gérard Courbouleix–Dénériaz, born 1950), a French poster artist * Razzia (song), "Razzia" (song), a 1982 song by Rainhard Fendrich * ''Razzia!'', a mafia-themed release of the board game ''Ra (board game), Ra'' See also *Razia (other) *Ghazi (di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Language
French ( or ) is a Romance languages, Romance language of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European family. Like all other Romance languages, it descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire. French evolved from Northern Old Gallo-Romance, a descendant of the Latin spoken in Northern Gaul. Its closest relatives are the other langues d'oïl—languages historically spoken in northern France and in southern Belgium, which French (Francien language, Francien) largely supplanted. It was also substratum (linguistics), influenced by native Celtic languages of Northern Roman Gaul and by the Germanic languages, Germanic Frankish language of the post-Roman Franks, Frankish invaders. As a result of French and Belgian colonialism from the 16th century onward, it was introduced to new territories in the Americas, Africa, and Asia, and numerous French-based creole languages, most notably Haitian Creole, were established. A French-speaking person or nation may be referred to as Fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
March (territory)
In Middle Ages, medieval Europe, a march or mark was, in broad terms, any kind of borderland, as opposed to a state's "heartland". More specifically, a march was a border between realms or a neutral buffer zone under joint control of two states in which different laws might apply. In both of these senses, marches served a political purpose, such as providing warning of Invasion, military incursions or regulating cross-border trade. Marches gave rise to the titles marquess (masculine) or marchioness (feminine). Etymology The word "march" derives ultimately from a Proto-Indo-European root *''merg-'', meaning "edge, boundary". The root *''merg-'' produced Latin ''margo'' ("margin"), Old Irish ''mruig'' ("borderland"), Welsh language, Welsh ''bro'' ("region, border, valley") and Persian language, Persian and Armenian language, Armenian ''Marz (country subdivision), marz'' ("borderland"). The Proto-Germanic ''*marko'' gave rise to the Old English language, Old English word ''mearc'' a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Africa
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of the Western Sahara in the west, to Egypt and Sudan's Red Sea coast in the east. The most common definition for the region's boundaries includes Algeria, Egypt, Libya, Morocco, Tunisia, and Western Sahara, the territory territorial dispute, disputed between Morocco and the list of states with limited recognition, partially recognized Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic. The United Nations’ definition includes all these countries as well as Sudan. The African Union defines the region similarly, only differing from the UN in excluding the Sudan and including Mauritania. The Sahel, south of the Sahara, Sahara Desert, can be considered as the southern boundary of North Africa. North Africa includes the Spanish cities of Ceuta and Melilla, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
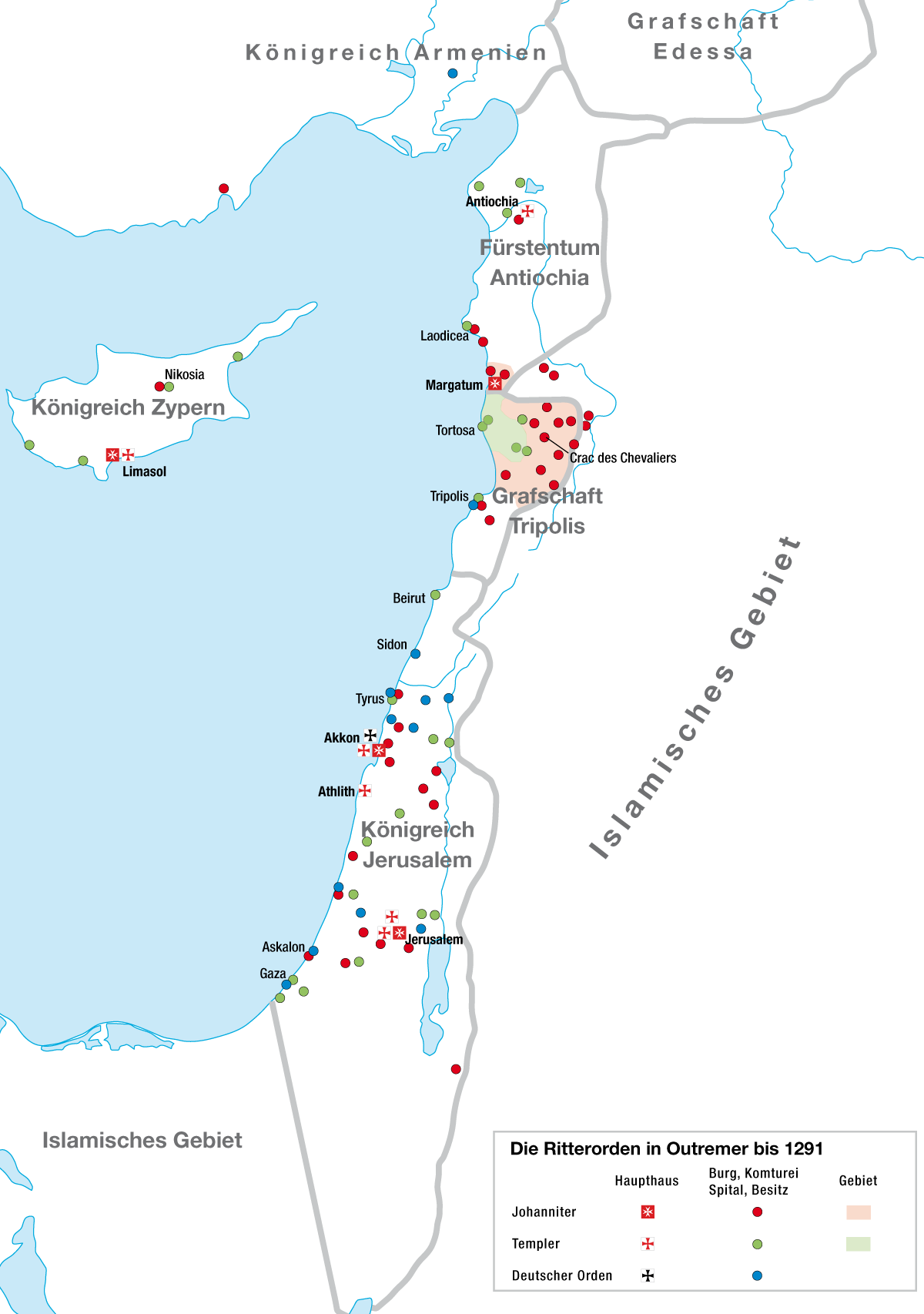
Military Order (religious Society)
A military order () is a Christianity, Christian religious society of Knight, knights. The original military orders were the Knights Templar, the Knights Hospitaller, the Order of the Holy Sepulchre (Catholic), Order of the Holy Sepulchre, the Order of Santiago, Order of Saint James, the Order of Calatrava, and the Teutonic Order, Teutonic Knights. They arose in the Middle Ages in association with the Crusades - in the Holy Land, the Baltic states, Baltics, and the Iberian Peninsula, Iberian peninsula; their members being initially dedicated to the protection of Christians , Christian pilgrims, and eventually to the defence of the Crusader states and the conquest of non-Christian or even non-Western Christianity , Catholic lands. They are the predecessors of Order of chivalry, chivalric orders. Most members of military orders were Laity, laymen who took religious vows, such as of Evangelical counsels, poverty, chastity, and obedience, according to Monasticism, monastic ideals. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribat
A ribāṭ (; hospice, hostel, base or retreat) is an Arabic term, initially designating a small fortification built along a frontier during the first years of the Muslim conquest of the Maghreb to house military volunteers, called ''murabitun'', and shortly after they also appeared along the Byzantine frontier, where they attracted converts from Greater Khorasan, an area that would become known as al-ʻAwāṣim in the ninth century CE. The ''ribat'' fortifications later served to protect commercial routes, as caravanserais, and as centers for isolated Muslim communities as well as serving as places of piety. Islamic meaning Historical meaning The word ''ribat'' in its abstract refers to voluntary defense of Islam, which is why ribats were originally used to house those who fought to defend Islam in jihad. They can also be referred to by other names such as ''khanqah'', most commonly used in Iran, and ''tekke'', most commonly used in Turkey. Classically, ribat referred to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th centuryAD, it endured until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. The term 'Byzantine Empire' was coined only after its demise; its citizens used the term 'Roman Empire' and called themselves 'Romans'. During the early centuries of the Roman Empire, the western provinces were Romanization (cultural), Latinised, but the eastern parts kept their Hellenistic culture. Constantine the Great, Constantine I () legalised Christianity and moved the capital to Constantinople. Theodosius I, Theodosius I () made Christianity the state religion and Greek gradually replaced Latin for official use. The empire adopted a defensive strategy and, throughout its remaining history, expe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean Sea to the west, the Turkish Straits to the northwest, and the Black Sea to the north. The eastern and southeastern limits have been expanded either to the entirety of Asiatic Turkey or to an imprecise line from the Black Sea to the Gulf of Alexandretta. Topographically, the Sea of Marmara connects the Black Sea with the Aegean Sea through the Bosporus and the Dardanelles, and separates Anatolia from Thrace in Southeast Europe. During the Neolithic, Anatolia was an early centre for the development of farming after it originated in the adjacent Fertile Crescent. Beginning around 9,000 years ago, there was a major migration of Anatolian Neolithic Farmers into Neolithic Europe, Europe, with their descendants coming to dominate the continent a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, the east and southeast, Jordan to Jordan–Syria border, the south, and Israel and Lebanon to Lebanon–Syria border, the southwest. It is a republic under Syrian transitional government, a transitional government and comprises Governorates of Syria, 14 governorates. Damascus is the capital and largest city. With a population of 25 million across an area of , it is the List of countries and dependencies by population, 57th-most populous and List of countries and dependencies by area, 87th-largest country. The name "Syria" historically referred to a Syria (region), wider region. The modern state encompasses the sites of several ancient kingdoms and empires, including the Eblan civilization. Damascus was the seat of the Umayyad Caliphate and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Awasim
''Al-ʿAwāṣim'' (, "the defences, fortifications"; sing. ''al-ʿāṣimah'', , "protectress") was the Arabic term used to refer to the Muslim side of the frontier zone between the Byzantine Empire and the Umayyad and Abbasid Caliphates in Cilicia, northern Syria and Upper Mesopotamia. It was established in the early 8th century, once the first wave of the Muslim conquests ebbed, and lasted until the mid-10th century, when the Byzantine advance overran it. It comprised the forward marches, comprising a chain of fortified strongholds, known as ''al-thughūr'' (; sing. ''al-thaghr'', , "cleft, opening"), and the rear or inner regions of the frontier zone, which was known as ''al-ʿawāṣim'' proper. On the Byzantine side, the Muslim marches were mirrored by the institution of the kleisourai and the akritai (border guards). The term ''thughūr'' was also used in the marches of al-Andalus and Transoxiana, and was revived by the Mamluk Sultanate in the 14th century, when the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akinji
Akinji or akindji (, ; plural: ''akıncılar'') were Turkish people, Turkish Irregular military, irregular light cavalry, scout divisions (deli) and advance troops of the Ottoman Empire's Military of the Ottoman Empire, military. When the pre-existing Turkish Ghazi (warrior), ghazis were incorporated into the Ottoman Empire's military they became known as "akıncı." Unpaid, they lived and operated as wikt:raider, raiders on the frontiers of the Ottoman Empire, subsisting on plunder. In German sources these troops were called ''Renner und Brenner'' (English: "Runner and burner"). There is a distinction made between "akıncı" and "deli (cavalry), deli" cavalry. History In war their main role was to act as advance troops on the front lines and demoralise the marching opposing army by using guerrilla tactics, and to put them in a state of confusion and shock. They could be likened to a scythe in a wheat field. They would basically Turkish archery, hit the enemy with arrows. When a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andalusi Arabic
Andalusi Arabic or Andalusian Arabic () was a variety or varieties of Arabic spoken mainly from the 8th to the 15th century in Al-Andalus, the regions of the Iberian Peninsula under the Muslim rule. Arabic spread gradually over the centuries of Muslim rule in Iberia, primarily through conversion to Islam, although it was also learned and spoken by Christians and Jews. Arabic became the language of administration and was the primary language of literature produced in al-Andalus; the Andalusi vernacular was distinct among medieval Arabic vernaculars in that it was used in poetry, in '' zajal'' and the '' kharjas'' of '' muwaššaḥāt''. Arabic in al-Andalus existed largely in a situation of bilingualism with Andalusi Romance (known popularly as ''Mozarabic'') until the 13th century. Arabic in Iberia was also characterized by diglossia: in addition to standard written Arabic, spoken varieties could be subdivided into an urban, educated idiolect and a register of the less-p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |