|
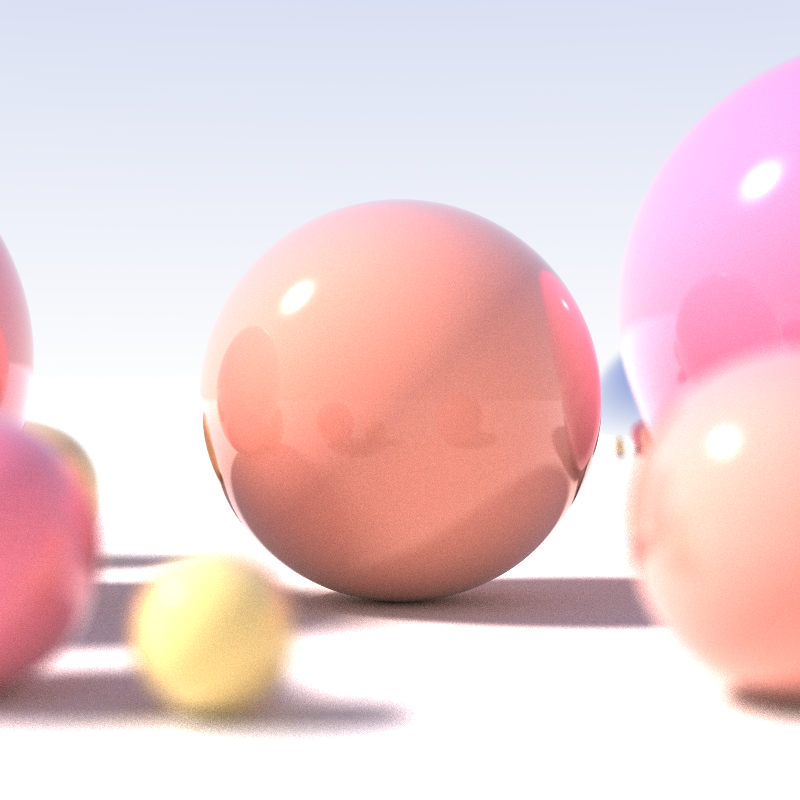
Ray Marching
Ray marching is a class of rendering methods for 3D computer graphics where rays are traversed iteratively, effectively dividing each ray into smaller ray segments, sampling some function at each step. For example, in volume ray casting the function would access data points from a 3D scan. In Sphere tracing, the function estimates a distance to step next. Ray marching is also used in physics simulations as an alternative to ray tracing where analytic solutions of the trajectories of light or sound waves are solved. Ray marching for computer graphics often takes advantage of SDFs to determine a maximum safe step-size, while this is less common in physics simulations a similar adaptive step method can be achieved using adaptive Runge-Kutta methods. The technique dates back to at least the 1980s; the 1989 paper "Hypertexture" by Ken Perlin contains an early example of a ray marching method. Distance-aided ray marching Sphere tracing In sphere tracing, or sphere-assisted ray ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3D Computer Graphics
3D computer graphics, sometimes called Computer-generated imagery, CGI, 3D-CGI or three-dimensional Computer-generated imagery, computer graphics, are graphics that use a three-dimensional representation of geometric data (often Cartesian coordinate system#Cartesian coordinates in three dimensions, Cartesian) that is stored in the computer for the purposes of performing calculations and rendering digital images, usually 2D images but sometimes 3D images. The resulting images may be stored for viewing later (possibly as an Computer animation, animation) or displayed in Real-time computer graphics, real time. 3D computer graphics, contrary to what the name suggests, are most often displayed on two-dimensional displays. Unlike 3D film and similar techniques, the result is two-dimensional, without visual depth perception, depth. More often, 3D graphics are being displayed on 3D displays, like in virtual reality systems. 3D graphics stand in contrast to 2D computer graphics which t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ray Tracing (graphics)
In 3D computer graphics, ray tracing is a technique for modeling Light transport theory, light transport for use in a wide variety of Rendering (computer graphics), rendering algorithms for generating digital image, digital images. On a spectrum of Computation time, computational cost and visual fidelity, ray tracing-based rendering techniques, such as ray casting, #Recursive ray tracing algorithm, recursive ray tracing, Distributed ray tracing, distribution ray tracing, photon mapping and path tracing, are generally slower and higher fidelity than scanline rendering methods. Thus, ray tracing was first deployed in applications where taking a relatively long time to render could be tolerated, such as still computer-generated imagery, CGI images, and film and television visual effects (VFX), but was less suited to real-time computer graphics, real-time applications such as video games, where Frame rate, speed is critical in rendering each Film frame, frame. Since 2018, however, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Normal
In geometry, a normal is an object (e.g. a line, ray, or vector) that is perpendicular to a given object. For example, the normal line to a plane curve at a given point is the infinite straight line perpendicular to the tangent line to the curve at the point. A normal vector is a vector perpendicular to a given object at a particular point. A normal vector of length one is called a unit normal vector or normal direction. A curvature vector is a normal vector whose length is the curvature of the object. Multiplying a normal vector by results in the opposite vector, which may be used for indicating sides (e.g., interior or exterior). In three-dimensional space, a surface normal, or simply normal, to a surface at point is a vector perpendicular to the tangent plane of the surface at . The vector field of normal directions to a surface is known as '' Gauss map''. The word "normal" is also used as an adjective: a line ''normal'' to a plane, the ''normal'' component of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deferred Shading
In the field of 3D computer graphics, deferred shading is a screen-space shading technique that is performed on a second Rendering (computer graphics), rendering pass, after the vertex and pixel shaders are rendered. It was first suggested by Michael Deering in 1988. On the first pass of a deferred shader, only data that is required for shading computation is gathered. Positions, normals, and materials for each surface are rendered into the geometry buffer (G-buffer) using "render to texture". After this, a pixel shader computes the direct and indirect lighting at each pixel using the information of the texture buffers in screen space. Screen space directional occlusion can be made part of the deferred shading pipeline to give directionality to shadows and interreflections. Advantages The primary advantage of deferred shading is the decoupling of scene geometry from lighting. Only one geometry pass is required, and each light is only computed for those pixels that it actually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Screen Space Reflection
Reflection in computer graphics is used to render reflective objects like mirrors and shiny surfaces. Accurate reflections are commonly computed using ray tracing whereas approximate reflections can usually be computed faster by using simpler methods such as environment mapping. Reflections on shiny surfaces like wood or tile can add to the photorealistic effects of a 3D rendering. Approaches to reflection rendering For rendering environment reflections there exist many techniques that differ in precision, computational and implementation complexity. Combination of these techniques are also possible. Image order rendering algorithms based on tracing rays of light, such as ray tracing or path tracing, typically compute accurate reflections on general surfaces, including multiple reflections and self reflections. However these algorithms are generally still too computationally expensive for real time rendering (even though specialized HW exists, such as Nvidia RTX) and require ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Screen Space Effect
Screen or Screens may refer to: Arts * Screen printing or ''silkscreening'', a printing method * Big screen, a nickname for motion pictures * Split screen (filmmaking), showing two or more images side by side * Stochastic screening and Halftone photographic screening, methods of simulating grays with one-color printing Filtration and selection processes * Screening (economics), the process of identifying or selecting members of a population based on one or more selection criteria * Screening (biology), idem, on a scientific basis, ** of which a genetic screen is a procedure to identify a particular kind of phenotype ** the Irwin screen is a toxicological procedure * Sieve, a mesh used to separate fine particles from coarse ones * Mechanical screening, a unit operation in material handling which separates product into multiple grades by particle size Media and music * ''Screen International'', a film magazine covering the international film markets * ''Screen'' (journal), a fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxicab Distance
Taxicab geometry or Manhattan geometry is geometry where the familiar Euclidean distance is ignored, and the distance between two points is instead defined to be the sum of the absolute differences of their respective Cartesian coordinates, a distance function (or metric) called the ''taxicab distance'', ''Manhattan distance'', or ''city block distance''. The name refers to the island of Manhattan, or generically any planned city with a rectangular grid of streets, in which a taxicab can only travel along grid directions. In taxicab geometry, the distance between any two points equals the length of their shortest grid path. This different definition of distance also leads to a different definition of the length of a curve, for which a line segment between any two points has the same length as a grid path between those points rather than its Euclidean length. The taxicab distance is also sometimes known as ''rectilinear distance'' or distance (see ''Lp'' space). This geometry ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boolean Algebra
In mathematics and mathematical logic, Boolean algebra is a branch of algebra. It differs from elementary algebra in two ways. First, the values of the variable (mathematics), variables are the truth values ''true'' and ''false'', usually denoted by 1 and 0, whereas in elementary algebra the values of the variables are numbers. Second, Boolean algebra uses logical operators such as Logical conjunction, conjunction (''and'') denoted as , disjunction (''or'') denoted as , and negation (''not'') denoted as . Elementary algebra, on the other hand, uses arithmetic operators such as addition, multiplication, subtraction, and division. Boolean algebra is therefore a formal way of describing logical operations in the same way that elementary algebra describes numerical operations. Boolean algebra was introduced by George Boole in his first book ''The Mathematical Analysis of Logic'' (1847), and set forth more fully in his ''An Investigation of the Laws of Thought'' (1854). According to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modulo Operation
In computing and mathematics, the modulo operation returns the remainder or signed remainder of a Division (mathematics), division, after one number is divided by another, the latter being called the ''modular arithmetic, modulus'' of the operation. Given two positive numbers and , modulo (often abbreviated as ) is the remainder of the Euclidean division of by , where is the Division (mathematics), dividend and is the divisor. For example, the expression "5 mod 2" evaluates to 1, because 5 divided by 2 has a quotient of 2 and a remainder of 1, while "9 mod 3" would evaluate to 0, because 9 divided by 3 has a quotient of 3 and a remainder of 0. Although typically performed with and both being integers, many computing systems now allow other types of numeric operands. The range of values for an integer modulo operation of is 0 to . mod 1 is always 0. When exactly one of or is negative, the basic definition breaks down, and programming languages differ in how these valu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shadertoy
Shadertoy is an online community and tool for creating and sharing shaders through WebGL, used for both learning and teaching 3D computer graphics in a web browser. Overview Shadertoy is an online community and platform for computer graphics professionals, academics and enthusiasts who share, learn and experiment with rendering techniques and procedural art through GLSL code. There are more than 52 thousand public contributions as of mid-2021 coming from thousands of users. WebGL allows Shadertoy to access the compute power of the GPU to generate procedural generation, procedural art, animation, models, lighting, state based logic and sound. History Shadertoy was created by Pol Jeremias and Inigo Quilez in January 2013 and came online in February the same year. The roots of the effort are in Inigo's "Shadertoy" section in his computer graphics educational website. With the arrival of the initial WebGL implementation by Mozilla's Firefox in 2009, Quilez created the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ray (optics)
In optics, a ray is an idealized geometrical model of light or other electromagnetic radiation, obtained by choosing a curve that is perpendicular to the ''wavefronts'' of the actual light, and that points in the direction of energy flow. Rays are used to model the propagation of light through an optical system, by dividing the real light field up into discrete rays that can be computationally propagated through the system by the techniques of '' ray tracing''. This allows even very complex optical systems to be analyzed mathematically or simulated by computer. Ray tracing uses approximate solutions to Maxwell's equations that are valid as long as the light waves propagate through and around objects whose dimensions are much greater than the light's wavelength. '' Ray optics'' or ''geometrical optics'' does not describe phenomena such as diffraction, which require wave optics theory. Some wave phenomena such as interference can be modeled in limited circumstances by adding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demoscene
The demoscene () is an international computer art subculture focused on producing demos: self-contained, sometimes extremely small, computer programs that produce audiovisual presentations. The purpose of a demo is to show off computer programming, programming, visual art, and musical skills. Demos and other demoscene productions (graphics, music, videos, games) are shared, voted on and released online at festivals known as Demoscene#Parties, demoparties. The scene started with the home computer revolution of the early 1980s, and the subsequent advent of software cracking. Crackers altered the code of computer games to remove copy protection, claiming credit by adding introduction screens of their own ("crack intro, cracktros"). They soon started competing for the best visual presentation of these additions. Through the making of intros and stand-alone demos, a new community eventually evolved, independent of the gaming and Warez scene, software sharing scenes. Demos are informa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |