|
Rauhut–Currier Reaction
The Rauhut–Currier reaction, also called the vinylogous Morita–Baylis–Hillman reaction, is an organic reaction describing (in its original scope) the dimerization or isomerization of electron-deficient alkenes such as enones by action of an organophosphine of the type R3P. In a more general description the RC reaction is any coupling of one active alkene / latent enolate to a second Michael acceptor, creating a new C–C bond between the alpha-position of one activated alkene and the beta-position of a second alkene under the influence of a nucleophilic catalyst. The reaction mechanism is essentially that of the related and better known Baylis–Hillman reaction (DABCO not phosphine, carbonyl not enone) but the Rauhut–Currier reaction actually predates it by several years. In comparison to the MBH reaction, the RC reaction lacks substrate reactivity and regioselectivity. The original 1963 reaction described the dimerization of the ethyl acrylate to the ethyl diester o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vinylogous
In organic chemistry, vinylogy is the transmission of electronic effects through a conjugated organic bonding system. The concept was introduced in 1926 by Ludwig Claisen to explain the acidic properties of formylacetone and related ketoaldehydes. Its adjectival form, vinylogous, is used to describe functional groups in which the standard moieties of the group are separated by a carbon–carbon double bond. For example, a carboxylic acid with a carbon-carbon double bond (, a "vinyl" moiety; actually a vinylene group) between a carbonyl group () and a hydroxyl group () is referred to as a ''vinylogous'' carboxylic acid. Due to the transmission of electronic information through conjugation, ''vinylogous'' functional groups often possess "''analogous''" reactivity or chemical properties compared to the parent functional group. Hence, vinylogy is a useful heuristic for the prediction of the behavior of systems that are structurally similar but contain intervening C=C bonds that are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glutaric Acid
Glutaric acid is the organic compound with the formula C3H6(COOH)2 . Although the related "linear" dicarboxylic acids adipic and succinic acids are water-soluble only to a few percent at room temperature, the water-solubility of glutaric acid is over 50% (w/w). Biochemistry Glutaric acid is naturally produced in the body during the metabolism of some amino acids, including lysine and tryptophan. Defects in this metabolic pathway can lead to a disorder called glutaric aciduria, where toxic byproducts build up and can cause severe encephalopathy. Production Glutaric acid can be prepared by the ring-opening of butyrolactone with potassium cyanide to give the mixed potassium carboxylate- nitrile that is hydrolyzed to the diacid. Alternatively hydrolysis, followed by oxidation of dihydropyran gives glutaric acid. It can also be prepared from reacting 1,3-dibromopropane with sodium or potassium cyanide to obtain the dinitrile, followed by hydrolysis. Uses *1,5-Pentanediol, a co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cysteine
Cysteine (symbol Cys or C; ) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine often participates in enzymatic reactions as a nucleophile. When present as a deprotonated catalytic residue, sometimes the symbol Cyz is used. The deprotonated form can generally be described by the symbol Cym as well. The thiol is susceptible to oxidation to give the disulfide derivative cystine, which serves an important structural role in many proteins. In this case, the symbol Cyx is sometimes used. When used as a food additive, it has the E number E920. Cysteine is encoded by the codons UGU and UGC. The sulfur-containing amino acids cysteine and methionine are more easily oxidized than the other amino acids. Structure Like other amino acids (not as a residue of a protein), cysteine exists as a zwitterion. Cysteine has chirality in the older / notation based on homology to - and -glyceraldehyde. In the newer ''R''/''S'' system of de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
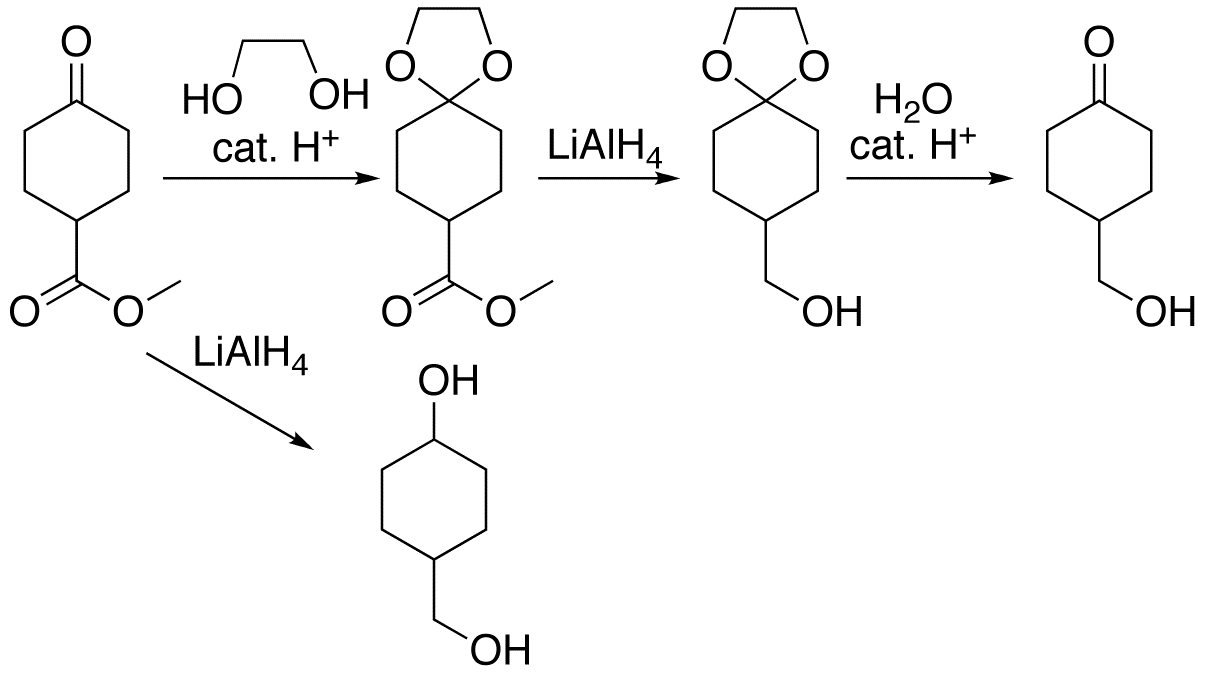
Protective Group
A protecting group or protective group is introduced into a molecule by chemical modification of a functional group to obtain chemoselectivity in a subsequent chemical reaction. It plays an important role in multistep organic synthesis. In many preparations of delicate organic compounds, some specific parts of their molecules cannot survive the required reagents or chemical environments. Then, these parts, or groups, must be protected. For example, lithium aluminium hydride is a highly reactive but useful reagent capable of reducing esters to alcohols. It will always react with carbonyl groups, and this cannot be discouraged by any means. When a reduction of an ester is required in the presence of a carbonyl, the attack of the hydride on the carbonyl has to be prevented. For example, the carbonyl is converted into an acetal, which does not react with hydrides. The acetal is then called a protecting group for the carbonyl. After the step involving the hydride is complete, the ace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organocatalysis
In organic chemistry, organocatalysis is a form of catalysis in which the rate of a chemical reaction is increased by an organic catalyst. This "organocatalyst" consists of carbon, hydrogen, sulfur and other nonmetal elements found in organic compounds.Special Issue: Because of their similarity in composition and description, they are often mistaken as a misnomer for enzymes due to their comparable effects on reaction rates and forms of catalysis involved. Organocatalysts which display secondary amine functionality can be described as performing either enamine catalysis (by forming catalytic quantities of an active enamine nucleophile) or iminium catalysis (by forming catalytic quantities of an activated iminium electrophile). This mechanism is typical for covalent organocatalysis. Covalent binding of substrate normally requires high catalyst loading (for proline-catalysis typically 20–30 mol%). Noncovalent interactions such as hydrogen-bonding facilitates low catalyst lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asymmetric Synthesis
Enantioselective synthesis, also called asymmetric synthesis, is a form of chemical synthesis. It is defined by IUPAC as "a chemical reaction (or reaction sequence) in which one or more new elements of chirality are formed in a substrate molecule and which produces the stereoisomeric (enantiomeric or diastereomeric) products in unequal amounts." Put more simply: it is the synthesis of a compound by a method that favors the formation of a specific enantiomer or diastereomer. Enantiomers are stereoisomers that have opposite configurations at every chiral center. Diastereomers are stereoisomers that differ at one or more chiral centers. Enantioselective synthesis is a key process in modern chemistry and is particularly important in the field of pharmaceuticals, as the different enantiomers or diastereomers of a molecule often have different biological activity. Overview Many of the building blocks of biological systems such as sugars and amino acids are produced exclusivel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael J
Michael may refer to: People * Michael (given name), a given name * Michael (surname), including a list of people with the surname Michael Given name "Michael" * Michael (archangel), ''first'' of God's archangels in the Jewish, Christian and Islamic religions * Michael (bishop elect), English 13th-century Bishop of Hereford elect * Michael (Khoroshy) (1885–1977), cleric of the Ukrainian Orthodox Church of Canada * Michael Donnellan (1915–1985), Irish-born London fashion designer, often referred to simply as "Michael" * Michael (footballer, born 1982), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born 1983), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born 1993), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born February 1996), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born March 1996), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born 1999), Brazilian footballer Rulers =Byzantine emperors= * Michael I Rangabe (d. 844), married the daughter of Emperor Nikephor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclopentene
Cyclopentene is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless liquid with a petrol-like odor. It has few applications, and thus is mainly used as a minor component of gasoline, present in concentrations of less than 1%. It is one of the principal cycloalkenes. Production Cyclopentene is produced industrially in large amounts by steam cracking of naphtha. In the laboratory, it is prepared by dehydration of cyclopentanol. It can also produced by the catalytic hydrogenation of cyclopentadiene Cyclopentadiene is an organic compound with the formula C5H6.LeRoy H. Scharpen and Victor W. Laurie (1965): "Structure of cyclopentadiene". ''The Journal of Chemical Physics'', volume 43, issue 8, pages 2765-2766. It is often abbreviated CpH beca ....D. Hönicke, R. Födisch, P. Claus, M. Olson: ''Cyclopentadiene and Cyclopentene'', in: '' Ullmanns Enzyklopädie der Technischen Chemie'' 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. Use in mechanistic organic chemistry Cyclopentene is used in an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intramolecular Reaction
Intramolecular in chemistry describes a process or characteristic limited within the structure of a single molecule, a property or phenomenon limited to the extent of a single molecule. Examples * intramolecular hydride transfer (transfer of a hydride ion from one part to another within the same molecule) * intramolecular hydrogen bond (a hydrogen bond formed between two functional groups of the same molecule) *cyclization of ω-haloalkylamines and alcohols to form the corresponding saturated nitrogen and oxygen heterocycles, respectively (an SN2 reaction within the same molecule) In intramolecular organic reactions, two reaction sites are contained within a single molecule. This creates a very high effective concentration (resulting in high reaction rates), and, therefore, many intramolecular reactions that would not occur as an intermolecular reaction between two compounds take place. Examples of intramolecular reactions are the Smiles rearrangement, the Dieckmann condensat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
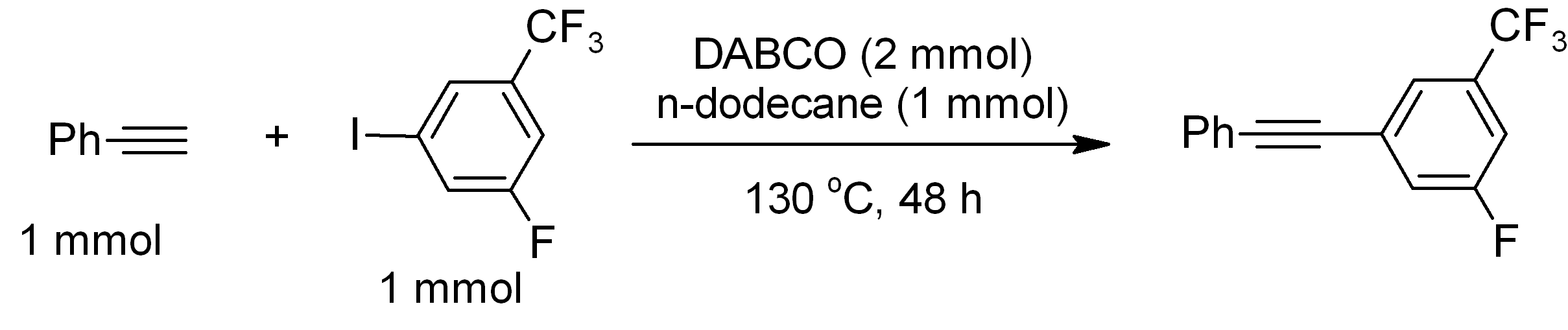
DABCO
DABCO (1,4-diazabicyclo .2.2ctane), also known as triethylenediamine or TEDA, is a bicyclic organic compound with the formula N2(C2H4)3. This colorless solid is a highly nucleophilic tertiary amine base, which is used as a catalyst and reagent in polymerization and organic synthesis. It is similar in structure to quinuclidine, but the latter has one of the nitrogen atoms replaced by a carbon atom. Reactions The p''K''a of DABCOsup>+ (the protonated derivative) is 8.8, which is almost the same as ordinary alkylamines. The nucleophilicity of the amine is high because the amine centers are unhindered. It is sufficiently basic to promote C–C coupling of terminal acetylenes, for example, phenylacetylene couples with electron-deficient iodoarenes. : Catalyst DABCO is used as a base-catalyst for: *formation of polyurethane from alcohol and isocyanate functionalized monomers and pre-polymers. * Baylis-Hillman reactions of aldehydes and unsaturated ketones and aldehydes. : ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acrylonitrile
Acrylonitrile is an organic compound with the formula and the structure . It is a colorless, volatile liquid although commercial samples can be yellow due to impurities. It has a pungent odor of garlic or onions. In terms of its molecular structure, it consists of a vinyl group () linked to a nitrile (). It is an important monomer for the manufacture of useful plastics such as polyacrylonitrile. It is reactive and toxic at low doses. Acrylonitrile was first synthesized by the French chemist Charles Moureu (1863–1929) in 1893. Occurrence Acrylonitrile is not naturally formed on Earth. It has been detected at the sub-ppm level at industrial sites. It persists in the air for up to a week. It decomposes by reacting with oxygen and hydroxyl radical to form formyl cyanide and formaldehyde. Acrylonitrile is harmful to aquatic life. Acrylonitrile has been detected in the atmosphere of Titan, a moon of Saturn. Computer simulations suggest that on Titan conditions exi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |