|
Rashid Rida During World War I
Before the outbreak of the World War I, First World War, scholars of the Salafi movement#Evolution, Arab Salafiyya movement represented the leading voice of Islamic religious dissent within the Ottoman Empire. Their most influential theologian Rashid Rida, Muhammad Rashid Rida, an ardent critic of Abdul Hamid II and Turkish nationalism, regarded Ottoman Sultans, Ottoman kings as unqualified to rule over the affairs of the Muslim world, Muslim World. While excoriating the Ottomans as an artificial caliphate based on unjust wars and conquests; Salafi scholars nonetheless strongly forbade rebellion against the Ottoman authority due to their insight of dangers posed by the expanding European colonialism. Rashid Rida and his pupils perceived the Ottoman state as an essential entity for allowing Muslims to successfully repel European imperial powers and rebuked the proponents for an alternative Caliphate; suspecting them of serving the aims of imperial powers. All of this changed with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Colonial Empire
The French colonial empire () comprised the overseas Colony, colonies, protectorates, and League of Nations mandate, mandate territories that came under French rule from the 16th century onward. A distinction is generally made between the "First French colonial empire", that existed until 1814, by which time most of it had been lost or sold, and the "Second French colonial empire", which began with the French conquest of Algeria, conquest of Algiers in 1830. On the eve of World War I, France's colonial empire was List of largest empires, the second-largest in the world after the British Empire. France began to establish colonies in the French colonization of the Americas, Americas, the Caribbean, and French India, India in the 16th century but lost most of its possessions after its defeat in the Seven Years' War. The North American possessions were lost to Britain and Spain, but Louisiana (New France), Spain later returned Louisiana to France in 1800. The territory was then Loui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
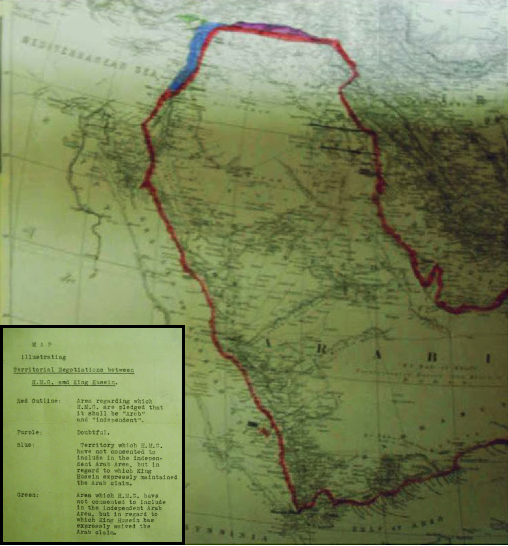
Sykes–Picot Agreement
The Sykes–Picot Agreement () was a 1916 secret treaty between the United Kingdom and France, with assent from Russia and Italy, to define their mutually agreed spheres of influence and control in an eventual partition of the Ottoman Empire. The agreement was based on the premise that the Triple Entente would achieve success in defeating the Ottoman Empire during World War I and formed part of a series of secret agreements contemplating its partition. The primary negotiations leading to the agreement took place between 23 November 1915 and 3 January 1916, on which date the British and French diplomats, Mark Sykes and François Georges-Picot, initialled an agreed memorandum. The agreement was ratified by their respective governments on 9 and 16 May 1916. The agreement effectively divided the Ottoman provinces outside the Arabian Peninsula into areas of British and French control and influence. The British- and French-controlled countries were divided by the Sykes–Picot line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khalifa
''Khalifa'' or ''Khalifah'' (; commonly "caliph" in English) is a name or title which means "successor", "ruler" or "leader". It most commonly refers to the leader of a Caliphate, but is also used as a title among various Islamic religious groups and others. There were four Rashidun caliphs after Muhammad died, beginning with Abu Bakr. The ''Khilaafat'' (or Caliphate) was then contested and gave rise to the eventual division of the Islamic Umma into two groups, the Sunni Islam, Sunni and the Shia Islam, Shi'a who interpret the word ''Khalifa'' in differently nuanced ways. The earliest Islamic uses include Khaleefa(ḥ)''' in The Qur'an, 2:30, where God in Islam, God commands the angels to bow down to Adam in Islam, Adam) with reverence. "Vicegerent", therefore, is more at "divinely-guided spokesman" than "deputy" in this context and leads to the discovery of the role of Imamah (Ismaili doctrine), Imam in Islam, from the ''Shi'i'' or Shia Islam, Shi'a point of view where, it is c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pan-Islamism
Pan-Islamism () is a political movement which advocates the unity of Muslims under one Islamic country or state – often a caliphate – or an international organization with Islamic principles. Historically, after Ottomanism, which aimed at the unity of all Ottoman citizens, Pan-Islamism was promoted in the Ottoman Empire during the last quarter of the 19th century by Sultan Abdul Hamid II for the purpose of preventing secession movements of the Muslim peoples in the empire. Pan-Islamism differentiates itself from pan-nationalistic ideologies, for example Pan-Arabism, by focusing on religion and not ethnicity and race. It sees the ummah (Muslim community) as the focus of allegiance and mobilization, including the Tawhid belief by the guidance of Quran and Sunnah's teachings. The major leaders of the Pan-Islamist movement were the triad of Jamal al-Din Afghani (1839–1897), Muhammad Abduh (1849–1905) and Sayyid Rashid Rida (1865–1935), who were active in anti-colon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jihad
''Jihad'' (; ) is an Arabic word that means "exerting", "striving", or "struggling", particularly with a praiseworthy aim. In an Islamic context, it encompasses almost any effort to make personal and social life conform with God in Islam, God's guidance, such as an introspection, internal struggle against evil in oneself, efforts to build a good Muslim community (''ummah''), and struggle to defend Islam. Literally meaning 'struggle', the term is most frequently Islam and war, associated with warfare. ''Jihad'' is classified into inner ("greater") ''jihad'', which involves a struggle against one's own passions and impulses, and outer ("lesser") ''jihad'', which is further subdivided into ''jihad'' of the pen/tongue (debate or persuasion) and ''jihad'' of the sword (warfare). Much of Muslim opinion considers inner ''jihad'' to have primacy over outer ''jihad'', although many Western scholars disagree. The analysis of a large survey from 2002 reveals considerable nuance in the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Imperialism
Imperialism is the maintaining and extending of power over foreign nations, particularly through expansionism, employing both hard power (military and economic power) and soft power ( diplomatic power and cultural imperialism). Imperialism focuses on establishing or maintaining hegemony and a more formal empire. While related to the concept of colonialism, imperialism is a distinct concept that can apply to other forms of expansion and many forms of government. Etymology and usage The word ''imperialism'' was derived from the Latin word , which means 'to command', 'to be sovereign', or simply 'to rule'. It was coined in the 19th century to decry Napoleon III's despotic militarism and his attempts at obtaining political support through foreign military interventions. The term became common in the current sense in Great Britain during the 1870s; by the 1880s it was used with a positive connotation. By the end of the 19th century, the term was used to describe the behavior of em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berlin–Baghdad Railway
The Baghdad railway, also known as the Berlin–Baghdad railway (, , , ), was started in 1903 to connect Berlin with the then Ottoman Empire, Ottoman city of Baghdad, from where the Germans wanted to establish a port on the Persian Gulf, with a line through modern-day Turkey, Syria, and Iraq. Jean-Pierre Filiu, in his 2022 History of the Middle East (p201), summing up the situation on the eve of the First World War, says of this (projected) railway, 'The British ensured that the last stretch of the railway line, linking Baghdad to the port of Basra on the Persian Gulf, was reserved for them.' The current line from Baghdad to Basra was not opened until 2014. The line was completed only in 1940. By the outbreak of World War I, the railway was still 960 km (600 miles) away from its intended objective. The last stretch to Baghdad was built in the late 1930s, and the first train to travel from Istanbul to Baghdad departed in 1940. Funding, engineering and construction were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Empire
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperial Germany, the Second Reich or simply Germany, was the period of the German Reich; . from the unification of Germany in 1871 until the German revolution of 1918–1919, November Revolution in 1918, when the German Reich changed its form of government from a monarchy to a Weimar Republic, republic. The German Empire consisted of States of the German Empire, 25 states, each with its own nobility: four constituent Monarchy, kingdoms, six Grand duchy, grand duchies, five Duchy, duchies (six before 1876), seven Principality, principalities, three Free imperial city, free Hanseatic League, Hanseatic City-state, cities, and Alsace–Lorraine, one imperial territory. While Prussia was one of four kingdoms in the realm, it contained about two-thirds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Sultan
The sultans of the Ottoman Empire (), who were all members of the Ottoman dynasty (House of Osman), ruled over the Boundaries between the continents, transcontinental empire from its perceived inception in 1299 to Dissolution of the Ottoman Empire, its dissolution in 1922. At its height, the Ottoman Empire spanned an area from Budin Eyalet, Hungary in the north to Yemen Eyalet, Yemen in the south and from Ottoman Algeria, Algeria in the west to Ottoman Iraq, Iraq in the east. Administered at first from the city of Söğüt since before 1280 and then from the city of Bursa since 1323 or 1324, the empire's capital was moved to Adrianople (now known as Edirne in English) in 1363 following Ottoman conquest of Adrianople, its conquest by Murad I and then to Constantinople (present-day Istanbul) in 1453 following Fall of Constantinople, its conquest by Mehmed the Conqueror, Mehmed II. The Rise of the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman Empire's early years have been the subject of varying narrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Empire In World War I
The Ottoman Empire was one of the Central Powers of World War I, allied with the German Empire, Austria-Hungary, and Tsardom of Bulgaria (1908–1946), Bulgaria. It Ottoman entry into World War I, entered the war on 29 October 1914 with a small Black Sea raid, surprise attack on the Black Sea coast of the Russian Empire, prompting Russia—and Triple Entente, its allies, France and Great Britain—to declare war the following month. World War I had erupted almost exactly three months prior, on 28 July, following July Crisis, a series of interrelated diplomatic and military escalations among the Great power, major powers of Europe triggered by the Assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria, Archduke Franz Ferdinand, heir presumptive to the Austria-Hungary, Austro-Hungarian throne, by Serbs of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bosnian Serb nationalist Gavrilo Princip. The Ottoman Empire, which had no stake in the immediate causes and consi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bay'ah
''Bayʿah'' (, "Pledge of allegiance"), in Islamic terminology, is an oath of allegiance to a leader. It is known to have been practiced by the Islamic prophet Muhammad. In Bedouin culture it was a procedure for choosing the leader of the tribe, and is sometimes taken under a written pact given on behalf of the subjects by leading members of the tribe with the understanding that as long as the leader abides by certain requirements towards his people, they are to maintain their allegiance to him. ''Bayʿah'' is still practiced in countries such as Saudi Arabia and Sudan. In Morocco, ''bayʿah'' is one of the foundations of the monarchy. Etymology and definitions ''Bay'ah'' derives from the Semitic triconsonantal root ''B-Y-’'', related to commerce, and shows the contractual nature of the bond between caliph and the people. ''Bay'ah'' originally referred to the striking together of hands between buyer and seller to mark an agreement. According to Bernard Lewis, ''bay'ah'' or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |