|
Raphe Perinealis
The perineal raphe is a visible line or ridge of tissue on the body that extends from the Human anus, anus through the perineum to the scrotum (male) or the Human vulva, vulva (female). It is found in both males and females, arises from the fusion of the urogenital folds, and is visible running medial through anteroposterior, to the anus where it resolves in a small knot of skin of varying size. In males, this structure continues through the midline of the scrotum (scrotal raphe) and upwards through the posterior midline aspect of the Human penis, penis (penile raphe). It also exists deeper through the scrotum where it is called the scrotal septum. It is the result of a fetus, fetal developmental phenomenon whereby the scrotum and penis close toward the midline and fuse. See also * Embryonic and prenatal development of the male reproductive system in humans * Frenulum of penis * Linea nigra * Raphe Images File:Gray1119.png, Stages in the development of the external sexual o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urogenital Folds
The development of the reproductive system is the part of embryonic growth that results in the sex organs and contributes to sexual differentiation. Due to its large overlap with development of the urinary system, the two systems are typically described together as the genitourinary system. The reproductive organs develop from the intermediate mesoderm and are preceded by more primitive structures that are superseded before birth. These embryonic structures are the mesonephric ducts (also known as ''Wolffian ducts'') and the paramesonephric ducts, (also known as ''Müllerian ducts''). The mesonephric duct gives rise to the male seminal vesicles, epididymides and vasa deferentia. The paramesonephric duct gives rise to the female fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, and upper part of the vagina. Mesonephric ducts The mesonephric duct originates from a part of the pronephric duct. Origin In the outer part of the intermediate mesoderm, immediately under the ectoderm, in the re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Anus
In humans, the anus (: anuses or ani; from Latin ''ānus'', "ring", "circle") is the external opening of the rectum located inside the intergluteal cleft. Two sphincters control the exit of Human feces, feces from the body during an act of defecation, which is the primary function of the anus. These are the internal anal sphincter and the external anal sphincter, which are circular muscles that normally maintain constriction of the orifice and which relax as required by normal physiological functioning. The inner sphincter is involuntary and the outer is voluntary. Above the anus is the perineum, which is also located beneath the vulva or scrotum. In part owing to its exposure to feces, a number of medical conditions may affect the anus, such as hemorrhoids. The anus is the site of potential infections and other conditions, including cancer (see anal cancer). With anal sex, the anus can play a role in Human sexuality, sexuality. Attitudes toward anal sex vary, and it is illeg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perineum
The perineum (: perineums or perinea) in placentalia, placental mammals is the space between the anus and the genitals. The human perineum is between the anus and scrotum in the male or between the anus and vulva in the female. The perineum is the region of the body between the pubic symphysis (pubic arch) and the coccyx (tail bone), including the perineal body and surrounding structures. The perineal raphe is visible and pronounced to varying degrees. Etymology The word entered English from late Latin via Greek language, Greek περίναιος ~ περίνεος ''perinaios, perineos'', itself from περίνεος, περίνεοι 'male genitals' and earlier περίς ''perís'' 'penis' through influence from πηρίς ''pērís'' 'scrotum'. The term was originally understood as a purely male body-part with the perineal raphe seen as a continuation of the scrotal septum since Virilization, masculinization causes the development of a large anogenital distance in men, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
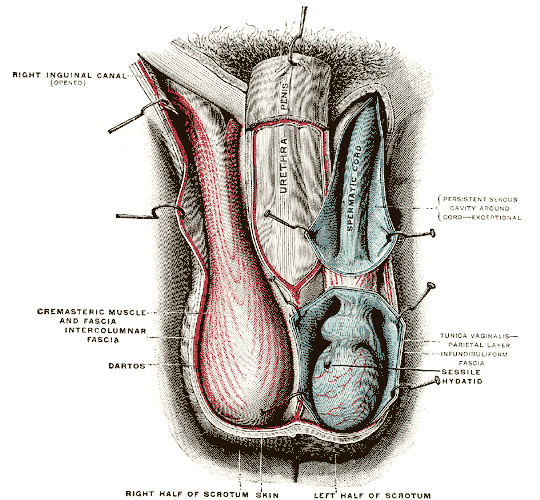
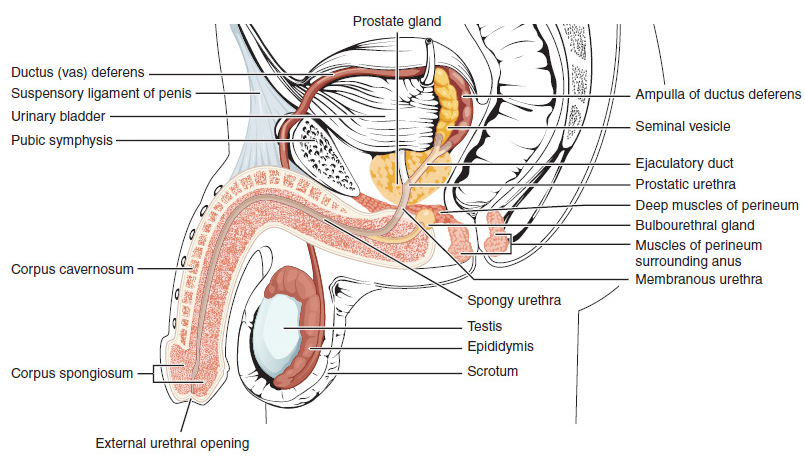
Scrotum
In most terrestrial mammals, the scrotum (: scrotums or scrota; possibly from Latin ''scortum'', meaning "hide" or "skin") or scrotal sac is a part of the external male genitalia located at the base of the penis. It consists of a sac of skin containing the external spermatic fascia, testicles, epididymides, and vasa deferentia. The scrotum will usually tighten when exposed to cold temperatures. The scrotum is homologous to the labia majora in females. Structure In regards to humans, the scrotum is a suspended two-chambered sac of skin and muscular tissue containing the testicles and the lower part of the spermatic cords. It is located behind the penis and above the perineum. The perineal raphe is a small, vertical ridge of skin that expands from the anus and runs through the middle of the scrotum front to back. The scrotum is also a distention of the perineum and carries some abdominal tissues into its cavity including the testicular artery, testicular vein, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Vulva
In mammals, the vulva (: vulvas or vulvae) comprises mostly external, visible structures of the female genitalia leading into the interior of the female reproductive tract. For humans, it includes the mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vestibule, urinary meatus, vaginal introitus, hymen, and openings of the vestibular glands ( Bartholin's and Skene's). The folds of the outer and inner labia provide a double layer of protection for the vagina (which leads to the uterus). Pelvic floor muscles support the structures of the vulva. Other muscles of the urogenital triangle also give support. Blood supply to the vulva comes from the three pudendal arteries. The internal pudendal veins give drainage. Afferent lymph vessels carry lymph away from the vulva to the inguinal lymph nodes. The nerves that supply the vulva are the pudendal nerve, perineal nerve, ilioinguinal nerve and their branches. Blood and nerve supply to the vulva contribute to the stages of sexual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urogenital Folds
The development of the reproductive system is the part of embryonic growth that results in the sex organs and contributes to sexual differentiation. Due to its large overlap with development of the urinary system, the two systems are typically described together as the genitourinary system. The reproductive organs develop from the intermediate mesoderm and are preceded by more primitive structures that are superseded before birth. These embryonic structures are the mesonephric ducts (also known as ''Wolffian ducts'') and the paramesonephric ducts, (also known as ''Müllerian ducts''). The mesonephric duct gives rise to the male seminal vesicles, epididymides and vasa deferentia. The paramesonephric duct gives rise to the female fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, and upper part of the vagina. Mesonephric ducts The mesonephric duct originates from a part of the pronephric duct. Origin In the outer part of the intermediate mesoderm, immediately under the ectoderm, in the re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Penis
In Human body, human anatomy, the penis (; : penises or penes; from the Latin ''pēnis'', initially 'tail') is an external sex organ (intromittent organ) through which males urination, urinate and ejaculation, ejaculate, as Penis, on other animals. Together with the testes and surrounding structures, the penis functions as part of the male reproductive system. The main parts of the penis are the Root of penis, root, Body of penis, body, the epithelium of the penis, including the shaft skin, and the foreskin covering the glans penis, glans. The body of the penis is made up of three columns of tissue (biology), tissue: two Corpus cavernosum penis, corpora cavernosa on the dorsal side and corpus spongiosum penis, corpus spongiosum between them on the ventral side. The Urethra#Male, urethra passes through the prostate gland, where it is joined by the ejaculatory ducts, and then through the penis. The urethra goes across the corpus spongiosum and ends at the tip of the glans as the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penile Raphe
The penile raphe is a visible line or ridge of tissue that runs on the ventral (urethral) side of the human penis beginning from the base of the shaft and ending in the prepuce between the penile frenulum. The line is typically darker than the rest of the shaft skin, even though its shape and pigmentation may vary greatly among males. The penile raphe is part of a broader line in the male reproductive organs, that runs from the anus through the perineum (perineal raphe) and continues to the scrotum and penis, collectively referred to as median raphe. The penile raphe along with the skin between it are homologous to the female labia minora. The line consists of a subcutaneous fibrous plate, which may vary in prominence and thickness in various areas of the genitals. In the scrotum, the line is located over the internal scrotal septum that divides the two sides of the sac and is densely occupied by nerve fibers. The raphe may become more prominent and darker when the scrotal s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scrotal Septum
The septum of scrotum or scrotal septum is an incomplete vertical wall (septum) that divides the scrotum into two compartments –each containing a single testis. It consists of flexible connective tissue and nonstriated muscle (dartos fascia The dartos fascia, dartos tunic or simply dartos is a layer of connective tissue found in the penile shaft, foreskin and scrotum. The penile portion is referred to as the superficial fascia of penis or the subcutaneous tissue of penis, while the ...). The site of the median septum is apparent on the surface of the scrotum along a median longitudinal ridge called the scrotal raphe. The perineal raphe further extends forward to the undersurface of the penis and backward to the anal opening. The purpose of the median septum is to compartmentalize each testis in order to prevent friction or trauma. The scrotal skin is vascularized via the two external pudental arteries and the internal pudental artery. The central territory of the scrotum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fetus
A fetus or foetus (; : fetuses, foetuses, rarely feti or foeti) is the unborn offspring of a viviparous animal that develops from an embryo. Following the embryonic development, embryonic stage, the fetal stage of development takes place. Prenatal development is a continuum, with no clear defining feature distinguishing an embryo from a fetus. However, in general a fetus is characterized by the presence of all the major body organs, though they will not yet be fully developed and functional, and some may not yet be situated in their final Anatomy, anatomical location. In human prenatal development, fetal development begins from the ninth week after Human fertilization, fertilization (which is the eleventh week of Gestational age (obstetrics), gestational age) and continues until the childbirth, birth of a newborn. Etymology The word ''wikt:fetus#English, fetus'' (plural ''wikt:fetuses#English, fetuses'' or rarely, the solecism ''wikt:feti#English, feti''''Oxford English Dict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embryonic And Prenatal Development Of The Male Reproductive System In Humans
The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that play a role in the process of human reproduction. These organs are located on the outside of the body, and within the pelvic cavity, pelvis. The main male sex organs are the human penis, penis and the scrotum, which contains the testicles that produce semen and sperm, which, as part of sexual intercourse, Fertilisation, fertilize an ovum in the female's body; the fertilized ovum (zygote) develops into a fetus, which is later born as an infant. The corresponding system in females is the female reproductive system. External genitalia Penis The penis is an intromittent organ with a long Body of penis, shaft, an enlarged bulbous-shaped tip called the Glans penis, glans and its foreskin for protection. Inside the penis is the Urethra#Male, urethra, which is used to ejaculation, ejaculate semen and to excrete urine. Both substances exit through the Urinary meatus, meatus. When a male becomes Sexual arousal, sex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frenulum Of Penis
The frenulum of the penis, often known simply as the frenulum (from ) or frenum, is a thin elastic strip of tissue on the underside of the glans and the neck of the human penis. In men who are not circumcised, it also connects the foreskin to the glans and the ventral mucosa. In adults, the frenulum is typically supple enough to allow manual movement of the foreskin over the glans and help retract the foreskin during erection. In flaccid state, it tightens to narrow the foreskin opening. The penile frenulum is homologous to the clitoral frenulum in the female. It is similar to the lingual frenulum between the tongue's lower surface and the lower jaw, or the frenulum between the upper lip and the outside of the upper gum. In some men, the frenulum may appear shorter than normal, a phenomenon known as frenulum breve. Treatment of frenulum breve may be non-surgical, or in other cases, especially with penile chordee, it may include frenulectomy or frenulum lengthening. Structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |