|
Ramesses XI
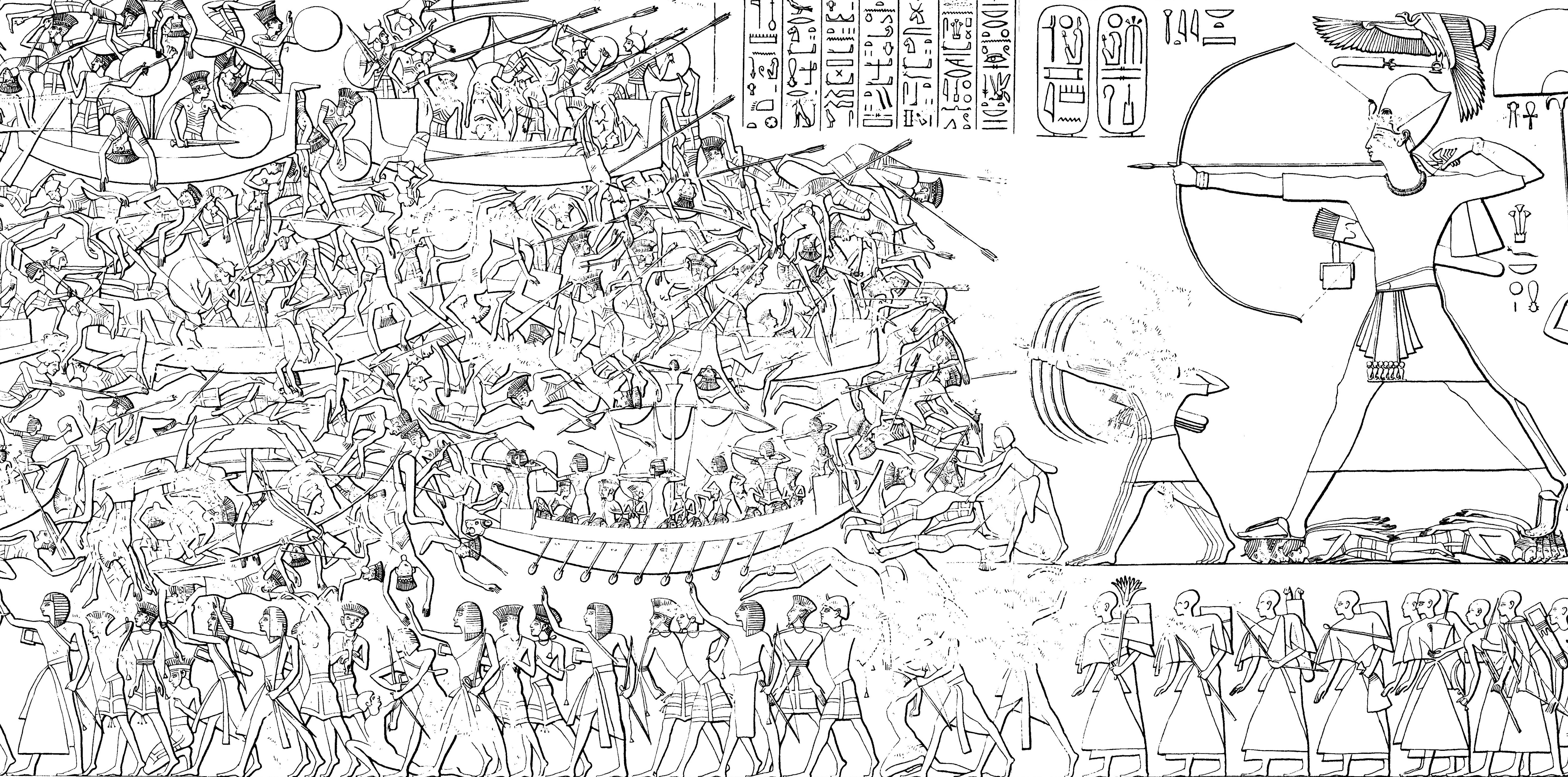
Menmaatre Ramesses XI (also written Ramses and Rameses) reigned from 1107 BC to somewhere between 1078 BC and 1068 BC and is generally considered the tenth and final pharaoh of the Twentieth Dynasty of Egypt and as such, the last king of the New Kingdom period. He ruled Egypt for at least 29 years although some Egyptologists think he could have ruled for as long as 30. The latter figure would be up to 2 years beyond this king's highest known date of Year 10 of the '' ''wḥm-mswt'''' ("Renaissance") era or Year 28 of his reign. One scholar, Ad Thijs, has suggested that Ramesses XI could even have reigned as long as 33 years. It is believed that Ramesses ruled into his Year 29 since a graffito records that the general and High Priest of Amun Piankh returned to Thebes from Nubia on III Shemu day 23—or just 3 days into what would have been the start of Ramesses XI's 29th regnal year. Piankh is known to have campaigned in Nubia during Year 28 of Ramesses XI's reign (or Year 10 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twentieth Dynasty Of Egypt
The Twentieth Dynasty of Egypt (notated Dynasty XX, alternatively 20th Dynasty or Dynasty 20) is the third and last dynasty of the Ancient Egyptian New Kingdom period, lasting from 1189 BC to 1077 BC. The 19th and 20th Dynasties together constitute an era known as the Ramesside period owing to the predominance of rulers with the given name "Ramesses". This dynasty is generally considered to mark the beginning of the decline of Ancient Egypt at the transition from the Late Bronze to Iron Age. During the period of the Twentieth Dynasty, Ancient Egypt faced the crisis of invasions by Sea Peoples. The dynasty successfully defended Egypt, while sustaining heavy damage. History After the death of the last pharaoh of the 19th Dynasty, Queen Twosret, Egypt entered into a period of civil war. Because of lost historical records, the cause of the civil war is unknown. The war was ended with the accession to the throne by Setnakhte, who founded the 20th Dynasty of Egypt. From the reign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinehesy
Pinehesy, Panehesy or Panehasy, depending on the transliteration, was Viceroy of Kush during the reign of Ramesses XI, the last pharaoh, king of the Ancient Egypt, Egyptian Twentieth dynasty of Egypt, 20th Dynasty. The sources He is named in the following dated sources: #his name appears in the very damaged first lines on the verso of Pap. B.M. 10053, dated to an anonymous year 9, which stems from the reign of Ramesses XI, but might be ascribed either to his actual "year 9" or alternatively to "year 9 of the Whm Mswt". This mention has often been taken as evidence that he was in office at the time and took part in the court case which is described there. However, it has been pointed out that that is an over interpretation of the evidence: there is no title remaining and the context present is too damaged to ascertain how the name functioned in the text. #in the Turin Taxation Papyrus, stemming from a year 12 of Ramesses XI (again, either the actual "year 12" or "year 12 of the Whm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian language, Egyptian: ''wikt:pr ꜥꜣ, pr ꜥꜣ''; Meroitic language, Meroitic: 𐦲𐦤𐦧, ; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') was the title of the monarch of ancient Egypt from the First Dynasty of Egypt, First Dynasty () until the Roman Egypt, annexation of Egypt by the Roman Republic in 30 BCE. However, the equivalent Egyptian language, Egyptian word for "king" was the term used most frequently by the ancient Egyptians for their monarchs, regardless of gender, through the middle of the Eighteenth Dynasty during the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom. The earliest confirmed instances of "pharaoh" used contemporaneously for a ruler were a letter to Akhenaten (reigned –1336 BCE) or an inscription possibly referring to Thutmose III (–1425 BCE). In the early dynasties, ancient Egyptian kings had as many as ancient Egyptian royal titulary, three titles: the Horus name, Horus, the prenomen (Ancient Egypt), Sedge and Bee (wikt:nswt-bjtj, ''nswt-bjtj''), and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viceroy Of Kush
The Kingdom of Kerma in Nubia was a province of ancient Egypt from the 16th century BCE to 11th century BCE. During this period, the region was ruled by a viceroy who reported directly to the Egyptian Pharaoh. Initially the position was titled "King's Son of the Southern Countries" and "King's Son, Overseer of the Southern Foreign Countries" but by the reign of Thutmose IV the title "King's Son of Kush" appears and becomes standard. The viceroy was responsible for overseeing the area north of the Third Cataract, which was divided into Wawat in the north, centered at Aniba, and Kush in the south, centered at Soleb during the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt and later at Amara West. They were supported in this task by two deputies, a number of scribes, an overseer of cattle, and the priests of local Egyptian built temples. Paintings in the tomb of Amenhotep Huy in the Theban necropolis depict some of the activities of a viceroy including overseeing the collection and tallying of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amenhotep, Priest Of Amun
Amenhotep was the High Priest of Amun towards the end of the Twentieth Dynasty of Egypt, serving under Ramesses IX, Ramesses X and Ramesses XI. He was the son of Ramessesnakht, the previous high priest of Amun. It is not beyond dispute who succeeded him in office. For a long time it was assumed that he was followed by the High Priest Herihor. However, Karl Jansen-Winkeln has suggested that Amenhotep was instead succeeded by the High Priest Piankh. We know the names of several of his brothers and a sister: * his (eldest?) brother, the prophet of Amun Meribast II * his brother, the Chief Steward Usimarenakth II * his sister Aatmeret I * his brother, the Second Prophet of Amun Nesamun I (see below) The "Transgression against the High Priest" From several references in the Tomb Robbery Papyri ( Pap. Mayer A; Pap. B.M. 10383; Pap. B.M. 10052) it can be deduced that, sometime prior to the start of the era known as the Wehem Mesut, the Viceroy of Kush Pinehesy attacked Thebes and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinedjem I
Pinedjem I (died 1032 BC) was ruler of Southern Egypt as the High Priests of Amun at Thebes, High Priest of Amun at Thebes in Ancient Egypt from 1070 to 1055 BC, and nominal pharaoh alongside Smendes from 1054 to 1032 BC. He was the son of the High Priest Piankh. However, many Egyptologists today believe that the succession in the Amun priesthood actually ran from Piankh to Herihor to Pinedjem I. Reign According to the new hypothesis regarding the succession of the Amun priesthood, Pinedjem I was too young to succeed to the High Priesthood of Amun after the death of Piankh. Herihor instead intervened to assume this office. After Herihor's death, Pinedjem I finally claimed this office which had once been held by his father Piankh. This interpretation is supported by the decorations from the Temple of Khonsu at Karnak where Herihor's wall reliefs here are immediately followed by those of Pinedjem I with no intervening phase for Piankh and also by the long career of Pinedjem I who se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramesses III
Usermaatre Meryamun Ramesses III was the second Pharaoh of the Twentieth dynasty of Egypt, Twentieth Dynasty in Ancient Egypt. Some scholars date his reign from 26 March 1186 to 15 April 1155 BC, and he is considered the last pharaoh of the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom to have wielded substantial power. His long reign saw the decline of Egyptian political and economic power, linked to a series of invasions and internal economic problems that also plagued pharaohs before him. This coincided with a decline in the cultural sphere of Ancient Egypt. However, his successful defense was able to slow down the decline, although it still meant that his successors would have a weaker military. He has also been described as a "warrior Pharaoh" due to his strong military strategies. He led the way by defeating the invaders known as "the Sea Peoples", who had caused destruction in other civilizations and empires. He was able to save Egypt from collapsing at the time when Late Bronze Age c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthony Charles Harris
Anthony Charles Harris (1790–1869) was a collector of ancient Egyptian papyri. As antiquary, merchant, and official supplier of the army he was based in Alexandria, Egypt for the last four decades of his life. He made many journeys on the Nile to Upper Egypt where he acquired papyri and artefacts. An amateur, he had a good understanding of hieroglyphs, as was acknowledged by Heinrich Karl Brugsch. His collection included * The Great Harris Papyrus, also known as Papyrus Harris I, mostly lists of temple endowments by Ramses III, but also some historical writings, which Harris acquired in 1855 * The Papyrus Harris II * The Papyrus Harris 500, a literary papyrus containing two tales and poetry * The Papyrus Harris 501 which contained a magical text Selima Harris, his natural daughter, offered his collection for sale in 1871 for £10,000; and it was bought by Samuel Birch of the British Museum The British Museum is a Museum, public museum dedicated to human history, art and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyti
Tyti was an ancient Egyptian queen of the 20th Dynasty. A wife and sister of Ramesses III and possibly the mother of Ramesses IV. Place of Tyti in the 20th Dynasty It was once uncertain which pharaoh was her husband, but he can now be identified as Ramesses III based on new evidence published in the 2010 issue of the ''Journal of Egyptian Archaeology'' (JEA). Her titles show that she was the daughter, sister, wife, and mother of kings. In the past, some thought she was married to Ramesses X, and that both she and her husband were the children of Ramesses IX, and their son was Ramesses XI but another theory by Jehon Grist placed her earlier in the 20th dynasty and identifies her as a daughter-wife of Ramesses III and the mother of Ramesses IV, based on the similarities in style of her tomb and those of princes who lived during this period. However, judging from the age of their child this would mean that Ramesses married his daughter before he ascended the throne, and father-dau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nubia
Nubia (, Nobiin language, Nobiin: , ) is a region along the Nile river encompassing the area between the confluence of the Blue Nile, Blue and White Nile, White Niles (in Khartoum in central Sudan), and the Cataracts of the Nile, first cataract of the Nile (south of Aswan in southern Egypt) or more strictly, Al Dabbah, Sudan, Al Dabbah. It was the seat of one of the earliest civilizations of ancient Africa, the Kerma culture, which lasted from around 2500 BC until its conquest by the New Kingdom of Egypt under Pharaoh Thutmose I around 1500 BC, whose heirs ruled most of Nubia for the next 400 years. Nubia was home to several African empires, empires, most prominently the Kingdom of Kush, which conquered Egypt in the eighth century BC during the reign of Piye and ruled the country as its Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt, 25th Dynasty. From the 3rd century BC to 3rd century AD, northern Nubia was invaded and annexed to Egypt, ruled by the Ptolemaic Kingdom, Greeks and Roman Empire, R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piankh
Piankh or Payankh was a High Priest of Amun during the 21st Dynasty. Piankh has been assumed to be a son of Herihor and the heir to the Theban office, however recent studies have shown that Piankh was actually Herihor's Predecessor. Piankh also held positions as the King's scribe, King's son of Kush, Overseer of the granaries, and commander of the archers of Upper Egypt. Piankh in his position as Viceroy of Kush, would lead an army into Nubia where he would confront a Pinehesy of the former Viceroy of Kush. There is a debate because Piankh would have been living in Nubia, if he wanted to meet them in battle or secretly negotiate with Pinehesy. Piankh may have not been a loyal servant of Ramesses XI because of the negotiations that were taking place between Piankh and Pinhesy. While it is not known as to what Piankh's motivations were he would reunify the viceroyalty and the High priesthood in Kush after defeating Pinehesy. However, this reunification would only last until his death ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |