|
Radogoszcz Prison
During World War II, the Radogoszcz prison was a German Order Police and Gestapo prison in Łódź (), used by the German authorities during the German occupation of Poland in 1939–1945. Today, it is a site of the museum commemorating its wartime victims.''The Book of the Łódź Martyrdom. A Guide to the Radogoszcz and other Sites of National Remembrance.'' Łódź 2005, Museum of Poland's Independence Traditions in Łódź (pl). Establishment The physical building dates from the early 1930s, when Samuel Abbe built a factory in village Radogoszcz (now Zgierska Street in Łódź). It was 4 storey factory building with an adjoining 1 storey factory floor. One month before the Nazi occupation, in August 1939, the Polish Army took control of the building. Use as a prison Radogoszcz was used as a Nazi Police Prison from November 1939. It was used to house prisoners for the many German groups such as the Gestapo, SS, and newly formed local Police. The first murders of Radogo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radogoszcz Mauzoleum
{{geodis ...
Radogoszcz may refer to the following places in Poland: * Radogoszcz, Lower Silesian Voivodeship (south-west Poland) * Radogoszcz, Pomeranian Voivodeship (north Poland) *Radogoszcz prison in Nazi-occupied Lodz * Radegast station (in ), railway station built by the Nazis at the outskirts of the Lodz ghetto * Radogoszcz, Łódź -district (part) of Łódź *Radgosc Rethra (also known as ''Radagoszcz'', ''Radegost'', ''Radigast'', ''Redigast'', ''Radgosc'' and other forms like ''Ruthengost'') was, in the 10th to the 12th centuries, the main town and political center of the Slavic peoples, Slavic Redarians, on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bundesarchiv R 49 Bild-1312, KZ Radogosc Bei Litzmannstadt, Juden
The German Federal Archives or Bundesarchiv (BArch) (, lit. "Federal Archive") are the national archives of Germany. They were established at the current location in Koblenz in 1952. They are subordinated to the Federal Commissioner for Culture and the Media (Claudia Roth since 2021) under the German Chancellery, and before 1998, to the Federal Ministry of the Interior. On 6 December 2008, the Archives donated 100,000 photos to the public, by making them accessible via Wikimedia Commons. History The federal archive for institutions and authorities in Germany, the first precursor to the present-day Federal Archives, was established in Potsdam, Brandenburg in 1919, a later date than in other European countries. This national archive documented German government dating from the founding of the North German Confederation in 1867. It also included material from the older German Confederation and the Imperial Chamber Court. The oldest documents in this collection dated back to the y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordnungspolizei
The ''Ordnungspolizei'' (''Orpo'', , meaning "Order Police") were the uniformed police force in Nazi Germany from 1936 to 1945. The Orpo was absorbed into the Nazi monopoly of power after regional police jurisdiction was removed in favour of the central Nazi government ("Reich-ification", ''Verreichlichung'', of the police). In 1936, Heinrich Himmler, the commander (''Reichsführer-SS'') of the ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS), was appointed Chief of the German Police in the Interior Ministry. The top and upper leadership positions of the Orpo were filled by police officers who belonged to or had joined the SS. Owing to their green uniforms, Orpo members were also referred to as ''Grüne Polizei'' (Green Police). The force was established as a centralised organisation based in Berlin uniting the municipal, city, and rural uniformed police that had been previously organised on a state-by-state basis. The ''Ordnungspolizei'' encompassed virtually all of Nazi Germany's law-enforcement and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gestapo
The (, ), Syllabic abbreviation, abbreviated Gestapo (), was the official secret police of Nazi Germany and in German-occupied Europe. The force was created by Hermann Göring in 1933 by combining the various political police agencies of Free State of Prussia, Prussia into one organisation. On 20 April 1934, oversight of the Gestapo passed to the head of the ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS), Heinrich Himmler, who was also appointed Chief of German Police by Hitler in 1936. Instead of being exclusively a Prussian state agency, the Gestapo became a national one as a sub-office of the (SiPo; Security Police). From 27 September 1939, it was administered by the Reich Security Main Office (RSHA). It became known as (Dept) 4 of the RSHA and was considered a sister organisation to the (SD; Security Service). The Gestapo committed widespread atrocities during its existence. The power of the Gestapo was used to focus upon political opponents, ideological dissenters (clergy and religious org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Łódź
Łódź is a city in central Poland and a former industrial centre. It is the capital of Łódź Voivodeship, and is located south-west of Warsaw. Łódź has a population of 655,279, making it the country's List of cities and towns in Poland, fourth largest city. Łódź first appears in records in the 14th century. It was granted city rights, town rights in 1423 by the Polish King Władysław II Jagiełło and it remained a private town of the Kuyavian bishops and clergy until the late 18th century. In the Second Partition of Poland in 1793, Łódź was annexed to Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia before becoming part of the Napoleonic Duchy of Warsaw; the city joined Congress Poland, a Russian Empire, Russian client state, at the 1815 Congress of Vienna. The Second Industrial Revolution (from 1850) brought rapid growth in textile manufacturing and in population owing to the inflow of migrants, a sizable part of which were Jews and Germans. Ever since the industrialization of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
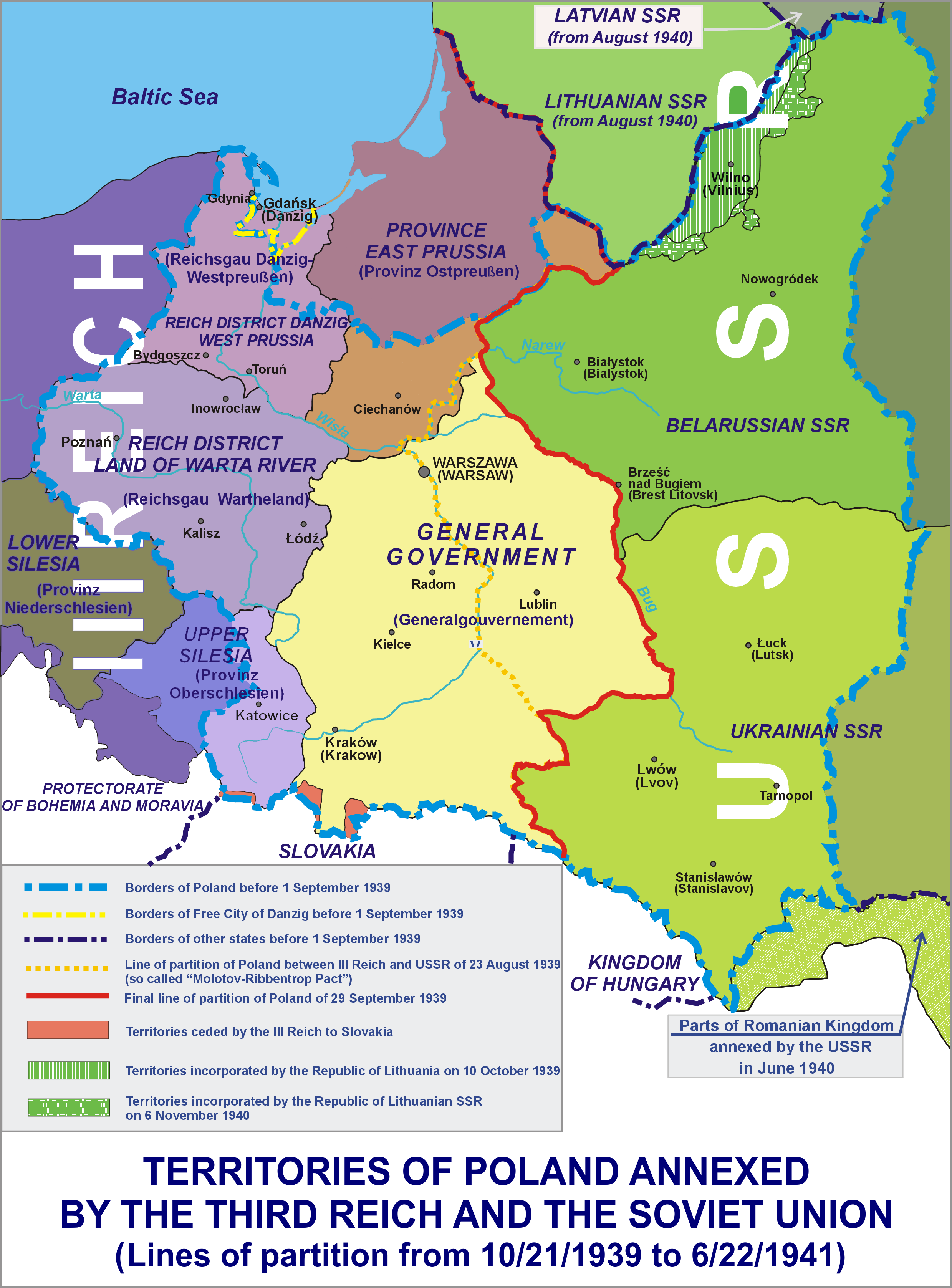
Occupation Of Poland (1939–1945)
During World War II, Poland was occupied by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union following the invasion in September 1939, and it was formally concluded with the defeat of Germany by the Allies in May 1945. Throughout the entire course of the occupation, the territory of Poland was divided between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union (USSR), both of which intended to eradicate Poland's culture and subjugate its people. In the summer-autumn of 1941, the lands which were annexed by the Soviets were overrun by Germany in the course of the initially successful German attack on the USSR. After a few years of fighting, the Red Army drove the German forces out of the USSR and crossed into Poland from the rest of Central and Eastern Europe. Sociologist Tadeusz Piotrowski argues that both occupying powers were hostile to the existence of Poland's sovereignty, people, and the culture and aimed to destroy them. Before Operation Barbarossa, Germany and the Soviet Union coordinated th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazi
Nazism (), formally named National Socialism (NS; , ), is the far-right politics, far-right Totalitarianism, totalitarian socio-political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Germany. During Hitler's rise to power, it was frequently referred to as Hitler Fascism () and Hitlerism (). The term "neo-Nazism" is applied to other far-right groups with similar ideology, which formed after World War II, and after Nazi Germany collapsed. Nazism is a form of fascism, with disdain for liberal democracy and the parliamentary system. Its beliefs include support for dictatorship, fervent antisemitism, anti-communism, anti-Slavism, anti-Romani sentiment, scientific racism, white supremacy, Nordicism, social Darwinism, homophobia, ableism, and the use of eugenics. The ultranationalism of the Nazis originated in pan-Germanism and the ethno-nationalist ''Völkisch movement, Völkisch'' movement which had been a prominent aspect of German nationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intelligenzaktion
The ''Intelligenzaktion'' (), or the Intelligentsia mass shootings, was a series of mass murders committed against the Polish people, Polish intelligentsia (teachers, priests, physicians, and other prominent members of Polish society) during the early years of the World War II, Second World War (1939–45) by Nazi Germany. The Germans conducted the operations in accordance with their plan to Germanization, Germanize the western regions of occupied Poland, before their territorial annexation to the Nazi Germany, German Reich. The mass murder operations of the ''Intelligenzaktion'' resulted in the killing of 100,000 Polish people; by way of forced disappearance, the Germans imprisoned and killed select members of Polish society, identified as enemies of the Reich before the war; they were buried in mass graves which were dug in remote places. To facilitate the depopulation of occupied Poland, the Germans Terrorism, terrorised the general populace by carrying out public, summary exe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Government
The General Government (, ; ; ), formally the General Governorate for the Occupied Polish Region (), was a German zone of occupation established after the invasion of Poland by Nazi Germany, Slovak Republic (1939–1945), Slovakia and the Soviet Union in 1939 at the onset of World War II. The newly occupied Second Polish Republic was split into three zones: the General Government in its centre, Polish areas annexed by Nazi Germany in the west, and territories of Poland annexed by the Soviet Union, Polish areas annexed by the Soviet Union in the east. The territory was expanded substantially in 1941, after the German Operation Barbarossa, Invasion of the Soviet Union, to include the new District of Galicia. The area of the ''Generalgouvernement'' roughly corresponded with the Austrian part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth after the Third Partition of Poland in 1795. The basis for the formation of the General Government was the "Annexation Decree on the Administration o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volksdeutsche
In Nazi Germany, Nazi German terminology, () were "people whose language and culture had Germans, German origins but who did not hold German citizenship." The term is the nominalised plural of ''wikt:volksdeutsch, volksdeutsch'', with denoting a singular female, and , a singular male. The words ''Volk (German word), Volk'' and ''Völkisch movement, völkisch'' conveyed the meanings of "folk". Ethnic Germans living outside Germany shed their identity as ''Auslandsdeutsche'' (Germans abroad), and morphed into the in a process of self-radicalisation. This process gave the Nazi regime the nucleus around which the new Volksgemeinschaft was established across the German borders. were further divided into "racial" groupsminorities within a state minoritybased on special cultural, social, and historic criteria elaborated by the Nazis. Origin of the term ''Volksdeutsche'' According to the historian Doris Bergen, Adolf Hitler Neologism, coined the definition of which appeared in a 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |