|
Radial Artery
In human anatomy, the radial artery is the main artery of the lateral aspect of the forearm. Structure The radial artery arises from the bifurcation of the brachial artery in the antecubital fossa. It runs distally on the anterior part of the forearm. There, it serves as a landmark for the division between the anterior compartment of the forearm, anterior and posterior compartment of the forearm, posterior compartments of the forearm, with the posterior compartment beginning just lateral to the artery. The artery winds laterally around the wrist, passing through the anatomical snuff box and between the heads of the first dorsal interossei of the hand, dorsal interosseous muscle. It passes anteriorly between the heads of the adductor pollicis, and becomes the deep palmar arch, which joins with the deep branch of the ulnar artery. Along its course, it is accompanied by a similarly named vein, the radial vein. Branches The named branches of the radial artery may be divided int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulnar Artery
The ulnar artery is the main blood vessel, with oxygenated blood, of the Human Anatomical Terms#Anatomical directions, medial aspects of the forearm. It arises from the brachial artery and terminates in the superficial palmar arch, which joins with the superficial branch of the radial artery. It is palpable on the anterior and medial aspect of the wrist. Along its course, it is accompanied by a similarly named vein or veins, the ulnar vein or ulnar veins. The ulnar artery, the larger of the two terminal branches of the brachial, begins a little below the bend of the Elbow-joint, elbow in the cubital fossa, and, passing obliquely downward, reaches the ulnar side of the forearm at a point about midway between the elbow and the wrist. It then runs along the ulnar border to the wrist, crosses the transverse carpal ligament on the radial side of the pisiform bone, and immediately beyond this bone divides into two branches, which enter into the formation of the Superficial palmar a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
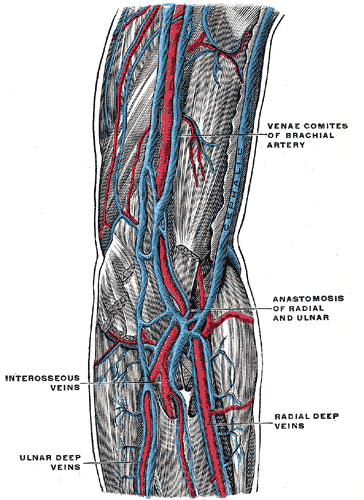
Anterior Compartment Of The Forearm
The anterior compartment of the forearm (or flexor compartment) contains the following muscles: The muscles are largely involved with flexion and supination. The superficial muscles have their origin on the common flexor tendon. The ulnar nerve and artery are also contained within this compartment. The flexor digitorum superficialis lies in between the other four muscles of the superficial group and the three muscles of the deep group. This is why it is also classified as the intermediate group. See also * Compartment syndrome * Posterior compartment of the forearm References External links * Topographical Anatomy of the Upper Limb - Listed Alphabetically University of Arkansas Additional images Image:Gray421.png, Transverse section across distal ends of radius and ulna. Image:Carpal-Tunnel.svg, Transverse section across the wrist In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart Rate
Heart rate is the frequency of the cardiac cycle, heartbeat measured by the number of contractions of the heart per minute (''beats per minute'', or bpm). The heart rate varies according to the body's Human body, physical needs, including the need to absorb oxygen and excrete carbon dioxide. It is also modulated by numerous factors, including (but not limited to) genetics, physical fitness, Psychological stress, stress or psychological status, diet, drugs, hormonal status, environment, and disease/illness, as well as the interaction between these factors. It is usually equal or close to the pulse rate measured at any peripheral point. The American Heart Association states the normal resting adult human heart rate is 60–100 bpm. An ultra-trained athlete would have a resting heart rate of 37–38 bpm. ''Tachycardia'' is a high heart rate, defined as above 100 bpm at rest. ''Bradycardia'' is a low heart rate, defined as below 60 bpm at rest. When a human sleeps, a heartbeat with ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radius (bone)
The radius or radial bone (: radii or radiuses) is one of the two large bones of the forearm, the other being the ulna. It extends from the Anatomical terms of location, lateral side of the Elbow-joint, elbow to the thumb side of the wrist and runs parallel to the ulna. The ulna is longer than the radius, but the radius is thicker. The radius is a long bone, Prism (geometry), prism-shaped and slightly curved longitudinally. The radius is part of two joint (anatomy), joints: the elbow and the wrist. At the elbow, it joins with the capitulum of the humerus, and in a separate region, with the ulna at the radial notch. At the wrist, the radius forms a joint with the ulna bone. The corresponding bone in the human leg, lower leg is the tibia. Structure The long narrow medullary cavity is enclosed in a strong wall of compact bone. It is thickest along the interosseous border and thinnest at the extremities, same over the cup-shaped articular surface (fovea) of the head. The tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalic Vein
In human anatomy, the cephalic vein (also called the antecubital vein) is a superficial vein in the arm. It is the longest vein of the upper limb. It starts at the anatomical snuffbox from the radial end of the dorsal venous network of hand, and ascends along the radial (lateral) side of the arm before emptying into the axillary vein. At the elbow, it communicates with the basilic vein via the median cubital vein. Anatomy The cephalic vein is situated within the superficial fascia along the anterolateral surface of the biceps. Origin The cephalic vein forms at the roof of the anatomical snuffbox at the radial end of the dorsal venous network of hand. Course and relations From its origin, it ascends up the lateral aspect of the radius. Near the shoulder, the cephalic vein passes between the deltoid and pectoralis major muscles ( deltopectoral groove) through the clavipectoral triangle, where it empties into the axillary vein. Anastomoses It communicates wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pronator Quadratus Muscle
Pronator quadratus is a square-shaped muscle on the distal forearm that acts to pronate (turn so the palm faces downwards) the hand. Structure Its fibres run perpendicular to the direction of the arm, running from the most distal quarter of the anterior ulna to the distal quarter of the radius. It has two heads: the superficial head originates from the anterior distal aspect of the diaphysis (shaft) of the ulna and inserts into the anterior distal diaphysis of the radius, as well as its anterior metaphysis. The deep head has the same origin, but inserts proximal to the ulnar notch. It is the only muscle that attaches only to the ulna at one end and the radius at the other end. Arterial blood comes via the anterior interosseous artery. Innervation Pronator quadratus muscle is innervated by the anterior interosseous nerve, a branch of the median nerve. Function When pronator quadratus contracts, it pulls the lateral Lateral is a geometric term of location which may als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radial Collateral Artery
The radial collateral artery (another term for the anterior descending branch of the profunda brachii artery) is a branch of the deep brachial artery The deep artery of arm (also known as deep brachial artery) is a large artery of the arm which arises from the brachial artery. It descends in the arm before ending by anastomosing with the radial recurrent artery. Structure Origin The deep .... It arises in the arm proper and anastomoses with the radial recurrent artery near the elbow. See also * superior ulnar collateral artery * inferior ulnar collateral artery * medial collateral artery Additional images File:Gray413_color.png, Cross-section through the middle of upper arm. File:Slide3FFFF.JPG, Radial collateral artery External links Arteries of the upper limb {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radial Vein
In anatomy, the radial veins are paired veins that accompany the radial artery through the back of the hand and the lateral aspect of the forearm. They join the ulnar veins to form the brachial veins. They follow the same course as the radial artery In human anatomy, the radial artery is the main artery of the lateral aspect of the forearm. Structure The radial artery arises from the bifurcation of the brachial artery in the antecubital fossa. It runs distally on the anterior part of the .... Severing the radial artery can result in unconsciousness in as little as 30 seconds, and death in as little as two minutes. The Brachial artery runs along the inside of your arms. This artery is deep, but severing it will result in unconsciousness in as little as 15 seconds, and death in as little as 90 seconds. External links * Veins of the upper limb {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vein
Veins () are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and fetal circulations which carry oxygenated blood to the heart. In the systemic circulation, arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, and veins return deoxygenated blood to the heart, in the deep veins. There are three sizes of veins: large, medium, and small. Smaller veins are called venules, and the smallest the post-capillary venules are microscopic that make up the veins of the microcirculation. Veins are often closer to the skin than arteries. Veins have less smooth muscle and connective tissue and wider internal diameters than arteries. Because of their thinner walls and wider lumens they are able to expand and hold more blood. This greater capacity gives them the term of ''capacitance vessels''. At any time, nearly 70% o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulnar Artery
The ulnar artery is the main blood vessel, with oxygenated blood, of the Human Anatomical Terms#Anatomical directions, medial aspects of the forearm. It arises from the brachial artery and terminates in the superficial palmar arch, which joins with the superficial branch of the radial artery. It is palpable on the anterior and medial aspect of the wrist. Along its course, it is accompanied by a similarly named vein or veins, the ulnar vein or ulnar veins. The ulnar artery, the larger of the two terminal branches of the brachial, begins a little below the bend of the Elbow-joint, elbow in the cubital fossa, and, passing obliquely downward, reaches the ulnar side of the forearm at a point about midway between the elbow and the wrist. It then runs along the ulnar border to the wrist, crosses the transverse carpal ligament on the radial side of the pisiform bone, and immediately beyond this bone divides into two branches, which enter into the formation of the Superficial palmar a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Palmar Arch
The deep palmar arch (deep volar arch) is an arterial network found in the palm. It is usually primarily formed from the terminal part of the radial artery. The ulnar artery also contributes through an anastomosis. This is in contrast to the superficial palmar arch, which is formed predominantly by the ulnar artery. Structure The deep palmar arch is usually primarily formed from the radial artery. The ulnar artery also contributes through an anastomosis. The deep palmar arch lies upon the bases of the metacarpal bones and on the interossei of the hand. It is deep to the oblique head of the adductor pollicis muscle, the flexor tendons of the fingers, and the lumbricals of the hand. Alongside of it, but running in the opposite direction—toward the radial side of the hand—is the deep branch of the ulnar nerve. The superficial palmar arch is more distally located than the deep palmar arch. If one were to fully extend the thumb and draw a line from the distal border of the thu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adductor Pollicis
In human anatomy, the adductor pollicis muscle is a muscle in the hand that functions to Adduction, adduct the thumb. It has two heads: transverse and oblique. It is a fleshy, flat, triangular, and fan-shaped muscle deep in the Thenar eminence, thenar compartment beneath the long flexor tendons and the Lumbricals of the hand, lumbrical muscles at the center of the palm. It overlies the Metacarpus, metacarpal bones and the Palmar interossei muscles, interosseous muscles. Structure Oblique head The oblique head (Latin: ''adductor obliquus pollicis'') arises by several slips from the capitate bone, the bases of the second and third metacarpus, metacarpals, the intercarpal ligaments, and the sheath of the tendon of the flexor carpi radialis. Gray's Anatomy 1918. (See infobox) From this origin the greater number of fibers pass obliquely downward and converge to a tendon, which, uniting with the tendons of the medial portion of the flexor pollicis brevis and the transverse head of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |