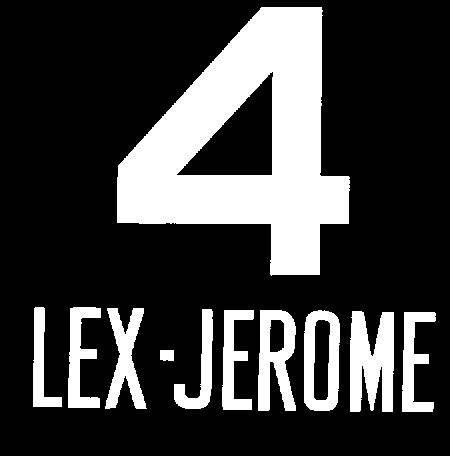|
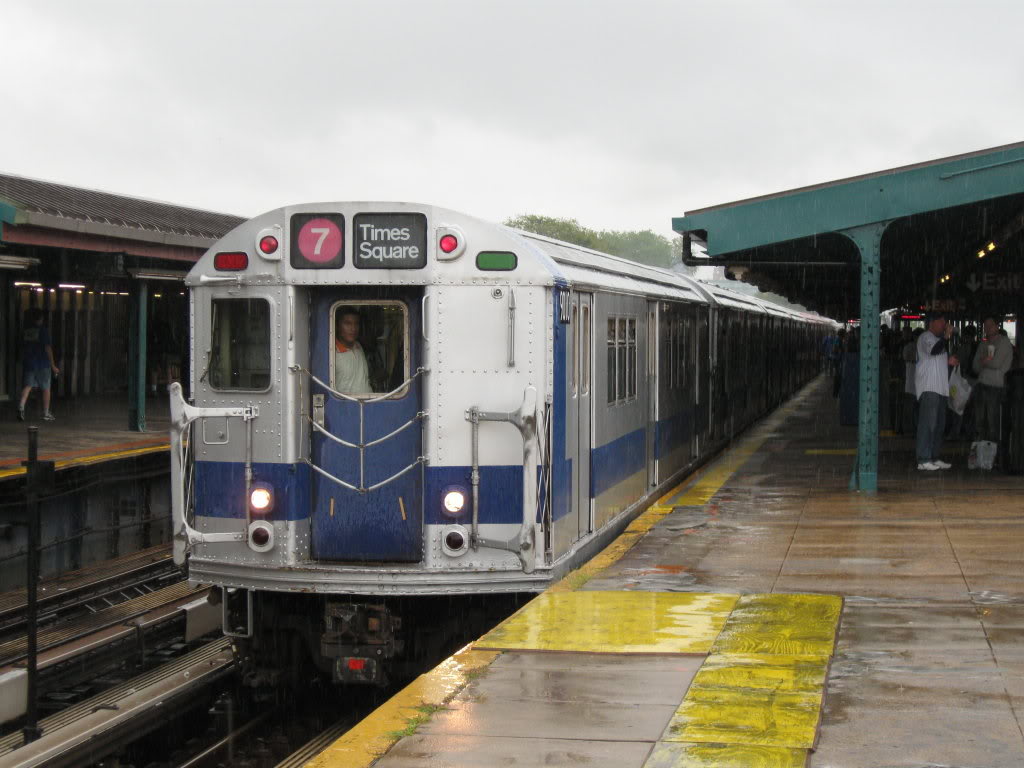
R142A (New York City Subway Car)
The R142A is the second order of New Technology Train, new technology cars (NTTs) for the A Division (New York City Subway), A Division of the New York City Subway. These cars were built by Kawasaki Heavy Industries in Kobe, Hyōgo Prefecture, Hyōgo, Japan and Lincoln, Nebraska, U.S. with final assembly performed at Yonkers, New York. Together with the R142 (New York City Subway car), R142s, they replaced the Redbird trains, including the R26 (New York City Subway car), R26, R28 (New York City Subway car), R28, R29 (New York City Subway car), R29, R33 (New York City Subway car), R33, R33S (New York City Subway car), R33S, and R36 (New York City Subway car), R36. The R142A fleet initially comprised 600 cars, arranged as five-car units. The first R142As were delivered on December 20, 1999. The cars initially experienced minor issues while undergoing testing, but entered service on July 10, 2000, as part of its 30-day revenue acceptance test. After successful completion, the cars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4 (New York City Subway Service)
The 4 Lexington Avenue Express is a rapid transit service in the A Division (New York City Subway), A Division of the New York City Subway. Its route emblem, or "bullet", is colored since it uses the IRT Lexington Avenue Line in Manhattan. The 4 operates 24 hours daily, although service patterns vary based on the time of day. Daytime service operates between Woodlawn (IRT Jerome Avenue Line), Woodlawn in the Bronx and Crown Heights–Utica Avenue (IRT Eastern Parkway Line), Utica Avenue in Crown Heights, Brooklyn, making all stops in Bronx and express stops in Manhattan and in Brooklyn; limited rush hour service, as well as overnight service, is extended beyond Utica Avenue and originates and terminates at New Lots Avenue (IRT New Lots Line), New Lots Avenue in East New York, Brooklyn. During rush hours in the peak direction, the 4 skips 138th Street–Grand Concourse (IRT Jerome Avenue Line), 138th Street–Grand Concourse. Overnight service makes all stops along the full rout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contact Shoe
A current collector (often called a "pickup") is a device used in trolleybuses, trams, electric locomotives and Electric multiple unit, EMUs to carry electric power (Electric current, current) from overhead lines, electric third rails, or ground-level power supply, ground-level power supplies to the electrical equipment of the vehicles. Those for overhead wires are roof-mounted devices, those for rails are mounted on the bogies. Typically, electric current connectors have one or more spring-loaded arms that press a collector or contact shoe against the rail or overhead wire. As the vehicle moves, the contact shoe slides along the wire or rail to draw the electricity needed to run the vehicle's motor. The current collector arms are electrical conductivity, electrically conductive but mounted Electrical insulation, insulated on the vehicle's roof, side or base. An insulated cable connects the collector with the switch, transformer or Electric motor, motor. The Rail profile, stee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communications-based Train Control
Communications-based train control (CBTC) is a railway signaling system that uses telecommunications between the train and track equipment for traffic management and infrastructure control. CBTC allows a train's position to be known more accurately than with traditional signaling systems. This can make railway traffic management safer and more efficient. Rapid transit systems (and other railway systems) are able to reduce headways while maintaining or even improving safety. A CBTC system is a "continuous, automatic train control system utilizing high-resolution train location determination, independent from track circuits; continuous, high-capacity, bidirectional train-to-wayside data communications; and trainborne and wayside processors capable of implementing automatic train protection (ATP) functions, as well as optional automatic train operation (ATO) and automatic train supervision (ATS) functions," as defined in the IEEE 1474 standard.1474.1–1999 – IEEE Standard fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IRT Lexington Avenue Line
The IRT Lexington Avenue Line (also known as the IRT East Side Line and the IRT Lexington–Fourth Avenue Line) is one of the lines of the A Division (New York City Subway), A Division of the New York City Subway, stretching from Lower Manhattan north to 125th Street (IRT Lexington Avenue Line), 125th Street in East Harlem, Manhattan, East Harlem. The line is served by the . The line was constructed in two main portions by the Interborough Rapid Transit Company (IRT), a private operator. The first portion, from City Hall (IRT Lexington Avenue Line), City Hall north to 42nd Street, was opened between 1904 and 1908, and is part of the Early history of the IRT subway, first subway line in the city. The original subway turned west across 42nd Street Shuttle, 42nd Street at the Grand Central–42nd Street (IRT 42nd Street Shuttle), Grand Central station, then went north at Broadway (Manhattan), Broadway, serving the present-day IRT Broadway–Seventh Avenue Line. The second portion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R33S (New York City Subway Car)
The R33S (also known as R33 World's Fair or R33WF) was a New York City Subway car that was built by St. Louis Car Company in 1963 for the IRT A Division. They were purchased for service on the IRT Flushing Line ( 7 and trains), which was the closest line to the 1964 New York World's Fair. A total of 40 cars were built, arranged as single cars. While in regular service, each R33S was coupled to five two-car consists of R36 cars to make 11-car trains for the 7 and routes. The R33S fleet entered service on September 26, 1963, and was originally painted in a light blue turquoise "Bluebird" scheme. The fleet was overhauled in the mid-1980s, during which the cars were painted red, leading to the nickname " Redbirds". The R33S fleet was replaced in the early 2000s with the delivery of the R142 and R142A cars, with the last train of R33S and R36s running on November 3, 2003. After being retired, some R33S cars were preserved, but most were kept for work service; many of the wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R33 (New York City Subway Car)
The R33 was a New York City Subway car model that was built by St. Louis Car Company in 1962 and 1963. The cars are a "follow-up" or supplemental stock for the A Division (New York City Subway), A Division's R29/R99 (New York City Subway car), R29s and closely resemble them. The cars were also referred to as R33MLs (R33 Main Line) to distinguish them from the R33S (New York City Subway car), R33Ss. A total of 500 cars were built, numbered 8806–9305, and arranged in pairs. The R33s entered service on November 15, 1962, and were the first A Division (New York City Subway), A Division fleet to be retrofitted with air conditioning, being retrofitted between 1972 and 1982. The R33 fleet was overhauled between 1986 and 1991. The R33s were replaced in the early 2000s with the delivery of the R142 (New York City Subway car), R142 and R142A (New York City Subway car), R142A cars, with the last train running on April 20, 2003. After being retired, most R33s were sunk into the ocean as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R29 (New York City Subway Car)
The R29 was a New York City Subway car model built by the St. Louis Car Company in 1962 for the IRT A Division. A total of 236 cars were built, arranged in married pairs. The R29s entered service on April 28, 1962, and received air conditioning by 1982. The fleet was rebuilt by Morrison–Knudsen between 1985 and 1987. The R29s were replaced in 2001 and 2002 with the delivery of the R142 and R142A cars, with the last train running on October 24, 2002. After being retired, most R29s were sunk into the ocean as artificial reefs, but two cars have survived. Description The R29s were numbered 8570–8805. Between 1985 and 1987, the R29s were overhauled under contract ''R99''. Therefore, the cars are also known as R99s in their post-overhaul state. The R29s are very similar to appearance to the R26s and R28s, with the exceptions that they were built by a different company and permanently paired with link bars (instead of couplers). The R29s were split into two sub groups: * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R28 (New York City Subway Car)
The R28 was a New York City Subway car model built by American Car and Foundry (ACF) from 1960 to 1961. The cars were a "follow-up" or supplemental stock for the A Division's R26s and closely resemble them. The average car cost per R28 was $114,495. A total of 100 cars were built, arranged in married pairs. The R28s entered service in late-1960 and received air conditioning by 1982. The fleet was rebuilt by Morrison–Knudsen between 1985 and 1987. The R28s were replaced in 2001 and 2002 with the delivery of the R142 and R142A cars with the last train running on October 7, 2002. After being retired, most R28s were sunk into the ocean as artificial reefs, but four cars have survived. Description The R28s were numbered 7860–7959. They were the second order of cars not to be built with operating cabs at both ends after the R26s. They were also the last passenger cars built by ACF, with the closure of the Berwick assembly plant following the delivery of the final cars delive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R142 (New York City Subway Car)
The R142 is the first mass-produced model class of the newest generation or new technology (NTT) A Division cars for the New York City Subway. It was built by Bombardier Transportation in La Pocatière, Quebec, Canada and Barre, Vermont, U.S. with final assembly performed at Plattsburgh, New York, from 1999 to 2003. There are 880 cars numbered 6301–7180 and another 150 cars numbered 1101–1250, for a total of 1,030 cars, all arranged as five-car sets. Together with the R142As, they replaced the Redbird trains, including the R26, R28, R29, R33, R33S, and R36. The R142s and R142As are the first New York City Subway cars to feature recorded announcements. The first R142s were delivered on November 16, 1999, though they initially experienced minor issues that were reported while undergoing testing. Following the completion of non-revenue service testing, the R142s were placed into revenue service on July 10, 2000 as part of its 30-day revenue acceptance test. After ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kawasaki Heavy Industries
is a Japanese Public company, public multinational corporation manufacturer of motorcycles, engines, Heavy equipment (construction), heavy equipment, aerospace and Military, defense equipment, rolling stock and ships, headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Minato, Tokyo, Japan. It is also active in the production of industrial robots, gas turbines, pumps, boilers and other industrial products. The company is named after its founder, Kawasaki Shōzō, Shōzō Kawasaki. KHI is known as one of the three major heavy industrial manufacturers of Japan, alongside Mitsubishi Heavy Industries and IHI Corporation, IHI. Prior to the World War II, Second World War, KHI was part of the Kobe Kawasaki ''zaibatsu'', which included JFE Holdings, Kawasaki Steel and K Line, Kawasaki Kisen. After the conflict, KHI became part of the DKB Group (''keiretsu''). History Kawasaki Shōzō, Shōzō Kawasaki, born in 1836, was involved with the marine industry from a young age. He was involved with two offshore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Division (New York City Subway)
The A Division, also known as the IRT Division, is a division of the New York City Subway, consisting of the lines operated with services designated by numbers ( 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7) and the 42nd Street Shuttle. These lines and services were operated by the Interborough Rapid Transit Company before the 1940 city takeover. A Division cars are narrower, shorter, and lighter than those of the B Division, measuring . List of lines The following lines are part of the A Division (services shown in parentheses; lines with colors next to them are trunk lines): * IRT 42nd Street Shuttle () * IRT Broadway–Seventh Avenue Line () * IRT Dyre Avenue Line () *IRT Eastern Parkway Line () * IRT Flushing Line () * IRT Jerome Avenue Line () * IRT Lenox Avenue Line () * IRT Lexington Avenue Line () * IRT New Lots Line () *IRT Nostrand Avenue Line () *IRT Pelham Line () * IRT White Plains Road Line () Service history Numbers were assigned to subway services in 1948: The 42nd Street Sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Train Stop
Part of a railway signalling system, a train stop, trip stop or tripcock (sometimes called a tripper) is a train protection device that automatically stops a train if it attempts to pass a signal when the signal aspect and operating rules prohibit such movement, or (in some applications) if it attempts to pass at an excessive speed. Basic operation The train stop system comprises two basic components. One is the trip arm mechanism, mounted on the ground adjacent to the rail, which essentially consists of a spring-loaded arm connected to an electric motor (or pneumatic cylinder in electro-pneumatic systems). The other is the train-mounted trip cock, which is connected either directly or electrically to the train's braking system. The trip arm is raised automatically whenever a train should be brought to a halt. When the signalling system determines it is safe for the train to proceed, the motor drives the trip arm down to the lowered position. The spring ensures that th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |