|
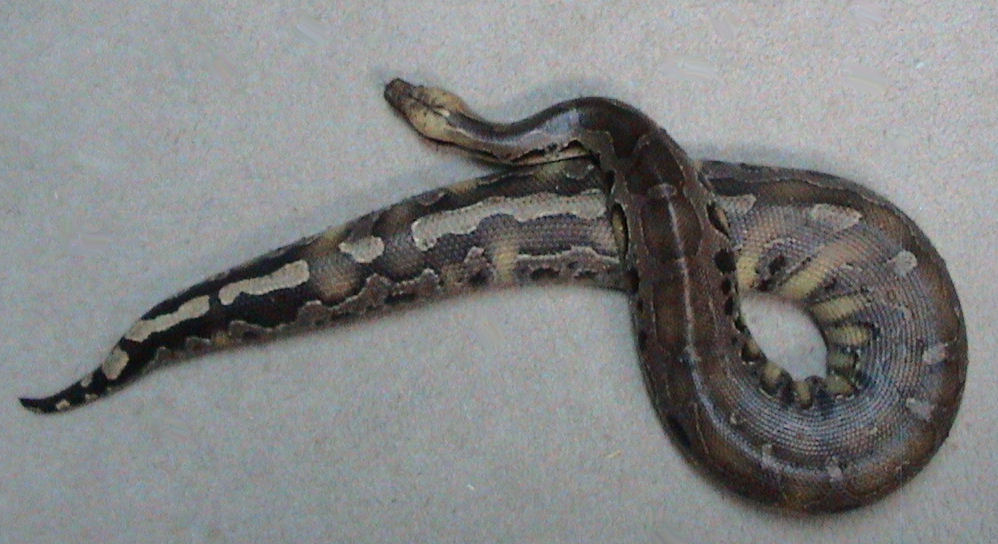
Python Curtus
The Sumatran short-tailed python (''Python curtus''), also called the Sumatra python, is a species of the family Pythonidae, a nonvenomous snake native to Sumatra. Taxonomy ''Python curtus'' was the scientific name proposed by Hermann Schlegel in 1872 for a python with a short tail from Sumatra. The Type locality (biology), type locality is Sumatra.McDiarmid, R. W., Campbell, J. A., Touré, T. 1999. Snake Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference, vol. 1. Herpetologists' League. 511 pp. (series). (volume). ''Python brongersmai'' and ''Python breitensteini, P. breitensteini'' were often considered the same species as ''P. curtus'' until confirmed distinct around 2000. Description The Sumatran short-tailed python has narrow subocular Scale (anatomy), scales between the bottom of the eye and the top of the labial scales. The parietal scales do not join each other. ''P. curtus'' and ''Python breitensteini, P. breitensteini'' can be distinguished by the frontal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermann Schlegel
Hermann Schlegel (10 June 1804 – 17 January 1884) was a German ornithologist, herpetologist and ichthyologist. Early life and education Schlegel was born at Altenburg, the son of a brassfounder. His father collected butterflies, which stimulated Schlegel's interest in natural history. The discovery, by chance, of a buzzard's nest led him to the study of birds, and a meeting with Christian Ludwig Brehm. Schlegel started to work for his father, but soon tired of it. He travelled to Vienna in 1824, where, at the university, he attended the lectures of Leopold Fitzinger and Johann Jacob Heckel. A letter of introduction from Brehm to Joseph Natterer gained him a position at the Naturhistorisches Museum. Ornithological career One year after his arrival, the director of this natural history museum, Carl Franz Anton Ritter von Schreibers, recommended him to Coenraad Jacob Temminck, director of the Rijksmuseum van Natuurlijke Historie, natural history museum of Leiden, who was seeking an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
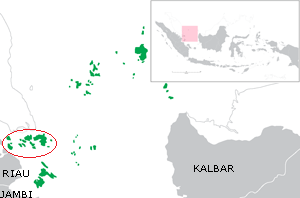
Lingga Islands
The Lingga Regency () is a group of 600 islands in Indonesia, located south of Singapore and along both sides of the equator, off the eastern coast of Riau Province on Sumatra island. They are due south of the populated Riau Archipelago, known for the industrial island of Batam and the tourist-frequented island of Bintan, although the Lingga Islands themselves are rarely visited due to the infrequent local transportation. The equator goes through the northern tip of Lingga Island, the main island in the archipelago. Administratively they form a Regencies of Indonesia, Regency of the Riau Islands Province with a land area of 2,250.45 km2 and a population of 86,244 people at the 2010 census and 98,633 at the 2020 census;Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2021. the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 102,474.Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 26 September 2024, ''Kabupaten Lingga Dalam Angka 2024'' (summation of Katalog reports on individual districts as specified in the reference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptiles Of Indonesia
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocephalia. About 12,000 living species of reptiles are listed in the Reptile Database. The study of the traditional reptile orders, customarily in combination with the study of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. Reptiles have been subject to several conflicting taxonomic definitions. In Linnaean taxonomy, reptiles are gathered together under the class Reptilia ( ), which corresponds to common usage. Modern cladistic taxonomy regards that group as paraphyletic, since genetic and paleontological evidence has determined that birds (class Aves), as members of Dinosauria, are more closely related to living crocodilians than to other reptiles, and are thus nested among reptiles from an evolutionary perspective. Many cladistic systems therefore redefine Reptilia as a clade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Python (genus)
''Python'' is a genus of constricting snakes in the Pythonidae family native to the tropics and subtropics of the Eastern Hemisphere. The name ''python'' was proposed by François Marie Daudin in 1803 for non-venomous flecked snakes. Currently, 10 python species are recognized as valid taxa. Three formerly considered python subspecies have been promoted, and a new species recognized. Taxonomy The generic name ''Python'' was proposed by François Marie Daudin in 1803 for non-venomous snakes with a flecked skin and a long split tongue. In 1993, seven python species were recognized as valid taxa. On the basis of phylogenetic analyses, between seven and 13 python species are recognized. Distribution and habitat In Africa, pythons are native to the tropics south of the Sahara, but not in the extreme south-western tip of southern Africa (Western Cape) or in Madagascar. In Asia, they occur from Bangladesh, Nepal, India, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka, including the Nicobar Islands, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
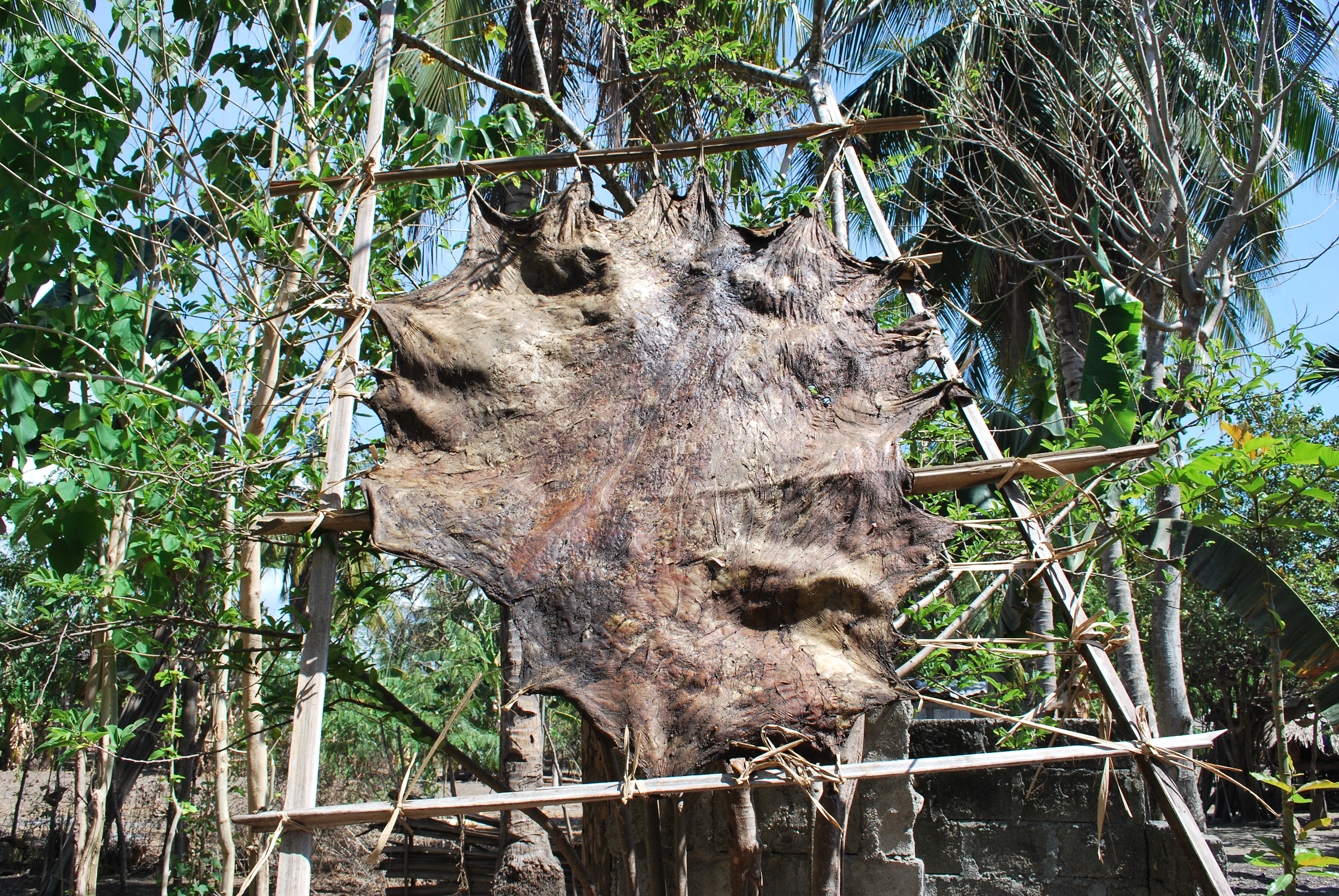
Leather
Leather is a strong, flexible and durable material obtained from the tanning (leather), tanning, or chemical treatment, of animal skins and hides to prevent decay. The most common leathers come from cattle, sheep, goats, equine animals, buffalo, pigs and hogs, ostriches, and aquatic animals such as seals and alligators. Leather can be used to make a variety of items, including clothing, footwear, handbags, furniture, tools and sports equipment, and lasts for decades. Leather making has been practiced for more than 7,000 years and the leading producers of leather today are China and India. Critics of tanneries claim that they engage in unsustainable practices that pose health hazards to the people and the environment near them. Production processes The leather manufacturing process is divided into three fundamental subprocesses: preparatory stages, tanning, and crusting. A further subprocess, finishing, can be added into the leather process sequence, but not all leathers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oviparous
Oviparous animals are animals that reproduce by depositing fertilized zygotes outside the body (i.e., by laying or spawning) in metabolically independent incubation organs known as eggs, which nurture the embryo into moving offsprings known as hatchlings with little or no embryonic development within the mother. This is the reproductive method used by most animal species, as opposed to viviparous animals that develop the embryos internally and metabolically dependent on the maternal circulation, until the mother gives birth to live juveniles. Ovoviviparity is a special form of oviparity where the eggs are retained inside the mother (but still metabolically independent), and are carried internally until they hatch and eventually emerge outside as well-developed juveniles similar to viviparous animals. Modes of reproduction The traditional modes of reproduction include oviparity, taken to be the ancestral condition, traditionally where either unfertilised oocytes or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marsh
In ecology, a marsh is a wetland that is dominated by herbaceous plants rather than by woody plants.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p More in general, the word can be used for any low-lying and seasonally waterlogged terrain. In Europe and in agricultural literature low-lying meadows that require draining and embanked polderlands are also referred to as marshes or marshland. Marshes can often be found at the edges of lakes and streams, where they form a transition between the aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems. They are often dominated by grasses, rushes or reeds. If woody plants are present they tend to be low-growing shrubs, and the marsh is sometimes called a carr. This form of vegetation is what differentiates marshes from other types of wetland such as swamps, which are dominated by trees, and mires, which are wetlands that have accumulated deposits of acidic peat. Marshes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rainforest
Rainforests are forests characterized by a closed and continuous tree Canopy (biology), canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforests can be generally classified as tropical rainforests or temperate rainforests, but other types have been described. Estimates vary from 40% to 75% of all biotic community, biotic species being Indigenous (ecology), indigenous to the rainforests. There may be many millions of species of plants, insects and microorganisms still undiscovered in tropical rainforests. Tropical rainforests have been called the "jewels of the Earth" and the "medicine chest (idiom), world's largest pharmacy", because over one quarter of natural medicines have been discovered there. Rainforests as well as endemic rainforest species are rapidly disappearing due to #Deforestation, deforestation, the resulting habitat loss and air pollution, pollution of the atmosphere. Definition Rainforests are cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalimantan
Kalimantan (; ) is the Indonesian portion of the island of Borneo. It constitutes 73% of the island's area, and consists of the provinces of Central Kalimantan, East Kalimantan, North Kalimantan, South Kalimantan, and West Kalimantan. The non-Indonesian parts of Borneo are Brunei and East Malaysia. In Indonesia the whole island of Borneo is also called "Kalimantan". In 2019, President of Indonesia Joko Widodo proposed that Capital of Indonesia, Indonesia's capital be moved to Kalimantan. The People's Consultative Assembly approved the Law on State Capital in January 2022. The future capital, Nusantara (city), Nusantara, is a planned city that will be carved out of East Kalimantan. A government official said construction is expected to be fully complete by 2045, but the unfinished capital officially celebrated Indonesian Independence Day for the first time and it was scheduled to be inaugurated as the capital city on 17 August 2024, but the move did not take place due to delays of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mentawai Islands
Mentawai may refer to: * Mentawai Islands, Indonesia ** Mentawai Strait ** Mentawai people, ethnic group of Indonesia ** Mentawai language, their Austronesian language {{dab Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bangka Island
Bangka is an island lying east of Sumatra, Indonesia. It is administered under the province of the Bangka Belitung Islands, being one of its namesakes alongside the smaller island of Belitung across the Gaspar Strait. The 9th largest island in Indonesia, it had a population of 1,146,581 at the 2020 census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 1,191,300.Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 28 February 2024, ''Provinsi Kepulauan Bangka Belitung Dalam Angka 2024'' (Katalog-BPS 1102001.19) It is the location of the provincial capital of Pangkal Pinang, and is administratively divided into four regencies and a city. The island itself and the surrounding sea suffers considerable environmental damage from its thriving tin mining industry which operates on- and offshore. Geography Bangka is the largest landmass of the province of the Bangka Belitung Islands. It lies just east of Sumatra, separated by the Bangka Strait; to the north lies the South China Sea, to the east, across the Ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riau Archipelago
The Riau Archipelago is a ''geographic'' term (as opposed to administrative region) for the core group of islands within the Riau Islands Province in Indonesia, and located south of Singapore and east of Riau on Sumatra. Before the province of Riau Islands was formed, there was no ambiguity in term; however, in Indonesian language, both the archipelago and administrative province are referred to simply as "Kepulauan Riau". The province may have the word "Provinsi" preceding it for clarity. Additionally, the term BBK for ''Batam Bintan Karimun'' may refer to the archipelago. History The name of this archipelago predates the creation of the Indonesian province, and historically did not include the Lingga Islands or Natuna Islands, which now belong to that province. On the other hand, Singapore was considered a part of the islands, at least in the Islamic eras. Srivijaya and Jambi From 650 CE–1377 CE are accepted dates for the Srivijaya empire, when the area seemed to be well wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |