|
Pulse Diagnosis
Pulse diagnosis is a diagnostic technique used in Ayurveda, traditional Chinese medicine, traditional Mongolian medicine, Siddha medicine, traditional Tibetan medicine, and Unani. Pulse diagnosis is ill-defined and subjective. Traditional Indian medicine (Ayurveda and Siddha-Veda) In Ayurveda, advocates claim that by taking a pulse examination, imbalances in the three Doshas ( Vata, Pitta, and Kapha) can be diagnosed. The ayurvedic pulse also claims to determine the balance of prana, tejas, and ojas.Peter Koch, December 1, 2012Ayurvedische Pulsdiagnose/ref> Ayurvedic pulse measurement is done by placing index, middle and ring finger on the wrist. The index finger is placed below the wrist bone on the thumb side of the hand (radial styloid). This index finger represents the Vata dosha. The middle finger and ring finger are placed next to the index finger and represents consequently the Pitta and Kapha doshas of the patient. Pulse can be measured in the superficial, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physician Taking Pulse
A physician, medical practitioner (British English), medical doctor, or simply doctor is a health professional who practices medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring health through the Medical education, study, Medical diagnosis, diagnosis, prognosis and therapy, treatment of disease, injury, and other physical and mental impairments. Physicians may focus their practice on certain disease categories, types of patients, and methods of treatment—known as Specialty (medicine), specialities—or they may assume responsibility for the provision of continuing and comprehensive medical care to individuals, families, and communities—known as general practitioner, general practice. Medical practice properly requires both a detailed knowledge of the Discipline (academia), academic disciplines, such as anatomy and physiology, pathophysiology, underlying diseases, and their treatment, which is the science of medicine, and a decent Competence (human resources ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kapha
Ayurveda (; ) is an alternative medicine system with historical roots in the Indian subcontinent. It is heavily practised throughout India and Nepal, where as much as 80% of the population report using ayurveda. The theory and practice of ayurveda is pseudoscientific and toxic metals including lead and Mercury (element), mercury are used as ingredients in many ayurvedic medicines. Ayurveda therapies have varied and evolved over more than two millennia. Therapies include herbal medicines, Dieting#Detox, special diets, Meditation#Hinduism, meditation, yoga, massage, Laxative#Historical and health fraud uses, laxatives, Enema#Alternative medicine, enemas, and medical oils. Ayurvedic preparations are typically based on complex herbal compounds, minerals, and metal substances (perhaps under the influence of early Indian alchemy or ''rasashastra''). Ancient ayurveda texts also taught surgical techniques, including rhinoplasty, lithotomy, sutures, cataract surgery, and the extraction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Canon Of Medicine
''The Canon of Medicine'' () is an encyclopedia of medicine in five books compiled by Avicenna (, ibn Sina) and completed in 1025. It is among the most influential works of its time. It presents an overview of the contemporary medical knowledge of the Islamic world, which had been influenced by earlier traditions including Greco-Roman medicine (particularly Galen), Persian medicine, Chinese medicine and Indian medicine. Its translation from Arabic to Latin in 12th century Toledo greatly influenced the development of medieval medicine. It became the standard textbook for teaching in European universities into the early modern period. ''The Canon of Medicine'' remained a medical authority for centuries. It set the standards for medicine in medieval Europe and the Islamic world and was used as a standard medical textbook through the 18th century in Europe. It is an important text in Unani medicine, a form of traditional medicine practiced in India. Title The English title ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medicine In The Medieval Islamic World
In the history of medicine, "Islamic medicine", also known as "Arabian medicine" is the Science in the medieval Islamic world, science of medicine developed in the Middle East, and usually written in Arabic language, Arabic, the ''lingua franca'' of Islamic civilization. Islamic medicine adopted, systematized and developed the medical knowledge of classical antiquity, including the major traditions of Hippocrates, Galen and Dioscorides. During the Post-classical history, post-classical era, Middle Eastern medicine was the most advanced in the world, integrating concepts of Ancient Greek medicine, Modern Greek, Medicine in ancient Rome, Roman, Mesopotamia#Medicine, Mesopotamian and Ancient Iranian medicine, Persian medicine as well as the ancient Indian tradition of Ayurveda, while making numerous advances and innovations. Islamic medicine, along with knowledge of Classical antiquity, classical medicine, was later adopted in the medieval medicine of Western Europe, after European ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doctor Taking Woman's Pulse
Doctor, Doctors, The Doctor or The Doctors may refer to: Titles and occupations * Physician, a medical practitioner * Doctor (title), an academic title for the holder of a doctoral-level degree ** Doctorate ** List of doctoral degrees awarded by country ** Arts and entertainment Fictional characters * The Doctor, the main character of the BBC series ''Doctor Who'' * List of fictional doctors * Doctor (comics), several fictional characters * Doctor, in the film ''My Giant'' * Doctor, in ''Black Cat'' * The Doctor, in ''Hellsing'' * The Doctor, in video game ''Cave Story'' * The Doctor (''Star Trek: Voyager'') * The Doctor, or Scalpel, in the ''Transformers'' film series * The Doctor or Cobra Commander,in ''G.I. Joe: A Real American Hero'' * The Doctor, in ''Little Nightmares II'' * Minoru Kamiya, also known as Doctor, in ''YuYu Hakusho'' Film * ''Doctor'' (film series), British comedy films of the 1950s–1960s * ''Doctor'' (1963 film), an Indian Malayalam-language fil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Jiao
San Jiao ("triple burner", or "triple energizer", or "triple heater") is a concept in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) and acupuncture. It is the sixth organ of Fu, which is the hollow space inside the trunk of the body. In TCM, there are five solid organs and each solid organ has its counterpart in a hollow organ. For instance, the heart is considered a solid organ, and the small intestine its hollow counterpart, or Fu organ. San Jiao is believed to be a body cavity of some kind which has the ability to influence other organs, and overall health, mainly through the free movement of Qi, the fundamental energy or life force on the microcosm and on the macrocosm it is associated with the interactions between The Heavens, humans and earth. San Jiao means "triple burner". The upper burner relates to organs the Heart, lungs in the thorax and the breathing function therefore relates to Heaven. The middle burner relates to the organs top of the stomach, the spleen, liver and the dig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wuxing (Chinese Philosophy)
( zh, c=五行, p=wǔxíng), usually translated as Five Phases or Five Agents, is a fivefold conceptual scheme used in many traditional Chinese fields of study to explain a wide array of phenomena, including terrestrial and celestial relationships, influences, and cycles, that characterise the interactions and relationships within Science and technology in China, science, Traditional Chinese medicine, medicine, Confucianism, politics, Taoism, religion and social relationships and education within Chinese culture. The five agents are traditionally associated with the classical planets Mars, Mercury (planet), Mercury, Jupiter, Venus, Saturn as depicted in the #Etymology, etymological section below. In ancient Chinese astronomy and Chinese astrology, astrology, that spread throughout East Asia, was a reflection of the seven-day planetary order of Fire (wuxing), Fire, Water (wuxing), Water, Wood (wuxing), Wood, Metal (wuxing), Metal, Earth (wuxing), Earth.), they are Wood, Fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eight Principles
The eight principles are a core concept of traditional Chinese medicine based on Confucianism. The identification and differentiation of syndromes according to the eight principles is one of the earliest examples of critical and deductive thinking for diagnosis.The Foundations of Chinese Medicine by Giovanni Maciocia Chapter 18 Identification of Patterns according to the Eight Principles Pages 179-189. The eight principles are: * Exterior and interior ( zh, t=裡表, s=里表, p=lǐ biǎo) * Cold and hot ( zh, t=寒熱, s=寒热, p=hán rè) * Empty and full ( zh, t=虛實, s=虛实, p=xū shí) * Yin and yang ( zh, t=陰陽, s=阴阳, p=yīn yáng) Exterior and interior Sometimes referred to as external and internal, this differentiation is not made on the basis of etiology (cause) of disease but location. It can also give an indication of the direction the illness is taking, becoming more external or going deeper into the body. Exterior affects the skin, muscles and jinglu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doshas
''Dosha'' (, IAST: ''doṣa'') is a central term in ayurveda originating from Sanskrit, and which refers to three categories or types of substances that are believed to be present conceptually in a person's body and mind. These Dosha are assigned specific qualities and functions. These qualities and functions are affected by external and internal stimuli received by the body. Beginning with twentieth-century ayurvedic literature, the "three-''dosha'' theory" (, ) has described how the quantities and qualities of three fundamental types of substances called wind, bile, and phlegm (, , ; , , ) fluctuate in the body according to the seasons, time of day, process of digestion, and several other factors and thereby determine changing conditions of growth, aging, health, and disease. ''Dosha''s are considered to shape the physical body according to a natural constitution established at birth, determined by the constitutions of the parents as well as the time of conception and othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
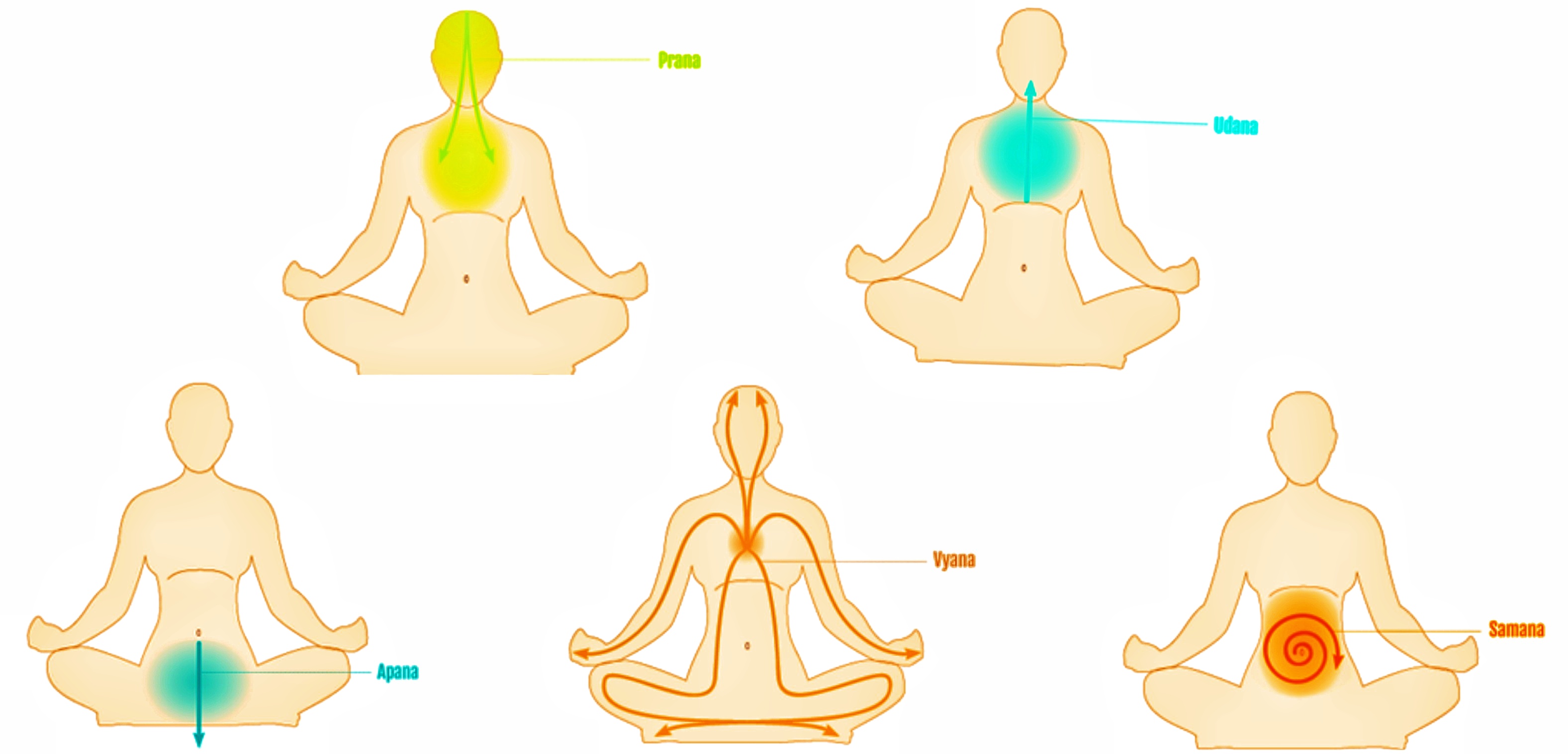
Prana
In yoga, Ayurveda, and Indian martial arts, prana (, ; the Sanskrit word for breath, " life force", or "vital principle") permeates reality on all levels including inanimate objects. In Hindu literature, prāṇa is sometimes described as originating from the Sun and connecting the elements. Five types of prāṇa, collectively known as the five '' vāyus'' ("winds"), are described in Hindu texts. Ayurveda, tantra and Tibetan medicine all describe ''prāṇa vāyu'' as the basic vāyu from which the other vāyus arise. Prana is divided into ten main functions: The five Pranas – Prana, Apana, Udana, Vyana and Samana – and the five Upa-Pranas – Naga, Kurma, Devadatta, Krikala and Dhananjaya. Pranayama, one of the eight limbs of yoga, is intended to expand conscious awareness of prana. Etymology V.S. Apte provides fourteen different meanings for the Sanskrit word ' () including breath or respiration; the breath of life, vital air, principle of life (usually plural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vata (Ayurveda)
Ayurveda (; ) is an alternative medicine system with historical roots in the Indian subcontinent. It is heavily practised throughout India and Nepal, where as much as 80% of the population report using ayurveda. The theory and practice of ayurveda is pseudoscientific and toxic metals including lead and mercury are used as ingredients in many ayurvedic medicines. Ayurveda therapies have varied and evolved over more than two millennia. Therapies include herbal medicines, special diets, meditation, yoga, massage, laxatives, enemas, and medical oils. Ayurvedic preparations are typically based on complex herbal compounds, minerals, and metal substances (perhaps under the influence of early Indian alchemy or ''rasashastra''). Ancient ayurveda texts also taught surgical techniques, including rhinoplasty, lithotomy, sutures, cataract surgery, and the extraction of foreign objects. Historical evidence for ayurvedic texts, terminology and concepts appears from the middle of the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |