|
Public Holidays In Serbia ...
The public holidays in Serbia are defined by the Law of national and other holidays in the Republic of Serbia. Public holidays 1 If one of the non-religious holidays falls on a Sunday, then the next working day is a non-working day. Religious holidays Additionally, the employees of Christian, Muslim and Jewish religion are allowed not to work on some of their religious holidays. Working holidays Some holidays are defined by the law as working holidays, hence they are not bank holidays, but they are observed by the state and people. See also * Public holidays in Yugoslavia References * {{DEFAULTSORT:Public Holidays In Serbia Serbia Holidays A holiday is a day or other period of time set aside for festivals or recreation. ''Public holidays'' are set by public authorities and vary by state or region. Religious holidays are set by religious organisations for their members and are often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serbia
, image_flag = Flag of Serbia.svg , national_motto = , image_coat = Coat of arms of Serbia.svg , national_anthem = () , image_map = , map_caption = Location of Serbia (green) and the claimed but uncontrolled territory of Kosovo (light green) in Europe (dark grey) , image_map2 = , capital = Belgrade , coordinates = , largest_city = capital , official_languages = Serbian language, Serbian , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = 2022 , religion = , religion_year = 2022 , demonym = Serbs, Serbian , government_type = Unitary parliamentary republic , leader_title1 = President of Serbia, President , leader_name1 = Aleksandar Vučić , leader_title2 = Prime Minister of Serbia, Prime Minister , leader_name2 = Đuro Macut , leader_title3 = Pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labour Day
Labour Day is an annual day of celebration of the labour movement and its labor rights, achievements. It has its origins in the trade union, labour union movement, specifically the Eight-hour day movement, eight-hour day movement, which advocated eight hours for work, eight hours for recreation, and eight hours for rest. In most countries, Labour Day is synonymous with, or linked with, International Workers' Day, which happens on 1 May, originally chosen to commemorate the 1886 general strike which culminated in the Haymarket affair. For other countries, Labour Day is celebrated on a different date, often one with special significance for the labour movement in that country. Labour Day is a public holiday in many countries. International Workers' Day For most countries, "Labour Day" is synonymous with, or linked with, International Workers' Day, which occurs on 1 May. Some countries vary the actual date of their celebrations so that the holiday occurs on a Monday close to 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yom Kippur
Yom Kippur ( ; , ) is the holiest day of the year in Judaism. It occurs annually on the 10th of Tishrei, corresponding to a date in late September or early October. For traditional Jewish people, it is primarily centered on atonement and repentance. The day's main observances consist of full fasting and asceticism, both accompanied by extended prayer services (usually at synagogue) and sin confessions. Some minor Jewish denominations, such as Reconstructionist Judaism, focus less on sins and more on one's goals and accomplishments and setting yearly intentions. Alongside the related holiday of Rosh Hashanah, Yom Kippur is one of the two components of the High Holy Days of Judaism. It is also the last of the Ten Days of Repentance. Name The formal Hebrew name of the holiday is , 'day fthe atonements'. This name is used in the Bible, Mishnah, and Shulchan Aruch. The word 'atonement' is one of many Biblical Hebrew words which, while using a grammatical plural form, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tishrei
Tishrei () or Tishri (; ''tīšrē'' or ''tīšrī''; from Akkadian ''tašrītu'' "beginning", from ''šurrû'' "to begin") is the first month of the civil year (which starts on 1 Tishrei) and the seventh month of the ecclesiastical year (which starts on 1 Nisan) in the Hebrew calendar. The name of the month is Babylonian. It is a month of 30 days. Tishrei usually occurs in September–October on the Gregorian calendar. In the Hebrew Bible the month is called Ethanim ( – ), or simply the seventh month. In the Babylonian calendar the month is known as Araḫ Tišritum, "Month of Beginning" (of the second half-year). Edwin R. Thiele has concluded, in '' The Mysterious Numbers of the Hebrew Kings'', that the ancient Kingdom of Judah counted years using the civil year starting in Tishrei, while the Kingdom of Israel counted years using the ecclesiastical new year starting in Nisan. Tishrei is the month used for the counting of the epoch year – i.e., the count of the year i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judaism
Judaism () is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic, Monotheism, monotheistic, ethnic religion that comprises the collective spiritual, cultural, and legal traditions of the Jews, Jewish people. Religious Jews regard Judaism as their means of observing the Mosaic covenant, which they believe was established between God in Judaism, God and the Jewish people. The religion is considered one of the earliest monotheistic religions. Jewish religious doctrine encompasses a wide body of texts, practices, theological positions, and forms of organization. Among Judaism's core texts is the Torah—the first five books of the Hebrew Bible—and a collection of ancient Hebrew scriptures. The Tanakh, known in English as the Hebrew Bible, has the same books as Protestant Christianity's Old Testament, with some differences in order and content. In addition to the original written scripture, the supplemental Oral Torah is represented by later texts, such as the Midrash and the Talmud. The Hebrew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eid Al-Adha
Eid al-Adha () is the second of the two main festivals in Islam alongside Eid al-Fitr. It falls on the 10th of Dhu al-Hijja, the twelfth and final month of the Islamic calendar. Celebrations and observances are generally carried forward to the three following days, known as the Tashreeq days. Eid al-Adha, depending on country and language is also called the Greater or Large Eid (). As with Eid al-Fitr, the Eid prayer is performed on the morning of Eid al-Adha, after which the '' udhiyah'' or the ritual sacrifice of a livestock animal, is performed. In Islamic tradition, it honours the willingness of Abraham to sacrifice his son as an act of obedience to God's command. Depending on the narrative, either Ishmael or Isaac are referred to with the honorific title "''Sacrifice of God''". Pilgrims performing the Hajj typically perform the tawaf and saee of Hajj on Eid al-Adha, along with the ritual stoning of the Devil on the Eid day and the following days. Etymology The Arabic w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dhu Al-Hijjah
Dhu al-Hijjah (also Dhu al-Hijja ) is the twelfth and final month in the Islamic calendar. Being one of the four sacred months during which war is forbidden, it is the month in which the '' Ḥajj'' () takes place as well as Eid al-Adha (). The Arabic name of the month, ''Dhu al-Hijjah'', means "Possessor of the Pilgrimage" or "The Month of the Pilgrimage". During this month, Muslim pilgrims from all around the world congregate at Mecca to visit the Kaaba. The Hajj rites begin on the eighth day and continue for four or five days. The Day of Arafah takes place on the ninth of the month. Eid al-Adha, the "Festival of the Sacrifice", begins on the tenth day and ends on the thirteenth day. The name of this month is also spelled Dhul-Hijja. In modern Turkish, the name is Zilhicce. Timing The Islamic calendar is a lunar calendar, and months begin when new moon is sighted. Since the Islamic lunar calendar year is 11 to 12 days shorter than the solar year, Dhu al-Hijjah migr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eid Al-Fitr
Eid al-Fitr () is the first of the two main Islamic holidays, festivals in Islam, the other being Eid al-Adha. It falls on the first day of Shawwal, the tenth month of the Islamic calendar. Eid al-Fitr is celebrated by Muslims worldwide because it marks the end of the Fasting in Islam, month-long dawn-to-dusk fasting (''sawm'') of Ramadan. The holiday is known under various other names in different languages and countries around the world. Eid al-Fitr has a particular that consists of two generally performed in an open field or large hall. It may only be performed in congregation () and features six additional (raising of the hands to the ears whilst reciting the Takbir, saying "Allāhu ʾAkbar", meaning "God is the greatest"). In the Hanafi school of Sunni Islam, there are three at the start of the first and three just before in the second . Other Sunni schools usually have 12 , similarly split in groups of seven and five. In Shia Islam, the has six in the first at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shawwal
Shawwal () is the tenth month of the Islamic calendar. It comes after Ramadan and before Dhu al-Qa'da. ''Shawwāl'' stems from the Arabic verb ''shāla'' (), which means to 'lift or carry', generally to take or move things from one place to another. Fasting during Shawwāl The first day of Shawwāl is Eid al-Fitr; fasting is prohibited. Some Muslims observe six days of optional fasting during Shawwāl beginning the day after Eid al-Fitr since fasting is prohibited on this day. These six days of fasting together with the Ramadan fasts are equivalent to fasting all year round. The reasoning behind this tradition is that a good deed in Islam is rewarded 10 times, hence fasting 30 days during Ramadan and 6 days during Shawwāl is equivalent to fasting the whole year in fulfillment of this obligation. The Shia scholars of the Ja'fari school do not place any emphasis on the six days being consecutive, while among the Sunnis, the majority of Shafi`i scholars consider it recommended ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world's Major religious groups, second-largest religious population after Christians. Muslims believe that Islam is the complete and universal version of a Fitra, primordial faith that was revealed many times through earlier Prophets and messengers in Islam, prophets and messengers, including Adam in Islam, Adam, Noah in Islam, Noah, Abraham in Islam, Abraham, Moses in Islam, Moses, and Jesus in Islam, Jesus. Muslims consider the Quran to be the verbatim word of God in Islam, God and the unaltered, final revelation. Alongside the Quran, Muslims also believe in previous Islamic holy books, revelations, such as the Torah in Islam, Tawrat (the Torah), the Zabur (Psalms), and the Gospel in Islam, Injil (Gospel). They believe that Muhammad in Islam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Orthodox Christians
Eastern Orthodoxy, otherwise known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity or Byzantine Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism. Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or " canonical") Eastern Orthodox Church is organised into autocephalous churches independent from each other. In the 21st century, the number of mainstream autocephalous churches is seventeen; there also exist autocephalous churches unrecognized by those mainstream ones. Autocephalous churches choose their own primate. Autocephalous churches can have jurisdiction (authority) over other churches, some of which have the status of " autonomous" which means they have more autonomy than simple eparchies. Many of these jurisdictions correspond to the territories of one or more modern states; the Patriarchate of Moscow, for example, corresponds to Russia and some of the other post-Soviet states. They can also include met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
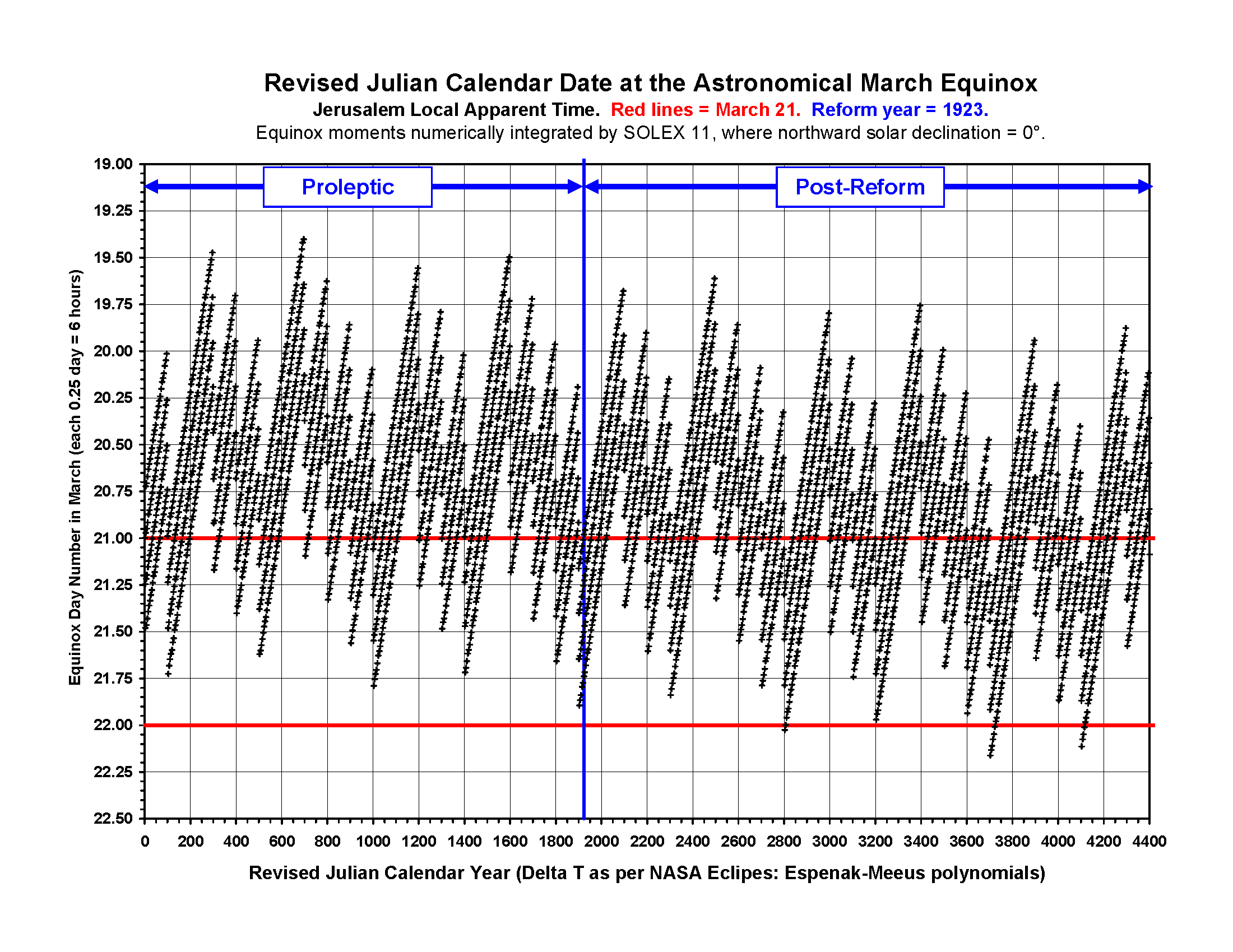
Revised Julian Calendar
The Revised Julian calendar, or less formally the new calendar and also known as the Milanković calendar, is a calendar proposed in 1923 by the Serbian scientist Milutin Milanković as a more accurate alternative to both Julian calendar, Julian and Gregorian calendar, Gregorian calendars. At the time, the Julian calendar was still in use by all of the Eastern Orthodox Church and affiliated nations, while the Catholic and Protestant nations were using the Gregorian calendar. Thus, Milanković's aim was to discontinue the divergence between the naming of dates in Eastern and Western churches and nations. It was intended to replace the Julian calendar in Eastern Orthodox Churches and nations. From 1 March 1600 through 28 February 2800, the Revised Julian calendar aligns its dates with the Gregorian calendar, which had been proclaimed in 1582 by Pope Gregory XIII. The Revised Julian calendar has been adopted for ecclesiastical use by the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |