|
Psychology Of Programming
The psychology of programming (PoP) is the field of research that deals with the psychological aspects of writing programs (often computer programs). The field has also been called the ''empirical studies of programming'' (ESP). It covers research into computer programmers' cognition, tools and methods for programming-related activities, and programming education. Psychologically, computer programming is a human activity which involves cognitions such as reading and writing Writing is the act of creating a persistent representation of language. A writing system includes a particular set of symbols called a ''script'', as well as the rules by which they encode a particular spoken language. Every written language ... computer language, learning, problem solving, and reasoning. History The history of psychology of programming dates back to late 1970s and early 1980s, when researchers realized that computational power should not be the only thing to be evaluated in programming ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Psychological
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Its subject matter includes the behavior of humans and nonhumans, both consciousness, conscious and Unconscious mind, unconscious phenomena, and mental processes such as thoughts, feelings, and motivation, motives. Psychology is an academic discipline of immense scope, crossing the boundaries between the Natural science, natural and social sciences. Biological psychologists seek an understanding of the Emergence, emergent properties of brains, linking the discipline to neuroscience. As social scientists, psychologists aim to understand the behavior of individuals and groups.Hockenbury & Hockenbury. Psychology. Worth Publishers, 2010. A professional practitioner or researcher involved in the discipline is called a psychologist. Some psychologists can also be classified as Behavioural sciences, behavioral or Cognitive science, cognitive scientists. Some psychologists attempt to understand the role of mental functions in i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Anchoring Bias
The anchoring effect is a psychological phenomenon in which an individual's judgments or decisions are influenced by a reference point or "anchor" which can be completely irrelevant. Both numeric and non-numeric anchoring have been reported through research. In numeric anchoring, once the value of the anchor is set, subsequent arguments, estimates, etc. made by an individual may change from what they would have otherwise been without the anchor. For example, an individual may be more likely to purchase a car if it is placed alongside a more expensive model (the anchor). Prices discussed in negotiations that are lower than the anchor may seem reasonable, perhaps even cheap to the buyer, even if said prices are still relatively higher than the actual market value of the car. Another example may be when estimating the orbit of Mars, one might start with the Earth's orbit (365 days) and then adjust upward until they reach a value that seems reasonable (usually less than 687 days, the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Cognition
Cognition is the "mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses". It encompasses all aspects of intellectual functions and processes such as: perception, attention, thought, imagination, intelligence, the formation of knowledge, memory and working memory, judgment and evaluation, reasoning and computation, problem-solving and decision-making, comprehension and production of language. Cognitive processes use existing knowledge to discover new knowledge. Cognitive processes are analyzed from very different perspectives within different contexts, notably in the fields of linguistics, musicology, anesthesia, neuroscience, psychiatry, psychology, education, philosophy, anthropology, biology, systemics, logic, and computer science. These and other approaches to the analysis of cognition (such as embodied cognition) are synthesized in the developing field of cognitive science, a progressively autonomou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Problem Solving
Problem solving is the process of achieving a goal by overcoming obstacles, a frequent part of most activities. Problems in need of solutions range from simple personal tasks (e.g. how to turn on an appliance) to complex issues in business and technical fields. The former is an example of simple problem solving (SPS) addressing one issue, whereas the latter is complex problem solving (CPS) with multiple interrelated obstacles. Another classification of problem-solving tasks is into well-defined problems with specific obstacles and goals, and ill-defined problems in which the current situation is troublesome but it is not clear what kind of resolution to aim for. Similarly, one may distinguish formal or fact-based problems requiring G factor (psychometrics), psychometric intelligence, versus socio-emotional problems which depend on the changeable emotions of individuals or groups, such as Emotional intelligence, tactful behavior, fashion, or gift choices. Solutions require suff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Learning
Learning is the process of acquiring new understanding, knowledge, behaviors, skills, value (personal and cultural), values, Attitude (psychology), attitudes, and preferences. The ability to learn is possessed by humans, non-human animals, and some machine learning, machines; there is also evidence for some kind of learning in certain plants. Some learning is immediate, induced by a single event (e.g. being burned by a Heat, hot stove), but much skill and knowledge accumulate from repeated experiences. The changes induced by learning often last a lifetime, and it is hard to distinguish learned material that seems to be "lost" from that which cannot be retrieved. Human learning starts at birth (it might even start before) and continues until death as a consequence of ongoing interactions between people and their environment. The nature and processes involved in learning are studied in many established fields (including educational psychology, neuropsychology, experimental psycho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Human Computer Interaction
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are great apes characterized by their hairlessness, bipedalism, and high intelligence. Humans have large brains, enabling more advanced cognitive skills that facilitate successful adaptation to varied environments, development of sophisticated tools, and formation of complex social structures and civilizations. Humans are highly social, with individual humans tending to belong to a multi-layered network of distinct social groups — from families and peer groups to corporations and political states. As such, social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of values, social norms, languages, and traditions (collectively termed institutions), each of which bolsters human society. Humans are also highly curious: the desire to understand and influence phenomena has motivated humanity's development ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Cognitive Psychology
Cognitive psychology is the scientific study of human mental processes such as attention, language use, memory, perception, problem solving, creativity, and reasoning. Cognitive psychology originated in the 1960s in a break from behaviorism, which held from the 1920s to 1950s that unobservable mental processes were outside the realm of empirical science. This break came as researchers in linguistics and cybernetics, as well as applied psychology, used models of mental processing to explain human behavior. Work derived from cognitive psychology was integrated into other branches of psychology and various other modern disciplines like cognitive science, linguistics, and economics. History Philosophically, ruminations on the human mind and its processes have been around since the times of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks. In 387 BCE, Plato had suggested that the brain was the seat of the mental processes. In 1637, René Descartes posited that humans are born with innate ideas and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
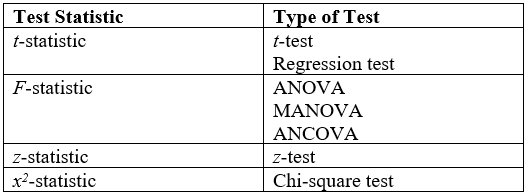 |
Hypothesis Testing
A statistical hypothesis test is a method of statistical inference used to decide whether the data provide sufficient evidence to reject a particular hypothesis. A statistical hypothesis test typically involves a calculation of a test statistic. Then a decision is made, either by comparing the test statistic to a critical value or equivalently by evaluating a ''p''-value computed from the test statistic. Roughly 100 specialized statistical tests are in use and noteworthy. History While hypothesis testing was popularized early in the 20th century, early forms were used in the 1700s. The first use is credited to John Arbuthnot (1710), followed by Pierre-Simon Laplace (1770s), in analyzing the human sex ratio at birth; see . Choice of null hypothesis Paul Meehl has argued that the epistemological importance of the choice of null hypothesis has gone largely unacknowledged. When the null hypothesis is predicted by theory, a more precise experiment will be a more severe test of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Logical Reasoning
Logical reasoning is a mind, mental Action (philosophy), activity that aims to arrive at a Logical consequence, conclusion in a Rigour, rigorous way. It happens in the form of inferences or arguments by starting from a set of premises and reasoning to a conclusion supported by these premises. The premises and the conclusion are propositions, i.e. true or false claims about what is the case. Together, they form an argument. Logical reasoning is norm-governed in the sense that it aims to formulate correct arguments that any rational person would find convincing. The main discipline studying logical reasoning is logic. Distinct types of logical reasoning differ from each other concerning the norms they employ and the certainty of the conclusion they arrive at. Deductive reasoning offers the strongest support: the premises ensure the conclusion, meaning that it is impossible for the conclusion to be false if all the premises are true. Such an argument is called a Validity (logic), v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Software Testing
Software testing is the act of checking whether software satisfies expectations. Software testing can provide objective, independent information about the Quality (business), quality of software and the risk of its failure to a User (computing), user or sponsor. Software testing can determine the Correctness (computer science), correctness of software for specific Scenario (computing), scenarios but cannot determine correctness for all scenarios. It cannot find all software bug, bugs. Based on the criteria for measuring correctness from an test oracle, oracle, software testing employs principles and mechanisms that might recognize a problem. Examples of oracles include specifications, Design by Contract, contracts, comparable products, past versions of the same product, inferences about intended or expected purpose, user or customer expectations, relevant standards, and applicable laws. Software testing is often dynamic in nature; running the software to verify actual output ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Confirmation Bias
Confirmation bias (also confirmatory bias, myside bias, or congeniality bias) is the tendency to search for, interpret, favor and recall information in a way that confirms or supports one's prior beliefs or Value (ethics and social sciences), values. People display this bias when they select information that supports their views, ignoring contrary information or when they interpret ambiguous evidence as supporting their existing attitudes. The effect is strongest for desired outcomes, for emotionally charged issues and for deeply entrenched beliefs. Biased search for information, biased interpretation of this information and biased memory recall, have been invoked to explain four specific effects: # ''attitude polarization'' (when a disagreement becomes more extreme even though the different parties are exposed to the same evidence) # ''belief perseverance'' (when beliefs persist after the evidence for them is shown to be false) # the ''irrational primacy effect'' (a greater relia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Availability Bias
The availability heuristic, also known as availability bias, is a mental shortcut that relies on immediate examples that come to a given person's mind when evaluating a specific topic, concept, method, or decision. This heuristic, operating on the notion that, if something can be recalled, it must be important, or at least more important than alternative solutions not as readily recalled, is inherently biased toward recently acquired information. The mental availability of an action's consequences is positively related to those consequences' perceived magnitude. In other words, the easier it is to recall the consequences of something, the greater those consequences are often perceived to be. Most notably, people often rely on the content of their recall if its implications are not called into question by the difficulty they have in recalling it. Overview and history In the late 1960s and early 1970s, Amos Tversky and Daniel Kahneman began work on a series of papers examining "heu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |