|
Psusennes
Psusennes is the Greek form of the ancient Egyptian name ''Pasebakhaenniut'' ''(p3-sb3-ḫˁỉ-n-nỉwt,'' "The star appearing in the city (= Thebes)". There are three major figures of that name: Two 21st Dynasty pharaohs: * Psusennes I * Psusennes II and a 21st dynasty High Priest of Amun, who may be the same person as Psusennes II: * Psusennes III Psusennes III was the High Priest of Amun at Thebes (976 Р943 BC) at the end of the 21st Dynasty. Little is known of this individual; he is thought by some to be the same person as pharaoh Psusennes II.Peden, A J. ''The Graffiti of Pharaon ... {{hndis Ancient Egyptian given names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psusennes II
Titkheperure or Tyetkheperre Psusennes II [Greek language, Greek Ψουσέννης] or Hor-Pasebakhaenniut II [Egyptian language, Egyptian ''ḥr-p3-sb3-ḫˁỉ--nỉwt''], was the last Pharaoh, king of the Twenty-first Dynasty of Egypt. His royal name means "Image of the transformations of Re" in Egyptian. Psusennes II is often considered the same person as the High-Priest of Amun known as Psusennes III. The Egyptologist Karl Jansen-Winkeln notes that an important Graffito (archaeology), graffito from the Temple of Abydos contains the complete titles of a king ''Tyetkheperre Setepenre Pasebakhaenniut Meryamun'' "who is simultaneously called the HPA (i.e., High Priest of Amun) and supreme military commander." This suggests that Psusennes was both king at Tanis and the High Priest in Thebes at the same time, meaning he did not resign his office as High Priest of Amun during his reign. The few contemporary attestations from his reign include the aforementioned Graffito (archaeolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psusennes I
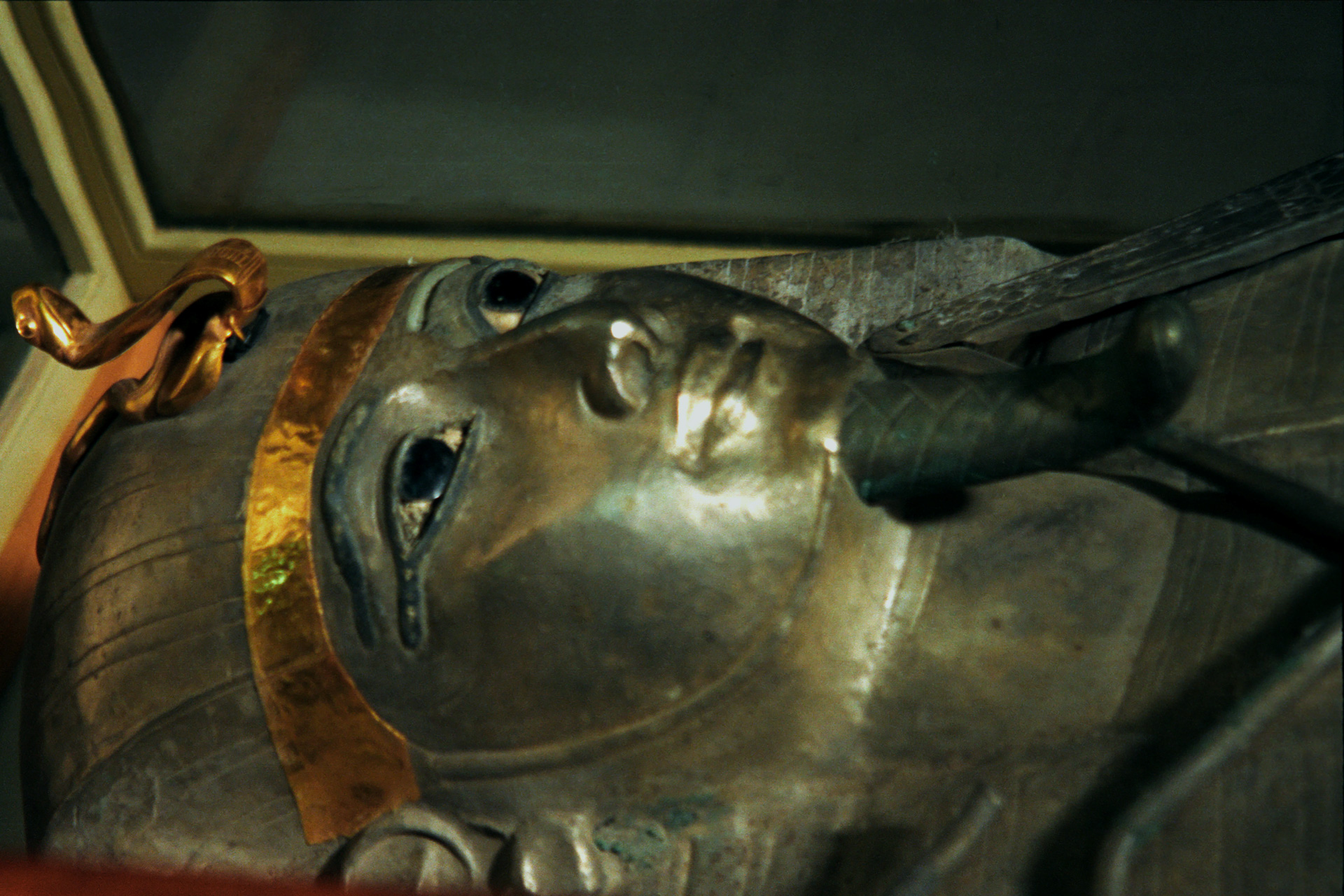
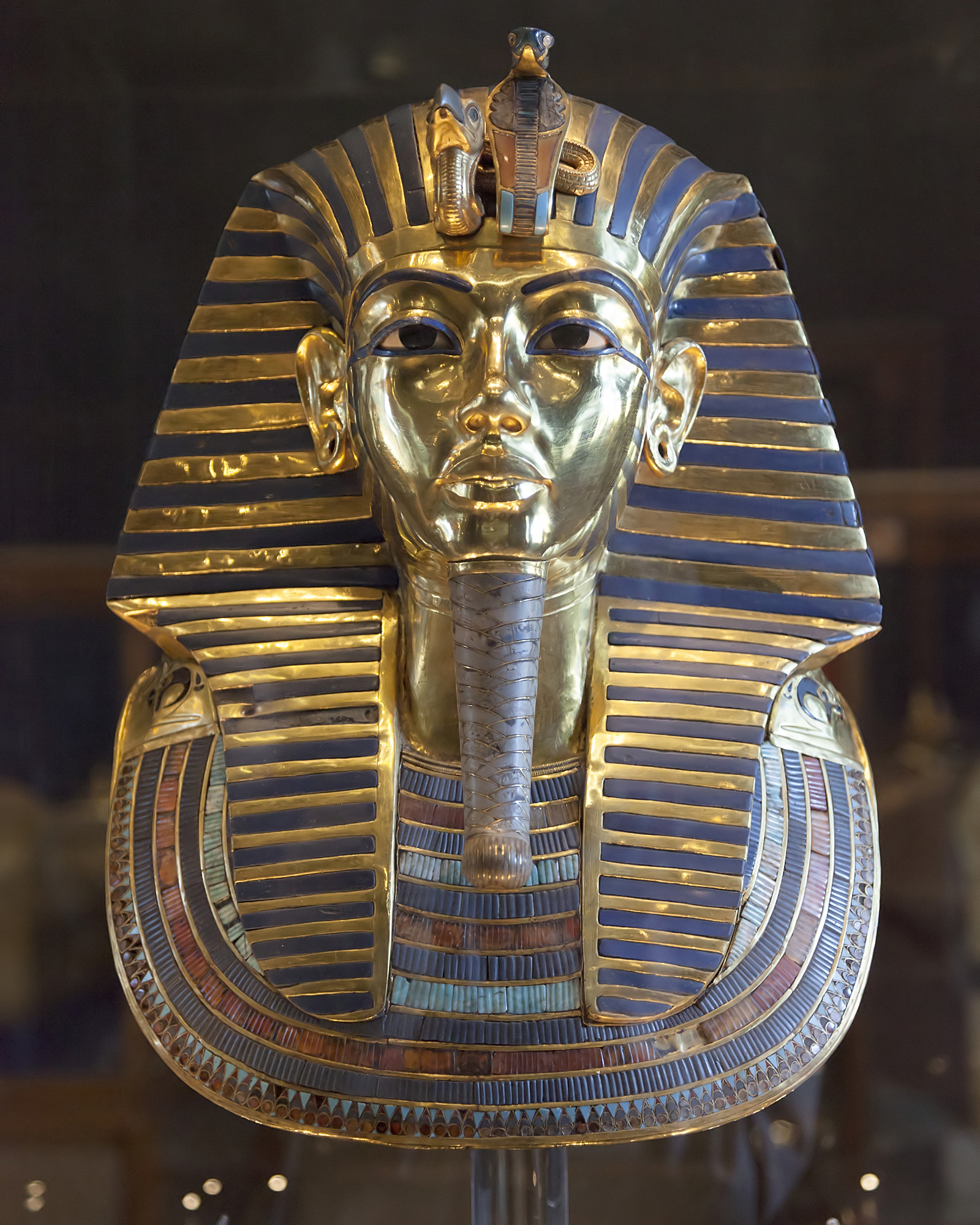
Psusennes I (; Greek Œ®ŒøœÖœÉŒ≠ŒΩŒΩŒ∑œÇ) was the third pharaoh of the 21st Dynasty who ruled from Tanis between 1047 and 1001 BC. ''Psusennes'' is the Greek version of his original name Pasibkhanu or Pasebakhaenniut (in reconstructed Late Egyptian: /p…ôsiw Ée ï…ônneÀê î…ô/), which means "The Star Appearing in the City" while his throne name, Akheperre Setepenamun, translates as "Great are the Manifestations of Ra, chosen of Amun." He was the son of Pinedjem I and Henuttawy, Ramesses XI's daughter by Tentamun. He married his sister Mutnedjmet. Psusennes's tomb, discovered in February 1940 by the French Egyptologist Pierre Montet, is notable for the condition in which it was found. All previously found pharaonic tombs had been graverobbed, including the tomb of Tutankhamun, and Psusennes's tomb was the only ancient Egyptian royal tomb discovered in fully intact condition. However, the humid climate of Lower Egypt meant only the metal objects had survived. Pharaoh Amenemope and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Priest Of Amun
The High Priest of Amun or First Prophet of Amun ('' ḥm nṯr tpj n jmn'') was the highest-ranking priest in the priesthood of the ancient Egyptian god Amun. The first high priests of Amun appear in the New Kingdom of Egypt, at the beginning of the Eighteenth Dynasty. History The priesthood of Amun rose in power during the early Eighteenth dynasty through significant tributes to the god Amun by rulers such as Hatshepsut and more importantly Thutmose III. The Amun priesthood in Thebes had four high-ranking priests: * The Chief Prophet of Amun at Karnak (''ḥm nṯr tpj n jmn''), also referred to as the Chief Priest of Amun. * The Second Prophet of Amun at Karnak (''ḥm nṯr snnw n jmn''), also referred to as the Second Priest of Amun. * The Third Prophet of Amun at Karnak (''ḥm nṯr ḫmtnw n jmn khemet-nu''), also referred to as the Third Priest of Amun. * The Fourth Prophet of Amun at Karnak (''ḥm nṯr jfdw n jmn''), also referred to as the Fourth Priest of Amun. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twenty-first Dynasty Of Egypt
The Twenty-first Dynasty of Egypt (notated Dynasty XXI, alternatively 21st Dynasty or Dynasty 21) is usually classified as the first Dynasty of the Ancient Egyptian Third Intermediate Period, lasting from 1077 BC to 943 BC. History After the reign of Ramesses III, a long, slow decline of royal power in Egypt followed. The pharaohs of the Twenty-first Dynasty ruled from Tanis, but were mostly active only in Lower Egypt, which they controlled. This dynasty is described as 'Tanite' because its political capital was based at Tanis. Meanwhile, the High Priests of Amun at Thebes effectively ruled Middle and Upper Egypt in all but name. The later Egyptian Priest Manetho of Sebennytos states in his Epitome on Egyptian royal history that "the 21st Dynasty of Egypt lasted for 130 years".Kenneth A. Kitchen, The Third Intermediate Period in Egypt (1100–650 BC), 3rd edition, 1986, Warminster: Aris & Phillips Ltd, p.531 Pharaohs of the 21st Dynasty Timeline of the 21st Dynasty ImageS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psusennes III
Psusennes III was the High Priest of Amun at Thebes (976 – 943 BC) at the end of the 21st Dynasty. Little is known of this individual; he is thought by some to be the same person as pharaoh Psusennes II.Peden, A J. ''The Graffiti of Pharaonic Egypt: Scope and Roles of Informal Writings (C. 3100-332 B.C (Probleme Der Agyptologie, 17. Bd)'' Brill Academic Publishers 2001 p. 267 His name appears on a document found at the 'mummy cache' DB320, which describes him as a son of the High Priest Pinedjem II. This makes him a possible candidate for Psusennes II because Pinedjem II died in Year 10 of Siamun Neterkheperre or Netjerkheperre-Setepenamun Siamun was the sixth pharaoh of Ancient Egypt, Egypt during the Twenty-first Dynasty of Egypt, Twenty-first Dynasty. He built extensively in Lower Egypt for a king of the Third Intermediate Period and ..., who was the immediate predecessor of this pharaoh. References Theban high priests of Amun People of the Twenty-first Dynas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian language, Egyptian: ''wikt:pr Íú•Íú£, pr Íú•Íú£''; Meroitic language, Meroitic: ê¶≤궧ê¶ß, ; Biblical Hebrew: ''Par ø≈ç'') was the title of the monarch of ancient Egypt from the First Dynasty of Egypt, First Dynasty () until the Roman Egypt, annexation of Egypt by the Roman Republic in 30 BCE. However, the equivalent Egyptian language, Egyptian word for "king" was the term used most frequently by the ancient Egyptians for their monarchs, regardless of gender, through the middle of the Eighteenth Dynasty during the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom. The earliest confirmed instances of "pharaoh" used contemporaneously for a ruler were a letter to Akhenaten (reigned ‚Äì1336 BCE) or an inscription possibly referring to Thutmose III (‚Äì1425 BCE). In the early dynasties, ancient Egyptian kings had as many as ancient Egyptian royal titulary, three titles: the Horus name, Horus, the prenomen (Ancient Egypt), Sedge and Bee (wikt:nswt-bjtj, ''nswt-bjtj''), and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Egyptian
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower Egypt were amalgamated by Menes, who is believed by the majority of List of Egyptologists, Egyptologists to have been the same person as Narmer. The history of ancient Egypt unfolded as a series of stable kingdoms interspersed by the "Periodization of ancient Egypt, Intermediate Periods" of relative instability. These stable kingdoms existed in one of three periods: the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old Kingdom of the Early Bronze Age; the Middle Kingdom of Egypt, Middle Kingdom of the Middle Bronze Age; or the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom of the Late Bronze Age. The pinnacle of ancient Egyptian power was achieved during the New Kingdom, which extended its rule to much of Nubia and a considerable portion of the Levant. After this period, Egypt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thebes, Egypt
Thebes (, , ''Thƒìbai''), known to the ancient Egyptians as Waset, was an ancient Egyptian city located along the Nile about south of the Mediterranean. Its ruins lie within the modern Egyptian city of Luxor. Thebes was the main city of the fourth Upper Egyptian nome (Sceptre nome) and was the capital of Egypt for long periods during the Middle Kingdom and New Kingdom eras. It was close to Nubia and the Eastern Desert, with its valuable mineral resources and trade routes. It was a religious center and the most venerated city during many periods of ancient Egyptian history. The site of Thebes includes areas on both the eastern bank of the Nile, where the temples of Karnak and Luxor stand and where the city was situated; and the western bank, where a necropolis of large private and royal cemeteries and funerary complexes can be found. In 1979, the ruins of ancient Thebes were classified by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site. Toponymy The Egyptian name for Thebes was ''wÍú ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |