|
Protection Island (Nanaimo)
Protection Island is a small island located 1.5 km north-east of downtown Nanaimo, British Columbia, Canada in the Nanaimo Harbour. The island was originally named Douglas Island, after James Douglas (governor), James Douglas the first Governor of the Colony of Vancouver Island and Colony of British Columbia (1858–1866), British Columbia. It was renamed ''Protection Island'' in 1960. The permanent year-round population is about 350 people. There are no paved roads on the island. Some residents move about the island in golf carts, others with cars, but most walk. Locals frequently transport their groceries from the community dock with their own wheelbarrows. Access to the island can be via private vessel or a small, privately run ferry which departs from downtown Nanaimo at Maffeo Sutton Park and docks at the Dinghy Dock Pub (which is Canada's only floating pub). Some residents also commute by kayak or rowboat as well. History Hangings on Execution Point In the winter of 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Situated in the Pacific Northwest between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains, the province has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, forests, lakes, mountains, inland deserts and grassy plains. British Columbia borders the province of Alberta to the east; the territories of Yukon and Northwest Territories to the north; the U.S. states of Washington (state), Washington, Idaho and Montana to the south, and Alaska to the northwest. With an estimated population of over 5.7million as of 2025, it is Canada's Population of Canada by province and territory, third-most populous province. The capital of British Columbia is Victoria, British Columbia, Victoria, while the province's largest city is Vancouver. Vancouver and its suburbs together make up List of census metropolitan areas and agglomerations in Canada, the third-largest metropolit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beaver (steamship)
''Beaver'' was a steamship originally owned and operated by the Hudson's Bay Company. She was the first steamship to operate in the Pacific Northwest of North America, and made remote parts of the west coast of Canada accessible for maritime fur trading. At one point she was chartered by the Royal Navy for surveying the coastline of British Columbia. She served off the coast from 1836 until 1888, when she was wrecked. Service ''Beaver'' served trading posts maintained by the Hudson's Bay Company between the Columbia River and Russian America (Alaska) and played an important role in helping maintain British control in British Columbia during the Fraser Canyon Gold Rush of 1858–59. In 1862 the Royal Navy chartered her to survey and chart the coast of the Colony of British Columbia. She also provided assistance to the Royal Navy at Bute Inlet during the Chilcotin War. Loss A consortium that became the British Columbia Towing and Transportation Company in 1874 purchased her, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Historic Places In The Nanaimo Regional District ...
The following list includes all of the Canadian Register of Historic Places listings in Nanaimo Regional District, British Columbia. See also *List of coal mines and landmarks in the Nanaimo area References :''(references appear in the table above as external links)'' {{Canadian Register of Historic Places listings in British Columbia Nanaimo Regional District The Regional District of Nanaimo is a regional district located on the eastern coast of Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada. It is bordered to the south by the Cowichan Valley Regional District, to the west by the Alberni-Clayoquot Reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Coal Mines And Landmarks In The Nanaimo Area
This is a list of landmarks and historic locations, mostly related to coal mining, in the vicinity of the City of Nanaimo in the Canadian province of British Columbia. Origins of Nanaimo - Coal Most of these landmarks relate to the city's history as a coal-mining town. Coal was discovered in the area in 1849. Joseph William McKay took possession of the deposits for the Hudson's Bay Company (HBC) in 1852 at the direction of Governor James Douglas. The area was first known as Wintuhuysen Inlet and then Colvile Town (named for HBC Governor Andrew Colvile) but became known as Nanaimo in 1860. The first church opened in 1861. In 1853 the population was 125. By 1869 it was about 650 and by 1874 it was close to 1,000. By 1859, 25,000 tons of coal had been shipped from Nanaimo, mostly to San Francisco. In 1862 the HBC sold its coal interests to an English Company known as the Vancouver Coal Mining and Land Company (VCML). Output was 100 tons a day by 1863 and double that by 1866. By 187 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newcastle Island Marine Provincial Park
Saysutshun (Newcastle Island Marine) Provincial Park, formally known as Newcastle Island Marine Provincial Park, is a provincial park located on Newcastle Island, a small island off the coast of Nanaimo, British Columbia, Canada. History For thousands of years, Saysutshun Island was used by the Coast Salish peoples as a seasonal fishing site. European explorers, including members of the Hudson's Bay Company (HBC), initially assumed the island was uninhabited. Owing to the abundant fish population, they established a herring industry in the region, constructing salteries and fisheries on the northwestern coast of the island. Ki’et’sa’kun, a Snuneymuxw man, told the English about coal on the island and they gave him the nickname "Coal Tyee" as a result. Coal mining became the primary industry in Nanaimo in the late nineteenth century. The HBC, aware of the importance of coal, named this island for Newcastle upon Tyne, an English area of coal production. While mining fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1887 Nanaimo Mine Explosion
The Nanaimo mine explosion occurred on May 3, 1887, in Nanaimo, British Columbia killing 150 miners. Only seven miners survived and the mine burned for one full day. The explosion started deep underground in the Number One Coal Mine after explosives were laid improperly. Although many miners died instantly, others were trapped by the explosion and the fires that followed. Most miners did not die from the primary explosions or the fires, but many actually died from choking on poisonous gas hours after the initial explosions. These men wrote farewell messages in the dust of their shovels. Nearly 150 children lost their fathers and 46 women became widows. Most of the men were settlers from Cornwall, Wales and Yorkshire. A plaque at the foot of Milton Street commemorates the event. Although past documents put the death toll at 148, researchers have since revised the number to 150, including 53 Chinese workers. Chinese workers were listed in the government inquest and annual report of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
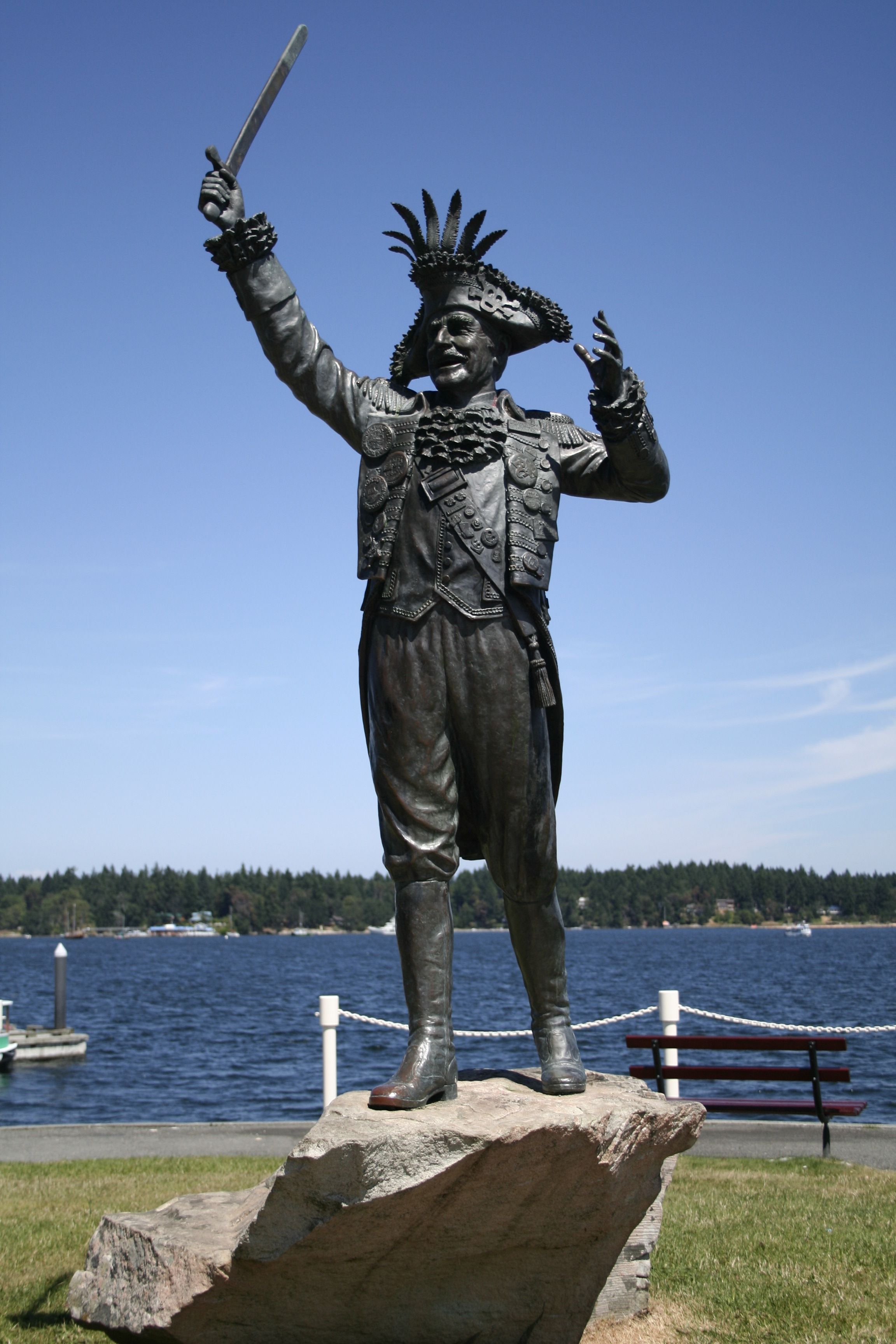
Frank Ney
Frank James Ney (May 12, 1918 – November 24, 1992) was a mayor of Nanaimo, British Columbia, Canada, serving for twenty-one years. Ney also served a term as a member of the Legislative Assembly of British Columbia. He was known for his outgoing personality, his habit of attending civic events and dressing up like a pirate for the appearances, and playing a central role in initiating the bathtub races across Georgia Strait from Nanaimo to Vancouver. He was an active skier, swimmer, figure skater and boater. During the 1950/1951 season he was President of the Nanaimo Figure Skating Club. He also, while Mayor, initiated the creation of cut-away corners of sidewalk curbs in downtown Nanaimo after spending one day in a wheelchair in order to experience for himself the difficulties in getting around experienced by those in wheelchairs. In his honour, Frank J. Ney Elementary School was named after him. Biography Born in London, England, Ney served in the RAF and RCAF as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piracy
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and valuable goods, or taking hostages. Those who conduct acts of piracy are called pirates, and vessels used for piracy are called pirate ships. The earliest documented instances of piracy were in the 14th century BC, when the Sea Peoples, a group of ocean raiders, attacked the ships of the Aegean and Mediterranean civilisations. Narrow channels which funnel shipping into predictable routes have long created opportunities for piracy, as well as for privateering and commerce raiding. Historic examples of such areas include the waters of Gibraltar, the Strait of Malacca, Madagascar, the Gulf of Aden, and the English Channel, whose geographic structures facilitated pirate attacks. The term ''piracy'' generally refers to maritime piracy, although the term has been generalized to refer to acts committed on land, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Register Of Historic Places
The Canadian Register of Historic Places (CRHP; , ), also known as Canada's Historic Places, is an online directory of historic places in Canada which have been formally recognized for their heritage value by a federal, provincial, territorial or municipal authority. It is administered by Parks Canada. Background The Canadian Register of Historic Places was created as part of Canada's "Historic Places Initiative". Commencing in 2001, the Historic Places Initiative was a collaboration between the federal, provincial and territorial governments to improve protection of the country's historic sites and to "promote and foster a culture of heritage conservation in Canada". The CRHP and the Standards and Guidelines for the Conservation of Historic Places in Canada (a common set of guidelines for the restoration and rehabilitation of historic sites throughout Canada) are the two major tools developed to assist in achieving the initiative's main objectives. The CRHP was official ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallows Point Lightkeeper's Cottage, Nanaimo 03
A gallows (or less precisely scaffold) is a frame or elevated beam, typically wooden, from which objects can be suspended or "weighed". Gallows were thus widely used to suspend public weighing scales for large and heavy objects such as sacks of grain or minerals, usually positioned in markets or toll gates. The term was also used for a projecting framework from which a ship's anchor might be raised so it is no longer sitting on the seabed, riverbed or dock; "weighing heanchor" meant raising it using this apparatus while avoiding striking the ship's hull. In modern usage the term has come to mean almost exclusively a scaffold or gibbet used for execution by hanging. Etymology The term "gallows" was derived from a Proto-Germanic word '' galgô'' that refers to a "pole", "rod" or "tree branch". With the beginning of Christianization, Ulfilas used the term ''galga'' in his Gothic Testament to refer to the cross of Christ, until the use of the Latin term (crux = cross) prevai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ship Grounding
Ship grounding or ship stranding is the impact of a ship on seabed or waterway side. It may be intentional, as in beaching (nautical), beaching to land crew or cargo, and careening, for maintenance or repair, or unintentional, as in a marine accident. In accidental cases, it is commonly referred to as "running aground". When unintentional, grounding may result simply in stranding, with or without damage to the submerged part of the ship's hull. Breach of the hull may lead to significant flooding, which in the absence of containment in watertight bulkheads may substantially compromise the ship's structural integrity, stability, and safety. As hazard Severe grounding applies extreme loads upon ship structures. In less severe accidents, it might result only in damage to the hull; however, in most serious accidents, it might lead to hull breaches, cargo spills, total loss of the vessel, and, in the worst cases, human casualties. Grounding accounts for about one-third of commercia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
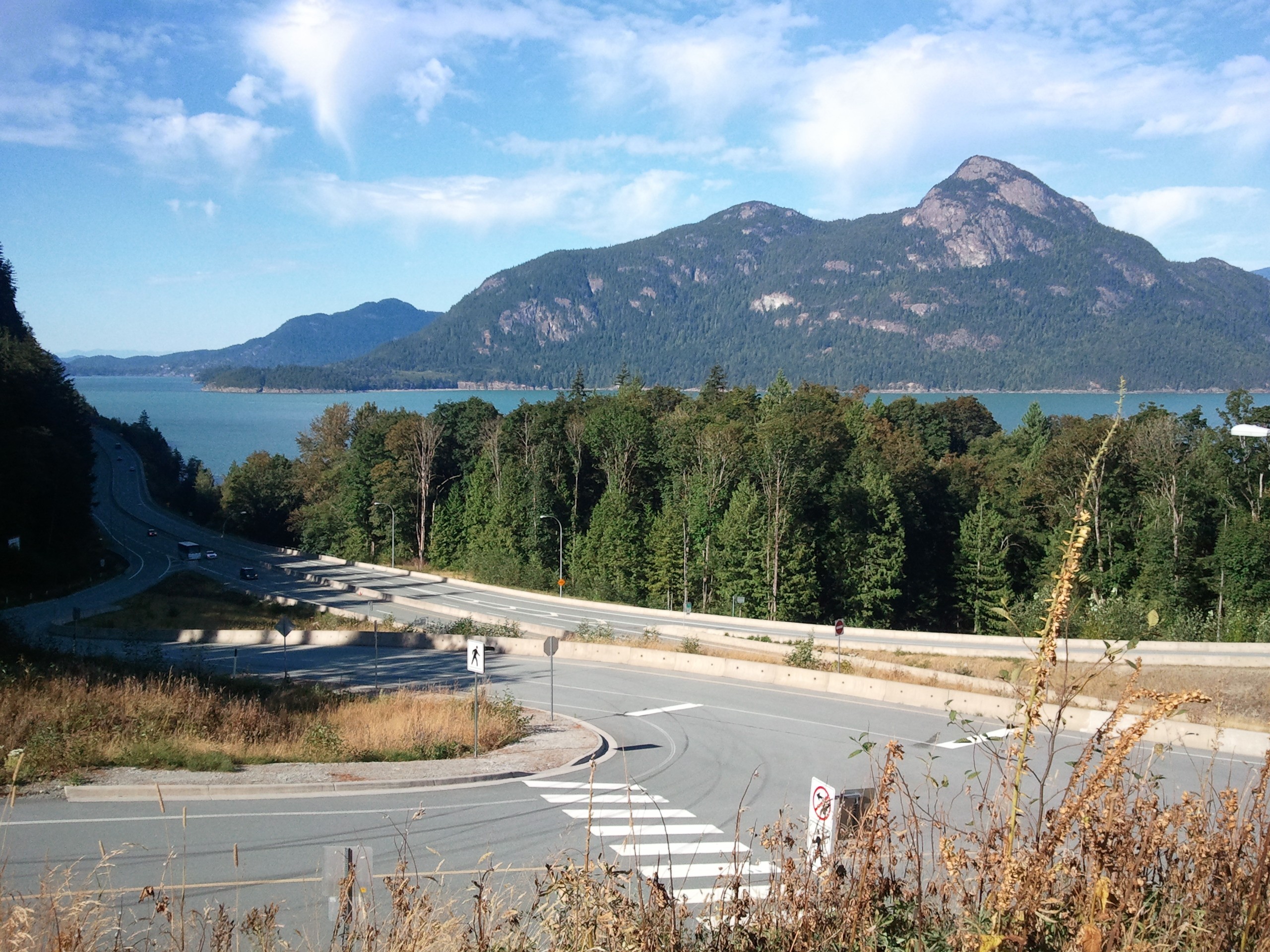
Howe Sound
Howe Sound (, ) is a roughly triangular sound (geography), sound, that joins a network of fjords situated immediately northwest of Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. It was designated as a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve in 2021. Geography Howe Sound's mouth at the Strait of Georgia is situated between West Vancouver and the Sunshine Coast (British Columbia), Sunshine Coast. The sound is triangular, opening to the southwest into the Strait of Georgia, and extends northeast to its head at Squamish, British Columbia, Squamish. There are several islands in the sound, three of which are large and mountainous in their own right. The steep-sided mainland shores funnel the breezes as the daily thermals build the wind to or more at the northern end of the sound on a typical summer day. A small outcrop of volcanic rock is located on the eastern shore of Howe Sound called the Watts Point volcanic centre. History The history of Howe Sound begins with the Indigenous people, the Squamish people, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |