|
Project 11356R Frigate
The ''Admiral Grigorovich'' class (also referred to as Krivak V class), Russian designation Project 11356R, is a class of frigates built by the Yantar Shipyard in Kaliningrad for the Russian Navy and Indian Navy, with a cost of $450-500 million. Based on the , six ships were ordered for the Russian Black Sea Fleet under two contracts in 2010 and 2011 as a complement to the frigates. History By 2010–2011, it was decided the Russian Navy will procure six vessels based on the proven design, mainly due to repeated delays with production of ''Admiral Gorshkov'' frigates and because of the urgent need for new frigates necessary for modernization of the Black Sea Fleet. The Yantar Shipyard won the contract for construction of the frigates and three vessels were to be completed in four years. Previously, six ships of the same design, known as ''Talwar'' class, were built for the Indian Navy between 1999 and 2011 by the Baltic Shipyard, Saint Petersburg and Yantar Shipyard, Kaliningra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yantar Shipyard
Yantar Shipyard () is a Russian shipbuilding company based in Kaliningrad, Russia. Yantar Shipyard builds military ships, including antisubmarine and patrol craft, as well as civil vessels such as fishing trawlers and seiners. It is a part of the United Shipbuilding Corporation. Before 1945, it was the Königsberg unit of the German Schichau-Werke shipbuilding company. The shipyard's facilities allow it to construct vessels of up to 20,000 tonnes Deadweight tonnage, DWT. Between 1945 and 2010 it has built more than 100 large and 400 small civilian ships. History Before 1945, the shipyard was the Königsberg unit of the Germany, German Schichau-Werke shipbuilding company. Following World War II, the shipyard was absorbed into the Soviet Union, Soviet state enterprise and operated as a government shipyard. Sometime following the Dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, the shipyard became a part of the Russian State corporation (Russia), state corporation United Shipbuilding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rossiyskaya Gazeta
' () is a Russian newspaper published by the Government of Russia. History ''Rossiyskaya Gazeta'' was founded in 1990 by the Supreme Soviet of the RSFSR, Supreme Soviet of the Russian SFSR during the ''glasnost'' reforms in Soviet Union, shortly before the Dissolution of the Soviet Union, country dissolved in 1991. ''Rossiyskaya Gazeta'' became official government newspaper of the Russian Federation, replacing ''Izvestia'' and ''Sovetskaya Rossiya'' newspapers, which were both privatized after the Soviet Union's dissolution. The role of ''Rossiyskaya Gazeta'' is determined by the Law of the Russian Federation N 5-FZ, dated 14 June 1994 and entitled "''On the Procedure of Publication and Enactment of Federal Constitutional Laws, Federal Laws and Acts of the Houses of the Federal Assembly''", by the Decrees of the President of the Russian Federation, dated 23 May 1996 No. 763, "''On the Procedure of Publication and Enactment of the Acts of the President of the Russian Federation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Navy
The Russian Navy is the Navy, naval arm of the Russian Armed Forces. It has existed in various forms since 1696. Its present iteration was formed in January 1992 when it succeeded the Navy of the Commonwealth of Independent States (which had itself succeeded the Soviet Navy following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in late December 1991). The Imperial Russian Navy was established by Peter the Great (Peter I) in October 1696. The symbols of the Russian Navy, the St. Andrew's ensign (seen to the right), and most of its traditions were established personally by Peter I. The Russian navy possesses the vast majority of the former Soviet naval forces, and currently comprises the Northern Fleet, the Pacific Fleet (Russia), Pacific Fleet, the Black Sea Fleet, the Baltic Fleet, the Caspian Flotilla, the Permanent task force of the Russian Navy in the Mediterranean Sea, permanent task force in the Mediterranean, Russian Naval Aviation, Naval Aviation, and the Coastal Troop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frigate
A frigate () is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied. The name frigate in the 17th to early 18th centuries was given to any full-rigged ship built for speed and maneuverability, intended to be used in scouting, escort and patrol roles. The term was applied loosely to ships varying greatly in design. In the second quarter of the 18th century, what is now generally regarded as the 'true frigate' was developed in France. This type of vessel was characterised by possessing only one armed deck, with an unarmed deck below it used for berthing the crew. Late in the 19th century (British and French prototypes were constructed in 1858), a type of powerful ironclad warships was developed, and because they had a single gun deck, the term 'frigate' was used to describe them. Later developments in ironclad ships rendered the 'frigate' designation obsolete and the term fell out of favour. During the Second World War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamov Ka-27
The Kamov Ka-27 (NATO reporting name 'Helix') is a military helicopter developed for the Soviet Navy, and as of 2024 is in service in various countries including Russia, Ukraine, Vietnam, China, South Korea, and India. Variants include the Ka-29 assault transport, the Ka-28 downgraded export version, and the Ka-32 for civilian use. Design and development The helicopter was developed for ferrying and anti-submarine warfare. Design work began in 1969 and the first prototype flew in 1973. It was intended to replace the decade-old Kamov Ka-25, and had to have identical or smaller external dimensions than its predecessor. Like other Kamov military helicopters it has coaxial rotors, removing the need for a tail rotor. In total, five prototypes and pre-series helicopters were built. Series production started at Kumertau in July 1979, and the new helicopter officially entered service with the Soviet Navy in April 1981. The Ka-27 has a crew of three with a pilot and navigator both stati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RBU-6000
The RBU-6000 Smerch-2 (Реактивно-Бомбовая Установка, ''Reaktivno-Bombovaja Ustanovka''; rocket-bomb installation & Смерч; waterspout) is a 213 mm caliber Soviet anti-submarine rocket launcher. The system entered service in 1960–1961 and is fitted to a wide range of Russian surface vessels. It consists of a horseshoe-shaped arrangement of twelve launch barrels, that are remotely directed by the Burya fire control system (that can also control the shorter-ranged RBU-1000). It fires RGB-60 rockets, which carry unguided depth charges. The rockets are normally fired in salvos of 1, 2, 4, 8 or 12 rounds. Reloading is automatic, with individual rounds being fed into the launcher by the 60UP loading system from a below-deck magazine. Typical magazine capacity is either 72 or 96 rounds per launcher. It can also be used for shore bombardment. The system is an upgrade of the RBU-6000 system, firing the 90R rocket, which releases a 90SG depth charge t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type 53 Torpedo
Type 53 is the common name for a family of 53 cm (21 inch) torpedoes manufactured in Russia, starting with the 53-27 torpedo and continuing to the modern UGST (Fizik-1), which is being replaced by the Futlyar. With the exception of the UGST which uses Mark 48 style monopropellants, Soviet 53 cm torpedoes generally use electric power (since middle of World War II), or kerosene mixed with various oxidizers for propulsion. Russian torpedoes are often named descriptively for their characteristics – examples include "acoustic homing" or "electric torpedo", all in Russian acronyms. History Early history Model 53-27 (1927) with of TNT was developed domestically in the so-called , and it had a poor range at . In 1932 USSR bought in Italy several types of torpedoes, and the model of Whitehead Torpedo Factory in Fiume (in the Soviet Union it was designated 53F) was considered superior. After adapting several features from the latter in unsuccessful 53-36 the decision was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
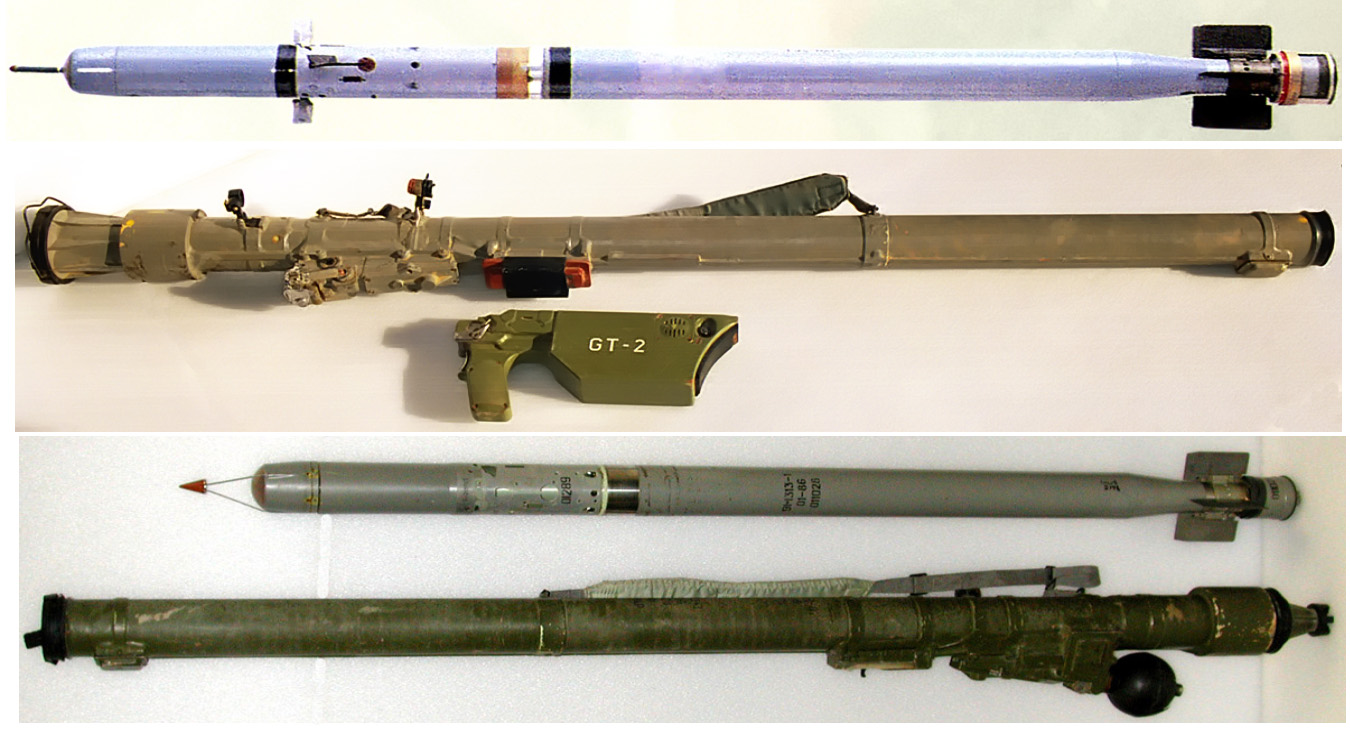
MANPADS
Man-portable air-defense systems (MANPADS or MPADS) are portable shoulder-launched surface-to-air missiles. They are guided weapons and are a threat to low-flying aircraft, especially helicopters and also used against low-flying cruise missiles. These short-range missiles can also be fired from vehicles, tripods, weapon platforms, and warships. Overview MANPADS were developed in the 1950s to provide military ground forces with protection from jet aircraft. They have received a great deal of attention, partly because armed terrorist groups have used them against commercial airliners. These missiles, affordable and widely available through a variety of sources, have been used successfully over the past three decades, both in military conflicts, by militant groups, and by terrorist organizations. Twenty-five countries, including China, Iran, Poland, Russia, Sweden, the United Kingdom and the United States produce man-portable air defense systems.CRS RL31741 page 1 Possession, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
9K333 Verba
The 9K333 ''Verba'' (, "Willow") is a Russian fourth-generation man-portable infrared homing surface-to-air missile (SAM) MANPADS. "9K333" is the Russian GRAU designation of the system. Its NATO reporting name is SA-29 Gizmo. History The 9K333 ''Verba'' was originally developed as a replacement for the 9K38 Igla The 9K38 Igla (, "needle", NATO reporting name SA-18 Grouse) is a Soviet/Russian man-portable infrared homing surface-to-air missile (SAM) system. A simplified, earlier version is known as the 9K310 Igla-1 (NATO: SA-16 Gimlet), and the latest .... The Verba's primary new feature is its multispectral optical seeker, using three sensors - ultraviolet, near infrared, and mid-infrared - as opposed to the Igla-S' two. Cross-checking sensors against one another better discriminates between relevant targets and decoys, and decreases the chance of disruption from countermeasures, including lasers that attempt to blind missiles. According to a KBM spokesperson, the Verba ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SA-16
The 9K38 Igla (, "needle", NATO reporting name SA-18 Grouse) is a Soviet/Russian man-portable infrared homing surface-to-air missile (SAM) system. A simplified, earlier version is known as the 9K310 Igla-1 (NATO: SA-16 Gimlet), and the latest variant is the 9K338 Igla-S (SA-24 Grinch). The Igla-1 entered service in 1981, the Igla in 1983, and the Igla-S in 2004. The Igla has been supplemented by the 9K333 Verba since 2014.New Russian Verba MANPADS will replace Igla-S - Armyrecognition.com, 15 September 2014 History The development of the Igla short-range man-portable air defense system ( |
CIWS
A close-in weapon system (CIWS ) is a point-defense weapon system for detecting and destroying short-range incoming missiles and enemy aircraft which have penetrated the outer defenses, typically mounted on a naval ship. Nearly all classes of larger modern warships are equipped with some kind of CIWS device. There are two types of CIWS systems. A gun-based CIWS usually consists of a combination of radars, computers, and rapid-firing multiple-barrel rotary cannons placed on a rotating turret. Missile-based CIWSs use either infra-red, passive radar/ ESM, or semi-active radar terminal guidance to guide missiles to the targeted enemy aircraft or other threats. In some cases, CIWS are used on land to protect military bases. In this case, the CIWS can also protect the base from shell and rocket fire. Gun systems A gun-based CIWS usually consists of a combination of radars, computers and rotary or revolver cannon placed on a rotating, automatically aimed gun mount. Example ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AK-630
The AK-630 is a Soviet Union, Soviet and Russian fully automatic naval, rotary cannon, close-in weapon system. The "630" designation refers to the weapon's six gun barrels and their 30 mm caliber. The system is mounted in an enclosed automatic turret and directed by MR-123 fire-control radar and television detection and tracking. The weapon's primary purpose is defense against aircraft and helicopters. As one of the tried-and-true CIWS systems available, effectiveness against anti-ship missiles has been demonstrated over the years in exercises, making it the staple anti-air weapon of most Soviet naval vessels. The AK-630 can also be employed against ships and other small craft, coastal targets, and floating mines. Once operational, the system was rapidly adopted and installed in every new Soviet warship (from mine-hunters to aircraft carriers) with up to eight units on larger vessels; hundreds have been produced in total. History It is reported that Gun and Shell Factory makes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |