|
Progon Family
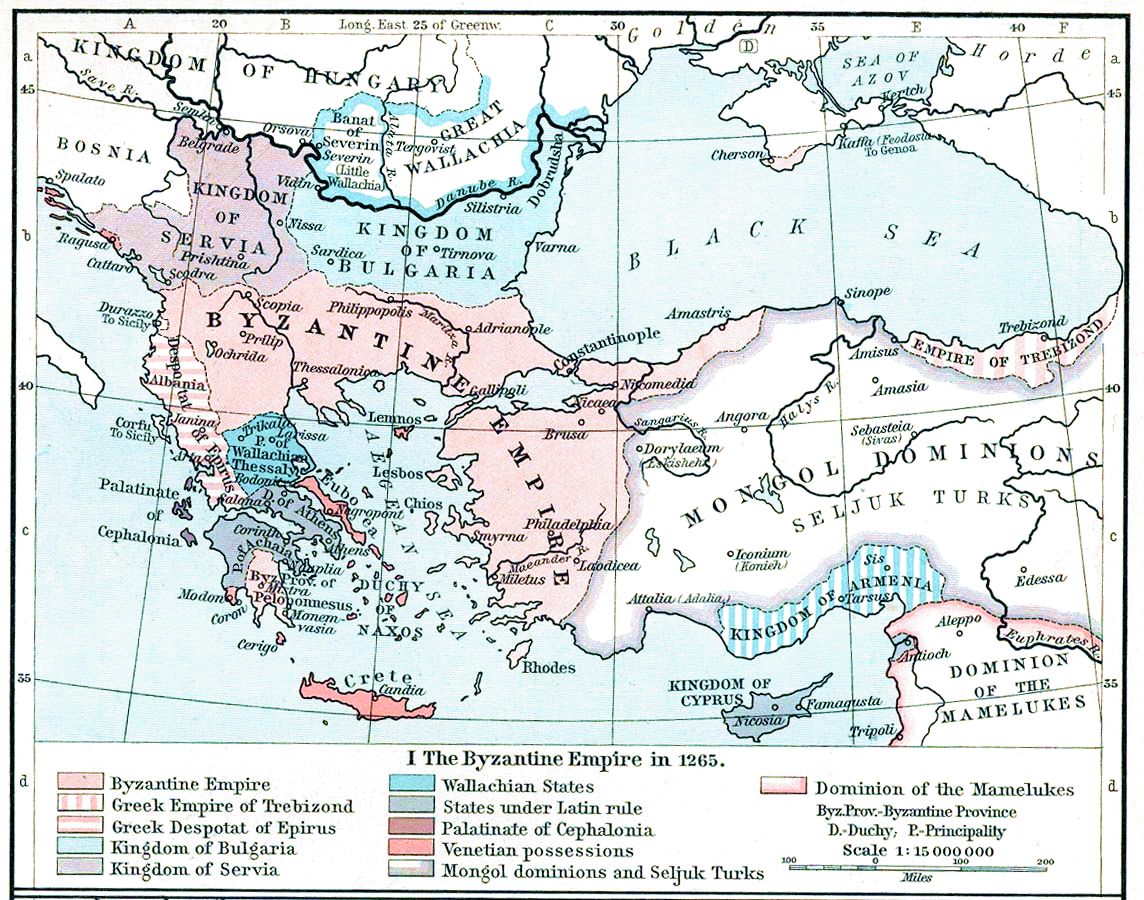
The Progoni were an Albanian noble family which established the first Albanian state in recorded history, the Principality of Arbanon. History Progon of Kruja, father of Dhimitër Progoni established his rule in Krujë in 1190. Before 1204, Arbanon was an autonomous principality of the Byzantine Empire. Little is known about ''archon'' Progon who ruled Krujë and its surroundings at least since the era between 1190 and 1198. The Krujë Castle and other territories remained in the Progoni, and Progon was succeeded by his sons Gjin, and later Demetrio Progoni. He used the title ''princeps Arbanorum'' ("prince of the Albanians") to refer to himself and was recognized as such by foreign dignitaries. In the correspondence with Innocent III, the territory he claimed as ''princeps Arbanorum'' was the area between Shkodra, Prizren, Ohrid and Durrës (''regionis montosae inter Scodram, Dyrrachium, Achridam et Prizrenam sitae''). In general, Progoni brought the principality to its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobility
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy. It is normally appointed by and ranked immediately below royalty. Nobility has often been an estate of the realm with many exclusive functions and characteristics. The characteristics associated with nobility may constitute substantial advantages over or relative to non-nobles or simply formal functions (e.g., precedence), and vary by country and by era. Membership in the nobility, including rights and responsibilities, is typically hereditary and patrilineal. Membership in the nobility has historically been granted by a monarch or government, and acquisition of sufficient power, wealth, ownerships, or royal favour has occasionally enabled commoners to ascend into the nobility. There are often a variety of ranks within the noble class. Legal recognition of nobility has been much more common in monarchies, but nobility also existed in such regimes as the Dutch Republic (1581–1795), the Republic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Durrës
Durrës ( , ; sq-definite, Durrësi) is the List of cities and towns in Albania#List, second most populous city of the Albania, Republic of Albania and county seat, seat of Durrës County and Durrës Municipality. It is one of Albania's oldest list of oldest continuously inhabited cities, continuously inhabited cities, with roughly 2,500 years of recorded history. It is located on a flat plain along the Albanian Adriatic Sea Coast between the mouths of the Erzen River, Erzen and Ishëm (river), Ishëm at the southeastern corner of the Adriatic Sea. Durrës' climate is profoundly influenced by a seasonal Mediterranean climate. Durrës was founded under the name of Epidamnos around the 7th century BC, by Ancient Greece, ancient Greek colonists from Corinth and Korkyra (polis), Corcyra in cooperation with the Taulantii, a local Illyrians, Illyrian tribe. Also known as Dyrrachium, Durrës developed as it became an integral part of the Roman Empire and its successor the Byzantine Em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arbanum
Arbanum is a town, former bishopric and present titular see in present Albania. Latin bishopric Arbanum was established circa 1100 as Diocese of Arbano (or Albania), suffragan of the Metropolitan Archbishopric of Durrës (Italian Durazzo). It was suppressed in 1640, its territory being merged into that of its Metropolitan, the Archdiocese of Durrës (Durazzo), to which its last incumbent was appointed. Episcopal Ordinaries (all Roman Rite) ;''Suffragan Bishops of Arbano'' (incomplete : first centuries unavailable) * Giacomo (1357.01.07 – ?) * Dionigi (? – ?) * Domenico Progoni (1369.11.21 – ?) * Andrea (? – death 1370?) * Giovanni Lourlis, Dominican Order (O.P.) (1370.06.28 – ?) * Gregorio da Venezia, Conventual? Franciscans (O.F.M.) (1385? – ?) * Pietro (? – ?) * Giovanni da Trieste, O.F.M. (1391.03.01 – ?) * Francesco Petri, Cistercians (O. Cist.) (1394.09.07 – ?) * Andrea de Rhegino, O.P. (? – death 1397.10.06) * Tommaso Butyller (? – 1401.05.16), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lezhë
Lezhë (, sq-definite, Lezha) is a List of cities and towns in Albania, city in the Republic of Albania and seat of Lezhë County and Lezhë Municipality. It is one of Albania's List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities, with roughly 2,400 years of recorded history. One of the main strongholds of the Labeatae, Labeatai, the earliest of the fortification walls of Lezhë are of typical Illyrians, Illyrian construction and are dated to the late 4th century BC. Lezhë was one of the main centres of the Illyrian kingdom. During the conflicts with Macedon, it was captured by Philip V of Macedon, Philip V becoming the Macedonian outlet to the Adriatic Sea. The city was later recovered by the Illyrians. It was subjected to Roman Republic, Rome after the Roman-Illyrian wars and the fall of Gentius' realm. Lezhë was the site of the League of Lezhë where Skanderbeg united the List of Princes of Albania, Albanian lords in the fight against the Ottom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protosebastos
The title of ''protosebastos'' (, ''prōtosébastos'', "first '' sebastos''") was a high Byzantine court title created by Emperor Alexios I Komnenos. History Although the title first appears in a document of 1049, where Domenico I Contarini, the Doge of Venice, uses it alongside the title of ''patrikios'' to refer to himself, it is commonly accepted that it was created by Emperor Alexios I Komnenos (). It was first conferred to his brother Adrianos, while another early holder, his brother-in-law Michael Taronites, was soon after raised to the even higher title of '' panhypersebastos''. It was also conferred on Sergius VI of Naples and his son, John VI, at about the same time. Later, during the 12th century, it was given to close relatives of the Byzantine emperor, such as the eldest son of a ''sebastokratōr''. In the Palaiologan period it was conferred to leading aristocratic families, such as the Tarchaneiotai, the Raoul, etc. The ''Book on Offices'' by Pseudo-Kodinos, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panhypersebastos
The title of () was a Byzantine court title created by Alexios I Komnenos () using the imperial root (the Greek translation of ). It was always conferred to members of aristocratic families closely allied to the imperial family. Michael Taronites, Alexios I's brother-in-law, was first awarded this title and regarded as almost equal to a . Under the Komnenian emperors, was one of the titles accorded to the emperor's sons-in-law (): the husband of the eldest daughter received the title of , the husband of the second daughter became , and those of the third and fourth received the titles of and respectively. The title remained very important through to the Palaiologan era, coming right after the , but under Andronikos III Palaiologos (), when the future emperor John VI Kantakouzenos was named , the latter office was raised above the . According to Pseudo-Kodinos George Kodinos (), also Pseudo-Kodinos or Codinus, is the conventional name of an anonymous late 15th-century aut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megas Archon
The title of ''megas archōn'' (; "grand archon") was a Byzantine court title during the 13th–14th centuries. History and functions The title of ''megas archōn'' appears originally as a translation of foreign titles, with the meaning of " grand prince"; thus in the middle of the 10th century Emperor Constantine VII Porphyrogennetos calls the Magyar ruler Árpád as "great prince of '' Tourkia'' ungary () in chapter 40 of his ''De Administrando Imperio''. The Nicaean emperor Theodore II Laskaris () first established it as a specific court rank, originally designating the highest-ranking officer of the emperor's retinue. By the time pseudo-Kodinos wrote his ''Book of Offices'' in the mid-14th century, however, it had become a purely honorific dignity without any duties attached. In the ''Book of Offices'', the post is listed in the 35th place of the imperial hierarchy, between the '' prōtospatharios'' and the '' tatas tēs aulēs'', but other contemporary lists of offic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archon
''Archon'' (, plural: , ''árchontes'') is a Greek word that means "ruler", frequently used as the title of a specific public office. It is the masculine present participle of the verb stem , meaning "to be first, to rule", derived from the same root as words such as monarch and hierarchy. Ancient Greece In the early literary period of ancient Greece, the chief magistrates of various Greek city states were called ''archontes''. The term was also used throughout Greek history in a more general sense, ranging from "club leader" to "master of the tables" at '' syssitia'' to "Roman governor". In Athens, a system of three concurrent archons evolved, the three office holders being known as ''archon eponymos'' (), the '' polemarch'' (), and the '' archon basileus'' (). According to Aristotle's '' Constitution of the Athenians'', the power of the king first devolved to the archons, and these offices were filled from the aristocracy by elections every ten years. During this period, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Albania
Southern Albania () is one of the three NUTS-2 Regions of Albania. It consists of five counties: Berat, Fier, Gjirokastër, Korçë and Vlorë. Combined, they have a population of 700,000 as of the 2023 census. The southwestern part of the country is rich in petroleum, and natural gas. Natural asphalt is mined near Selenicë. Four main ethnographic regions traditionally compose Southern Albania: Myzeqeja, Toskëria, Labëria, and Chamëria. In a broader context, Toskëria is sometimes used to describe the whole cultural and linguistic area of southern Albanians (also broadly referred to as Tosks), in duality with Gegëria, which on the other hand is used for that of northern Albanians (also broadly referred to as Ghegs). Southern Albania is often called Northern Epirus by modern Greeks, which Albania rejects as an irredentist term. See also *Northern Albania Northern Albania () is one of the three NUTS-2 regions of Albania, along with Central Albania and South ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progonat
Progonat is a village in the former Kurvelesh municipality, Gjirokastër County, Albania. It is the largest village of upper Kurvelesh and until 1992 was the administrative center of the commune. At the 2015 local government reform it became part of the municipality Tepelenë. Name Its name contains the Albanian suffix -at, widely used to form toponyms from personal names and surnames. The village may be linked to the Progoni family which were an Albanian noble family which established the first Albanian state in recorded history, the Principality of Arbanon. Their descendants may have possibly migrated to this region and founded the village. History Due to the etymology of the village name it has led many historians to believe the village was founded by members of the Progoni family which may have migrated and settled here after the Principality of Arbanon collapsed. This may have happened during the late 13th century. First attested in the Ottoman register of 1432, the vill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mirdita
Mirdita is a region of northern Albania whose territory is synonymous with the historic Albanian tribe of the same name. Etymology The name Mirdita derives from a legendary ancestor named Mir Diti from whom the tribe claims descent. Other alternative folk etymologies have been presented. Another folk etymology links the word to the Albanian greeting "mirëdita" meaning hello, "good day". Geography Historically Mirdita was the largest tribal region of Albania in terms of geographic spread and population. The region is situated in northern Albania, and it borders the traditional tribal areas of Puka (Berisha, Kabashi, Qerreti) in the north; the Lezha highlands (Vela, Bulgëri, Manatia, Kryeziu) in the west and southwest; the northern Albanian coastal plain of Lezha and Zadrima between the Drin and Mat rivers in the west; the river Mat and region of Mat in the south and the area of the Black Drin river in the east. The traditional areas and settlements of Mirdita are: Bisak, B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Albania (medieval)
The Kingdom of Albania (, ) was established by Charles I of Naples, Charles of Anjou in the Albanian territories he conquered from the Byzantine Empire in 1271, with the help of the local Albanian nobility. The Kingdom of Albania was declared in late February 1272. The kingdom extended from the region of Durazzo (Dyrrhachium, modern Durrës) south along the coast to Butrint. A major attempt to advance further in direction of Constantinople failed at the Siege of Berat (1280–1281). A Byzantine counteroffensive soon ensued, which drove the Capetian House of Anjou, Angevins out of the interior by 1281. The Sicilian Vespers further weakened the position of Charles, and the Kingdom was soon reduced by the Byzantine Empire, Byzantines to a small area around Durazzo. The Angevins held out here, however, until 1368, when the city was captured by Karl Thopia. In 1392, Karl Thopia's son surrendered the city to the Republic of Venice. History Background During the conflict between the De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |