|
Productive Efficiency
In microeconomic theory, productive efficiency (or production efficiency) is a situation in which the economy or an economic system (e.g., bank, hospital, industry, country) operating within the constraints of current industrial technology cannot increase production of one good without sacrificing production of another good. In simple terms, the concept is illustrated on a production possibility frontier (PPF), where all points on the curve are points of productive efficiency. An equilibrium may be productively efficient without being allocatively efficient — i.e. it may result in a distribution of goods where social welfare is not maximized (bearing in mind that social welfare is a nebulous objective function subject to political controversy). Productive efficiency is an aspect of economic efficiency that focuses on how to maximize output of a chosen product portfolio, without concern for whether your product portfolio is making goods in the right proportion; in misgu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Production Possibilities Frontier Curve
Production may refer to: Economics and business * Production (economics) * Production, the act of manufacturing goods * Production, in the outline of industrial organization, the act of making products (goods and services) * Production as a statistic, gross domestic product * Production line Arts, entertainment, and media * Production, the act or role of assembling, crafting, creating, or presenting, a work of art, or the work of art itself. Motion pictures * Production, film distributor of a company * Production, phase of filmmaking * Production, video production Other uses in arts, entertainment, and media * ''Production'' (album), by Mirwais, 2000 * Production, category of illusory magic trick * Production, phase of video games development * Production, Record producer's role * Production, theatrical performance Science and technology * Production, deployment environment where changes go "live" and users interact with it * Production (computer science), formal-grammar co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Managerial
Management (or managing) is the administration of organizations, whether businesses, nonprofit organizations, or a government bodies through business administration, nonprofit management, or the political science sub-field of public administration respectively. It is the process of managing the resources of businesses, governments, and other organizations. Larger organizations generally have three hierarchical levels of managers, organized in a pyramid structure: * Senior management roles include the board of directors and a chief executive officer (CEO) or a president of an organization. They set the strategic goals and policy of the organization and make decisions on how the overall organization will operate. Senior managers are generally executive-level professionals who provide direction to middle management. Compare governance. * Middle management roles include branch managers, regional managers, department managers, and section managers. They provide direction to front- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Envelopment Analysis
Data envelopment analysis (DEA) is a nonparametric method in operations research and economics for the estimation of production frontiers.Charnes et al (1978) DEA has been applied in a large range of fields including international banking, economic sustainability, police department operations, and logistical applicationsCharnes et al (1995)Emrouznejad et al (2016)Thanassoulis (1995) Additionally, DEA has been used to assess the performance of natural language processing models, and it has found other applications within machine learning.Zhou et al (2022)Guerrero et al (2022) Description DEA is used to empirically measure productive efficiency of decision-making units (DMUs). Although DEA has a strong link to production theory in economics, the method is also used for benchmarking in operations management, whereby a set of measures is selected to benchmark the performance of manufacturing and service operations. In benchmarking, the efficient DMUs, as defined by DEA, may not nece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economies Of Scale
In microeconomics, economies of scale are the cost advantages that enterprises obtain due to their scale of operation, and are typically measured by the amount of Productivity, output produced per unit of cost (production cost). A decrease in unit cost, cost per unit of output enables an increase in scale that is, increased production with lowered cost. At the basis of economies of scale, there may be technical, statistical, organizational or related factors to the degree of Market (economics), market control. Economies of scale arise in a variety of organizational and business situations and at various levels, such as a production, plant or an entire enterprise. When average costs start falling as output increases, then economies of scale occur. Some economies of scale, such as capital cost of manufacturing facilities and friction loss of transportation and industrial equipment, have a physical or engineering basis. The economic concept dates back to Adam Smith and the idea o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
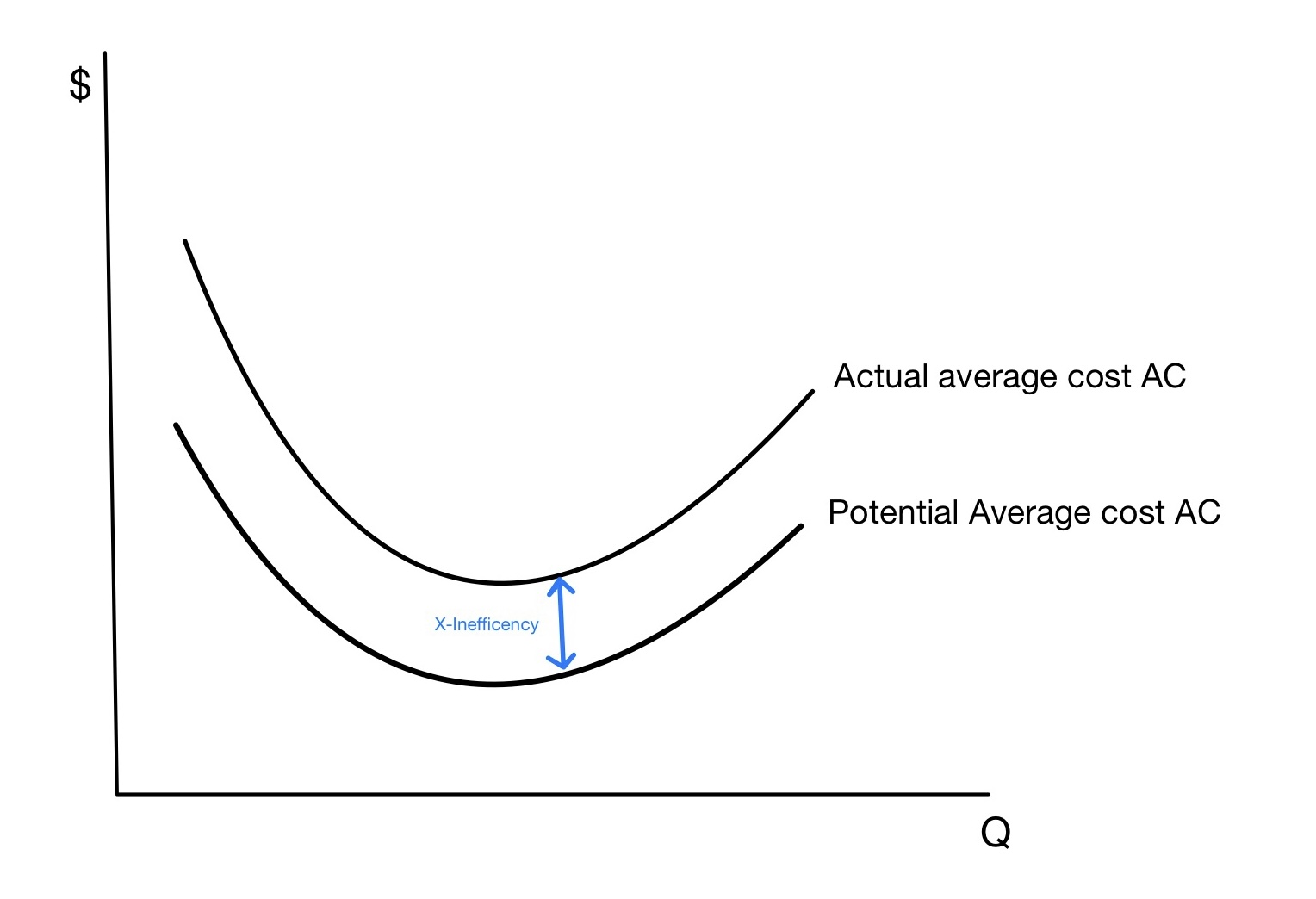
X-inefficiency
X-inefficiency is a concept used in economics to describe instances where firms go through internal inefficiency resulting in higher production costs than required for a given output. This inefficiency can result from various factors, such as outdated technology, inefficient production processes, poor management, and lack of competition, and it results in lower profits for the inefficient firm(s) and higher prices for consumers. The concept of X-inefficiency was introduced by Harvey Leibenstein. in 1966, Harvard University Professor Harvey Leibenstein first introduced the concept of X-inefficiency in his paper "Allocative Efficiency vs. X- Efficiency", which was published in '' American Economic Review''. X-Inefficiency refers to a firm's inability to fully utilize its resources, resulting in an output level that falls short of the maximum potential achievable given the resources and environment which is referred to as the efficiency frontier. More so, X-inefficiency focuses on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monopolistic
A monopoly (from Greek and ) is a market in which one person or company is the only supplier of a particular good or service. A monopoly is characterized by a lack of economic competition to produce a particular thing, a lack of viable substitute goods, and the possibility of a high monopoly price well above the seller's marginal cost that leads to a high monopoly profit. The verb ''monopolise'' or ''monopolize'' refers to the ''process'' by which a company gains the ability to raise prices or exclude competitors. In economics, a monopoly is a single seller. In law, a monopoly is a business entity that has significant market power, that is, the power to charge overly high prices, which is associated with unfair price raises. Although monopolies may be big businesses, size is not a characteristic of a monopoly. A small business may still have the power to raise prices in a small industry (or market). A monopoly may also have monopsony control of a sector of a market. A mono ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marginal Cost
In economics, the marginal cost is the change in the total cost that arises when the quantity produced is increased, i.e. the cost of producing additional quantity. In some contexts, it refers to an increment of one unit of output, and in others it refers to the rate of change of total cost as output is increased by an infinitesimal amount. As Figure 1 shows, the marginal cost is measured in dollars per unit, whereas total cost is in dollars, and the marginal cost is the slope of the total cost, the rate at which it increases with output. Marginal cost is different from average cost, which is the total cost divided by the number of units produced. At each level of production and time period being considered, marginal cost includes all costs that vary with the level of production, whereas costs that do not vary with production are fixed. For example, the marginal cost of producing an automobile will include the costs of labor and parts needed for the additional automobile but not t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Average Cost
In economics, average cost (AC) or unit cost is equal to total cost (TC) divided by the number of units of a good produced (the output Q): AC=\frac. Average cost is an important factor in determining how businesses will choose to price their products. Short-run average cost Short-run costs are those that vary with almost no time lagging. Labor cost and the cost of raw materials are short-run costs, but physical capital is not. An average cost curve can be plotted with cost on the vertical axis and quantity on the horizontal axis. Marginal costs are often also shown on these graphs, with marginal cost representing the cost of the last unit produced at each point; marginal costs in the short run are the slope of the variable cost curve (and hence the first derivative of variable cost). A typical average cost curve has a U-shape, because fixed costs are all incurred before any production takes place and marginal costs are typically increasing, because of diminishing mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perfect Competition
In economics, specifically general equilibrium theory, a perfect market, also known as an atomistic market, is defined by several idealizing conditions, collectively called perfect competition, or atomistic competition. In Economic model, theoretical models where conditions of perfect competition hold, it has been demonstrated that a Market (economics), market will reach an Economic equilibrium, equilibrium in which the quantity supplied for every Goods and services, product or service, including Workforce, labor, equals the quantity demanded at the current price. This equilibrium would be a Pareto optimum. Perfect competition provides both allocative efficiency and productive efficiency: * Such markets are ''allocatively efficient'', as output will always occur where marginal cost is equal to average revenue i.e. price (MC = AR). In perfect competition, any Profit maximization, profit-maximizing producer faces a market price equal to its marginal cost (P = MC). This implies that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long-run Equilibrium
In economics, the long-run is a theoretical concept in which all markets are in equilibrium, and all prices and quantities have fully adjusted and are in equilibrium. The long-run contrasts with the short-run, in which there are some constraints and markets are not fully in equilibrium. More specifically, in microeconomics there are no fixed factors of production in the long-run, and there is enough time for adjustment so that there are no constraints preventing changing the output level by changing the capital stock or by entering or leaving an industry. This contrasts with the short-run, where some factors are variable (dependent on the quantity produced) and others are fixed (paid once), constraining entry or exit from an industry. In macroeconomics, the long-run is the period when the general price level, contractual wage rates, and expectations adjust fully to the state of the economy, in contrast to the short-run when these variables may not fully adjust. History The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Workforce
In macroeconomics, the workforce or labour force is the sum of people either working (i.e., the employed) or looking for work (i.e., the unemployed): \text = \text + \text Those neither working in the marketplace nor looking for work are out of the labour force. The sum of the labour force and out of the labour force results in the noninstitutional civilian population, that is, the number of people who (1) work (i.e., the employed), (2) can work but don't, although they are looking for a job (i.e., the unemployed), or (3) can work but don't, and are not looking for a job (i.e., out of the labour force). Stated otherwise, the noninstitutional civilian population is the total population minus people who cannot or choose not to work (children, retirees, soldiers, and incarcerated people). The noninstitutional civilian population is the number of people potentially available for civilian employment. \begin \text &= \text + \text \\ & ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Capital
Physical capital represents in economics one of the three primary factors of production. Physical capital is the apparatus used to produce a good and services. Physical capital represents the tangible man-made goods that help and support the production. Inventory, cash, equipment or real estate are all examples of physical capital. Definition N.G. Mankiw definition from the book Economics: '' Capital is the equipment and structures used to produce goods and services. Physical capital consists of man-made goods (or input into the process of production) that assist in the production process. Cash, real estate, equipment, and inventory are examples of physical capital.'' Capital goods represents one of the key factors of corporation function. Generally, capital allows a company to preserve liquidity while growing operations, it refers to physical assets in business and the way a company have reached their physical capital. While referring how companies have obtained their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |