|
Proculeia Gens
The gens Proculeia was a minor plebeian family at ancient Rome. Members of this gens are first mentioned at the end of the Republic. Gaius Proculeius was one of the most trusted friends and advisers of Octavian, and one of those whom he considered a possible heir. None of the Proculeii ever obtained the consulship, but a number are known from inscriptions. Origin The nomen ''Proculeius'', belongs to a common class of gentilicia ending in the diminutive suffix '-eius', often although not exclusively formed from other names ending in '-a' or '-as'. In this case, the name is a patronymic surname derived from the old praenomen '' Proculus'', which Festus reported was originally given to a child born when his father was far from home, although the name has the appearance of a diminutive of some other word or name, such as ''procus'', a suitor, or perhaps more likely ''procer'', a prince.Chase, p. 145. ''Proca'', sometimes given as ''Procas'', another possibility, was the name of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plebs
In ancient Rome, the plebeians (also called plebs) were the general body of free Roman citizens who were not patricians, as determined by the census, or in other words " commoners". Both classes were hereditary. Etymology The precise origins of the group and the term are unclear, but may be related to the Greek, ''plēthos'', meaning masses. In Latin, the word is a singular collective noun, and its genitive is . Plebeians were not a monolithic social class. Those who resided in the city and were part of the four urban tribes are sometimes called the , while those who lived in the country and were part of the 31 smaller rural tribes are sometimes differentiated by using the label . ( List of Roman tribes) In ancient Rome In the annalistic tradition of Livy and Dionysius, the distinction between patricians and plebeians was as old as Rome itself, instituted by Romulus' appointment of the first hundred senators, whose descendants became the patriciate. Modern hypothese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sextus (praenomen)
''Sextus'' () is a Latin ''praenomen'', or personal name, which was common throughout all periods of Roman history. It was used by both patrician and plebeian families, and gave rise to the patronymic ''gentes Sextia'' and '' Sextilia''. The feminine form is ''Sexta''. The name was regularly abbreviated Sex., but occasionally is found abbreviated S. (usually used for the praenomen ''Spurius''), or Sext.''Dictionary of Greek & Roman Biography & Mythology'' ''Sextus'' was about the tenth most-common praenomen for most of Roman history, although it became slightly more common in imperial times, as other praenomina declined in popularity. Many families did not use it, but it was widespread amongst all social classes, and was favored by some families. The name survived the collapse of Roman civil institutions in the 5th and 6th centuries, and has continued in use into modern times. Origin and meaning of the name ''Sextus'' is the Latin word for ''sixth'', and it falls into a class of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cologne
Cologne ( ; german: Köln ; ksh, Kölle ) is the largest city of the German western state of North Rhine-Westphalia (NRW) and the fourth-most populous city of Germany with 1.1 million inhabitants in the city proper and 3.6 million people in the urban region. Centered on the left (west) bank of the Rhine, Cologne is about southeast of NRW's state capital Düsseldorf and northwest of Bonn, the former capital of West Germany. The city's medieval Catholic Cologne Cathedral (), the third-tallest church and tallest cathedral in the world, constructed to house the Shrine of the Three Kings, is a globally recognized landmark and one of the most visited sights and pilgrimage destinations in Europe. The cityscape is further shaped by the Twelve Romanesque churches of Cologne, and Cologne is famous for Eau de Cologne, that has been produced in the city since 1709, and "cologne" has since come to be a generic term. Cologne was founded and established in Germanic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
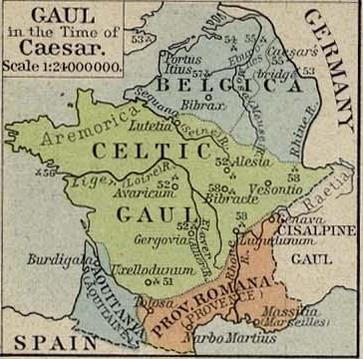
Gallia Lugdunensis
Gallia Lugdunensis (French: ''Gaule Lyonnaise'') was a province of the Roman Empire in what is now the modern country of France, part of the Celtic territory of Gaul formerly known as Celtica. It is named after its capital Lugdunum (today's Lyon), possibly Roman Europe's major city west of Italy, and a major imperial mint. Outside Lugdunum was the Sanctuary of the Three Gauls, where representatives met to celebrate the cult of Rome and Augustus. History In ''De Bello Gallico'' describing his conquest of Gaul (58–50 BC), Julius Caesar distinguished between ''provincia nostra'' in the south of Gaul, which already was a Roman province in his time, and the three other parts of Gaul: the territories of the ''Aquitani'', of the ''Belgae'', and of the ''Galli'' also known as the ''Celtae''. The territory of the Galli extended from the rivers Seine and Marne in the north-east, which formed the boundary with Gallia Belgica, to the river Garonne in the south-west, which formed the bor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lugdunum
Lugdunum (also spelled Lugudunum, ; modern Lyon, France) was an important Roman city in Gaul, established on the current site of Lyon. The Roman city was founded in 43 BC by Lucius Munatius Plancus, but continued an existing Gallic settlement with a likely population of several thousands. It served as the capital of the Roman province of Gallia Lugdunensis and was an important city in the western half of the Roman Empire for centuries. Two emperors, Claudius and Caracalla, were born in Lugdunum. In the period 69–192 AD, the city's population may have numbered 50,000 to 100,000, and possibly up to 200,000 inhabitants. The original Roman city was situated west of the confluence of the Rhône and Saône, on the Fourvière heights. By the late centuries of the empire much of the population was located in the Saône River valley at the foot of Fourvière. Name The Roman city was founded as ''Colonia Copia Felix Munatia'', a name invoking prosperity and the blessing of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Syria
Roman Syria was an early Roman province annexed to the Roman Republic in 64 BC by Pompey in the Third Mithridatic War following the defeat of Kingdom of Armenia (antiquity), King of Armenia Tigranes the Great. Following the partition of the Herodian Kingdom of Judea into Tetrarchy, tetrarchies in 6 AD, it was gradually absorbed into Roman provinces, with Roman Syria annexing Iturea and Trachonitis (tetrarchy), Iturea and Trachonitis. Provincia Syria Syria was annexed to the Roman Republic in 64 BC, when Pompey, Pompey the Great had the Seleucid Empire, Seleucid king Antiochus XIII Asiaticus executed and deposed his successor Philip II Philoromaeus. Pompey appointed Marcus Aemilius Scaurus (praetor 56 BC), Marcus Aemilius Scaurus to the post of Proconsul of Syria. Following the fall of the Roman Republic and its transformation into the Roman Empire, Syria became a Roman imperial province, governed by a Legatus, Legate. During the early empire, the Roman army in Syria accounte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latakia
, coordinates = , elevation_footnotes = , elevation_m = 11 , elevation_ft = , postal_code_type = , postal_code = , area_code = Country code: 963 City code: 41 , geocode = C3480 , blank_name = Climate , blank_info = Csa , blank_name_sec2 = International airport , blank_info_sec2 = Bassel Al-Assad International Airport , timezone = EET , utc_offset = +2 , timezone_DST = EEST , utc_offset_DST = +3 , blank1_name = , blank1_info = , website eLatakia, footnotes = Latakia or Lattakia ( ar, ٱللَّاذْقِيَّة/ ٱللَّاذِقِيَّة, '; Syrian pronunciation: ) is the principal port city of Syria and capital city of the Latakia Governorate located on the Mediterranean The Mediterranean Sea is a sea conne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hierophant
A hierophant ( grc, ἱεροφάντης) is a person who brings religious congregants into the presence of that which is deemed ''holy''. As such, a hierophant is an interpreter of sacred mysteries and arcane principles. The word comes from ancient Greece, where it was constructed from the combination of ''ta hiera'' ('the holy') and ''phainein'' ('to show'). Greek priesthood In Attica, ''Hierophant'' was the title of the chief priest at the Eleusinian Mysteries. It was an office inherited within the Philaidae or Eumolpidae families. The office of Hierophant, High Priestess and Dadouchousa Priestess were all inherited within the Philaidae or Eumolpidae families, and the Hierophant and the High Priestess were of equal rank.Pomeroy, Sarah B, Goddesses, whores, wives, and slaves: women in classical antiquity, Schocken Books, New York, 1995 It was the task of the High Priestess to impersonate the roles of the goddesses Demeter and Persephone in the enactment during the Mysteries. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proclus Of Laodicea
Proclus ( el, Πρόκλος) or Proculeius, son of the physician Themison, was a hierophant at Laodiceia in Syria. He wrote, according to the Suda, the following works: *''On the gods'' (θεολογία) *''On the myth of Pandora in Hesiod'' (εἰς τὴν παρ' Ἡσιόδῳ τῆς Πανδώρας μῦθον) *''On golden words'' (εἰς τὰ χρυσᾶ ἔπη) *''On Nicomachus' introduction to number theory'' (εἰς τὴν Νικομάχου εἰσαγωγὴν τῆς ἀριθμητικῆς) *some geometrical treatises He is also mentioned by Damascius in a commentary on Plato. Although a commentary on the Pythagorean ''Golden Verses The ''Golden Verses'' ( grc-gre, Χρύσεα Ἔπη, ; la, Aurea Carmina) are a collection of moral exhortations comprising 71 lines written in dactylic hexameter. They are traditionally attributed to Pythagoras. Overview The exact origins o ...'', known through a translation into Arabic (in the El Escorial library ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaius Maecenas
Gaius Cilnius Maecenas ( – 8 BC) was a friend and political advisor to Octavian (who later reigned as emperor Augustus). He was also an important patron for the new generation of Augustan poets, including both Horace and Virgil. During the reign of Augustus, Maecenas served as a quasi- culture minister to the Roman emperor but in spite of his wealth and power he chose not to enter the Senate, remaining of equestrian rank. Biography Expressions in Propertius seem to imply that Maecenas had taken some part in the campaigns of Mutina, Philippi, and Perugia. He prided himself on his ancient Etruscan lineage, and claimed descent from the princely house of the Cilnii, who excited the jealousy of their townsmen by their preponderant wealth and influence at Arretium in the 4th century BC. Horace makes reference to this in his address to Maecenas at the opening of his first books of '' Odes'' with the expression "atavis edite regibus" (descendant of kings). Tacitus refers to him ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aulus Terentius Varro Murena
Aulus Terentius Varro Murena (died 24 BC) was a Roman general and politician of the 1st century BC. Biography Murena was the natural born son of Aulus Terentius Varro, and adopted brother to Lucius Licinius Varro Murena. He was well connected to the Augustan regime, with his sister, Terentia, married to Gaius Maecenas, the prominent adviser and friend of Augustus and patron of the arts, while his half-brother, Gaius Proculeius, was an intimate friend of Augustus during his rise to power. Augustus dispatched Murena to lead an expedition against the Salassi tribe of the Aosta Valley region in the northwestern Alps in 25 BC. The Salassi had proved troublesome to Roman armies using the Great St Bernard pass, which, as the shortest route from Italy to the Upper Rhine river, had become strategically vital to the Romans since the completion of Julius Caesar's conquest of Gaul in 51 BC. The Salassi were utterly defeated and, according to Strabo, Murena deported and sold into slavery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Actium
The Battle of Actium was a naval battle fought between a maritime fleet of Octavian led by Marcus Agrippa and the combined fleets of both Mark Antony and Cleopatra VII Philopator. The battle took place on 2 September 31 BC in the Ionian Sea, near the former Roman colony of Actium, Greece, and was the climax of over a decade of rivalry between Octavian and Antony. In early 31 BC, the year of the battle, Antony and Cleopatra were temporarily stationed in Greece. Mark Antony possessed 500 ships and 70,000 infantry, and made his camp at Actium, and Octavian, with 400 ships and 80,000 infantry, arrived from the north and occupied Patrae and Corinth, where he managed to cut Antony’s southward communications with Egypt (via the Peloponnese) with help from Marcus Agrippa. Octavian previously gained a preliminary victory in Greece, where his navy successfully ferried troops across the Adriatic Sea under the command of Marcus Agrippa. Octavian landed on mainland Greece, opposite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |