|
Process Capability Index
The process capability index, or process capability ratio, is a statistical measure of process capability: the ability of an engineering process to produce an output within specification limits. The concept of process capability only holds meaning for processes that are in a state of statistical control. This means it cannot account for deviations which are not expected, such as misaligned, damaged, or worn equipment. Process capability indices measure how much "natural variation" a process experiences relative to its specification limits, and allows different processes to be compared to how well an organization controls them. Somewhat counterintuitively, higher index values indicate better performance, with zero indicating high deviation. Example for non-specialists A company produces axles with nominal diameter 20 mm on a lathe. As no axle can be made to ''exactly'' 20 mm, the designer specifies the maximum admissible deviations (called tolerances or specification li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Process Capability
The process capability is a measurable property of a process to the specification, expressed as a process capability index (e.g., Cpk or Cpm) or as a process performance index (e.g., Ppk or Ppm). The output of this measurement is often illustrated by a histogram and calculations that predict how many parts will be produced out of specification (OOS). Two parts of process capability are: 1) measure the variability of the output of a process, and 2) compare that variability with a proposed specification or product tolerance. Capabilities The input of a process usually has at least one or more measurable characteristics that are used to specify outputs. These can be analyzed statistically; where the output data shows a normal distribution the process can be described by the process mean (average) and the standard deviation. A process needs to be established with appropriate process controls in place. A control chart analysis is used to determine whether the process is "in statist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butterworth-Heinemann
Butterworth–Heinemann is a British publishing company specialised in professional information and learning materials for higher education and professional training, in printed and electronic forms. It was formed in 1990 by the merger of Heinemann Professional Publishing and Butterworths Scientific, both subsidiaries of Reed International. With its earlier constituent companies, the founding dates back to 1923. It has publishing units in Oxford (UK) and Waltham, Massachusetts (United States). As of 2006, it is an imprint of Elsevier. See also *LexisNexis Butterworths LexisNexis is a part of the RELX corporation that sells data analytics products and various databases that are accessed through online portals, including portals for computer-assisted legal research (CALR), newspaper search, and consumer informa ... References External links * Book publishing companies of the United Kingdom Elsevier imprints {{publish-corp-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Process Performance Index
In process improvement efforts, the process performance index is an estimate of the process capability of a process during its initial set-up, ''before'' it has been brought into a state of statistical control. Formally, if the upper and lower specifications of the process are USL and LSL, the estimated mean of the process is \hat, and the estimated variability of the process (expressed as a standard deviation) is \hat, then the process performance index is defined as: :\hat_ = \min \Bigg , \Bigg/MATH> \hat is estimated using the sample standard deviation. Ppk may be negative if the process mean falls outside the specification limits (because the process is producing a large proportion of defective output). Some specifications may only be one sided (for example, strength). For specifications that only have a lower limit, \hat_ = ; for those that only have an upper limit, \hat_ = . Practitioners may also encounter \hat_ = \frac , a metric that does not account for process perf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Process Capability
The process capability is a measurable property of a process to the specification, expressed as a process capability index (e.g., Cpk or Cpm) or as a process performance index (e.g., Ppk or Ppm). The output of this measurement is often illustrated by a histogram and calculations that predict how many parts will be produced out of specification (OOS). Two parts of process capability are: 1) measure the variability of the output of a process, and 2) compare that variability with a proposed specification or product tolerance. Capabilities The input of a process usually has at least one or more measurable characteristics that are used to specify outputs. These can be analyzed statistically; where the output data shows a normal distribution the process can be described by the process mean (average) and the standard deviation. A process needs to be established with appropriate process controls in place. A control chart analysis is used to determine whether the process is "in statist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
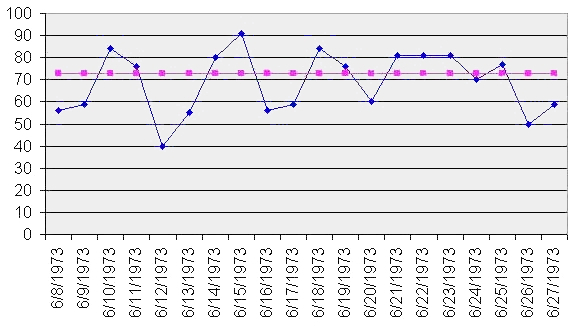
Run Chart
A run chart, also known as a run-sequence plot is a graph that displays observed data in a time sequence. Often, the data displayed represent some aspect of the output or performance of a manufacturing or other business process. It is therefore a form of line chart. Overview Run sequence plots are an easy way to graphically summarize a univariate data set. A common assumption of univariate data sets is that they behave like:NIST/SEMATECH (2003)"Run-Sequence Plot"In: ''e-Handbook of Statistical Methods'' 6/01/2003 (Date created). * random drawings; * from a fixed distribution; * with a common location; and * with a common scale. With run sequence plots, shifts in location and scale are typically quite evident. Also, outliers can easily be detected. Examples could include measurements of the fill level of bottles filled at a bottling plant or the water temperature of a dish-washing machine each time it is run. Time is generally represented on the horizontal (x) axis and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrometre
The micrometre ( international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: μm) or micrometer ( American spelling), also commonly known as a micron, is a unit of length in the International System of Units (SI) equalling (SI standard prefix " micro-" = ); that is, one millionth of a metre (or one thousandth of a millimetre, , or about ). The nearest smaller common SI unit is the nanometre, equivalent to one thousandth of a micrometre, one millionth of a millimetre or one billionth of a metre (). The micrometre is a common unit of measurement for wavelengths of infrared radiation as well as sizes of biological cells and bacteria, and for grading wool by the diameter of the fibres. The width of a single human hair ranges from approximately 20 to . The longest human chromosome, chromosome 1, is approximately in length. Examples Between 1 μm and 10 μm: * 1–10 μm – length of a typical bacterium * 3–8 μm � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Control Chart
Control charts is a graph used in production control to determine whether quality and manufacturing processes are being controlled under stable conditions. (ISO 7870-1) The hourly status is arranged on the graph, and the occurrence of abnormalities is judged based on the presence of data that differs from the conventional trend or deviates from the control limit line. Control charts are classified into Shewhart individuals control chart (ISO 7870-2) and CUSUM(CUsUM)(or cumulative sum control chart)(ISO 7870-4). Control charts, also known as Shewhart charts (after Walter A. Shewhart) or process-behavior charts, are a statistical process control tool used to determine if a manufacturing or business process is in a state of control. It is more appropriate to say that the control charts are the graphical device for Statistical Process Monitoring (SPM). Traditional control charts are mostly designed to monitor process parameters when the underlying form of the process distributio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normally Distributed
In statistics, a normal distribution or Gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real-valued random variable. The general form of its probability density function is : f(x) = \frac e^ The parameter \mu is the mean or expectation of the distribution (and also its median and mode), while the parameter \sigma is its standard deviation. The variance of the distribution is \sigma^2. A random variable with a Gaussian distribution is said to be normally distributed, and is called a normal deviate. Normal distributions are important in statistics and are often used in the natural and social sciences to represent real-valued random variables whose distributions are not known. Their importance is partly due to the central limit theorem. It states that, under some conditions, the average of many samples (observations) of a random variable with finite mean and variance is itself a random variable—whose distribution converges to a normal distrib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probability Density Function
In probability theory, a probability density function (PDF), or density of a continuous random variable, is a function whose value at any given sample (or point) in the sample space (the set of possible values taken by the random variable) can be interpreted as providing a ''relative likelihood'' that the value of the random variable would be close to that sample. Probability density is the probability per unit length, in other words, while the ''absolute likelihood'' for a continuous random variable to take on any particular value is 0 (since there is an infinite set of possible values to begin with), the value of the PDF at two different samples can be used to infer, in any particular draw of the random variable, how much more likely it is that the random variable would be close to one sample compared to the other sample. In a more precise sense, the PDF is used to specify the probability of the random variable falling ''within a particular range of values'', as opposed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parts Per Million
In science and engineering, the parts-per notation is a set of pseudo-units to describe small values of miscellaneous dimensionless quantities, e.g. mole fraction or mass fraction. Since these fractions are quantity-per-quantity measures, they are pure numbers with no associated units of measurement. Commonly used are parts-per-million (ppm, ), parts-per-billion (ppb, ), parts-per-trillion (ppt, ) and parts-per-quadrillion (ppq, ). This notation is not part of the International System of Units (SI) system and its meaning is ambiguous. Overview Parts-per notation is often used describing dilute solutions in chemistry, for instance, the relative abundance of dissolved minerals or pollutants in water. The quantity "1 ppm" can be used for a mass fraction if a water-borne pollutant is present at one-millionth of a gram per gram of sample solution. When working with aqueous solutions, it is common to assume that the density of water is 1.00 g/mL. Therefore, it is common to e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defects Per Million Opportunities
In process improvement efforts, defects per million opportunities or DPMO (or nonconformities per million opportunities (NPMO)) is a measure of process performance. It is defined as :DPMO = \frac A defect can be defined as a nonconformance of a quality characteristic (e.g. strength, width, response time) to its specification. DPMO is stated in opportunities per million units for convenience: Processes that are considered highly capable (e.g., processes of Six Sigma quality) are those that experience fewer than 3.4 defects per million opportunities (or services provided). Note that DPMO differs from reporting defective parts per million (PPM) in that it comprehends the possibility that a unit under inspection may be found to have multiple defects of the same type or may have multiple types of defects. Identifying specific opportunities for defects (and therefore how to count and categorize defects) is an art, but generally organizations consider the following when defining the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)