|
Principality Of Lippe
Lippe (later Lippe-Detmold and then again Lippe) was a state in Germany, ruled by the House of Lippe. It was located between the Weser river and the southeast part of the Teutoburg Forest. It originated as a state during the Holy Roman Empire, and was promoted to the status of principality in 1789. During this period the ruling house split into a number of branches, with the main line residing at Detmold. During the Reformation, Lippe had converted to Lutheranism in 1538 and then to Calvinism in 1604. From the demise of the empire in 1806, the principality was independent, but it joined the North German Confederation in 1866 and became one of the States of the German Empire in 1871. Over the course of the nineteenth century it gradually developed into a constitutional monarchy with moderate participation in government for the landed nobility. Its economy was overwhelmingly agrarian and among the weakest in the German Empire. After the last prince abdicated in 1918, it continued a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
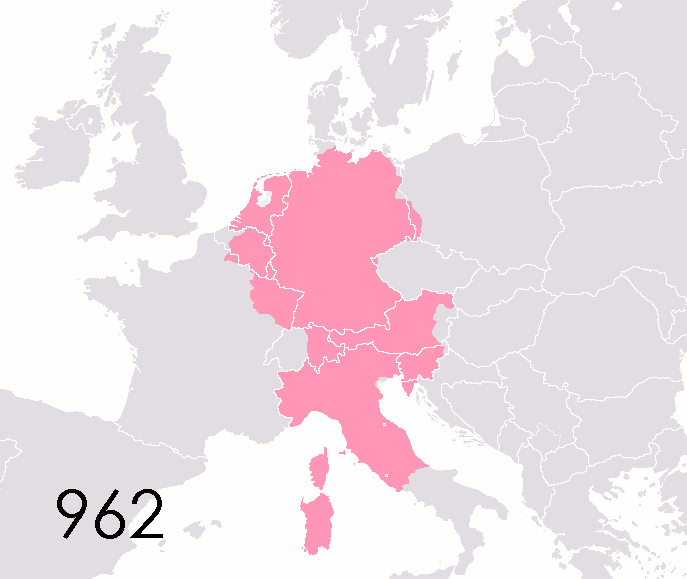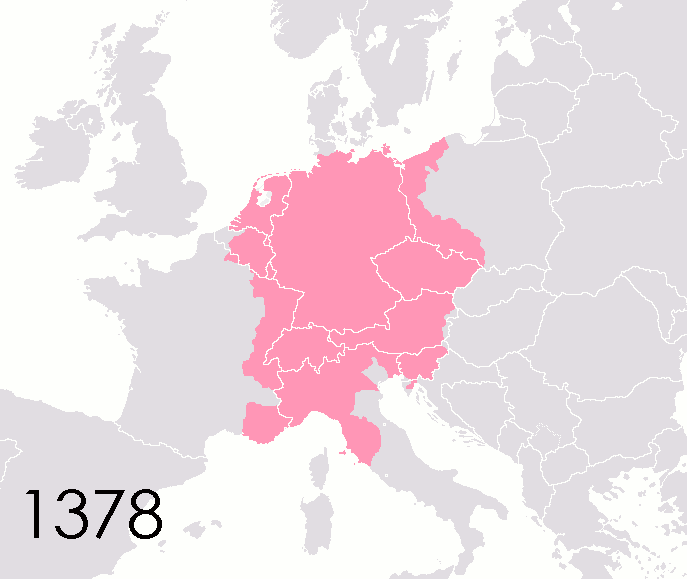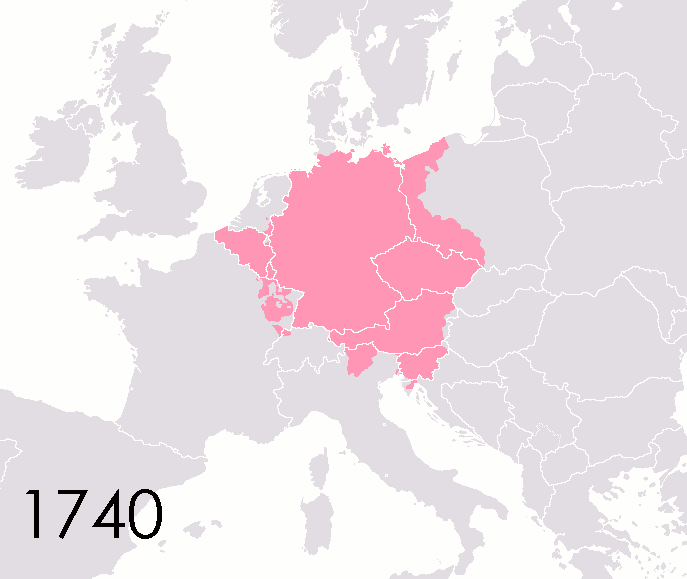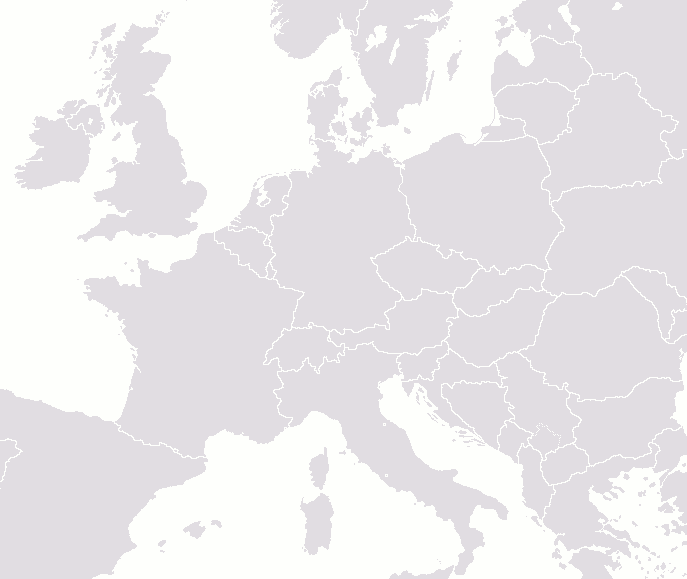
States Of The Holy Roman Empire
This list of states in the Holy Roman Empire includes any territory ruled by an authority that had been granted imperial immediacy, as well as many other feudal entities such as lordships, sous-fiefs, and allodial fiefs. The Holy Roman Empire was a complex political entity that existed in central Europe for most of the medieval and early modern periods and was generally ruled by a German-speaking Emperor. The states that composed the Empire, while enjoying a form of territorial authority called '' Landeshoheit'' that granted them many attributes of sovereignty, were never fully sovereign states in the sense that term is understood presently. In the 18th century, the Holy Roman Empire consisted of approximately 1,800 such territories, the majority being tiny estates owned by the families of Imperial Knights. This page does not directly contain the list but discusses the format of the various lists and offers some background to understand the complex organisation of the Holy Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teutoburg Forest
The Teutoburg Forest ( ; ) is a range of low, forested hills in the German states of Lower Saxony and North Rhine-Westphalia. Until the 17th century, the official name of the hill ridge was Osning. It was first renamed the ''Teutoburg Forest'' in 1616 in commemoration of the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest in 9 AD, which most likely took place at Kalkriese instead. Geography The Teutoburg Forest is a peripheral section in the north of the German Central Uplands, and forms a long narrow range of hills (comprising three ridges) extending from the eastern surroundings of Paderborn in the south to the western surroundings of Osnabrück in the northwest. South of the city centre of Bielefeld, a gap called the Bielefeld Pass bisects the range into the ''Northern Teutoburg Forest'' (two thirds) and ''Southern Teutoburg Forest'' (one third). In addition, the northeastern and southwestern ridges are cut by the exits of the longitudinal valleys between the ridges. The geologically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graf
(; feminine: ) is a historical title of the German nobility and later also of the Russian nobility, usually translated as "count". Considered to be intermediate among noble ranks, the title is often treated as equivalent to the British title of "earl" (whose female version is "countess"). The German nobility was gradually divided into high and low nobility. The high nobility included those counts who ruled immediate imperial territories of "princely size and importance" for which they had a seat and vote in the Imperial Diet (Holy Roman Empire), Imperial Diet. Etymology and origin The word derives from , which is usually derived from . is in turn thought to come from the Byzantine Empire, Byzantine title , which ultimately derives from the Greek verb () 'to write'. Other explanations have been put forward, however; Jacob Grimm, Jacob and Wilhelm Grimm, while still noting the potential of a Greek derivation, suggested a connection to , meaning 'decision, decree'. However, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simon V, Count Of Lippe
Count Simon V of Lippe (1471September 17, 1536) was Noble Lord of Lippe, and from 1528 Count of Lippe. During his reign, the Reformation was introduced in Lippe. Life Simon V was the fifth child and eldest son of Bernard VII, Lord of Lippe, Bernard VII "the Bellicose" and Anna of Holstein-Pinneberg and inherited Lippe after his father's death, around 1511. In 1528, he was raised to Imperial Count and Lippe became one of about 140 Imperial Counties. Since 1518, the Reformation had prevailed, first in Lemgo and then in other cities in Lippe. An open conflict arose in 1530 when Protestant hymns were sung during a Catholic Easter Mass. Simon, who remained a Catholic all his life, was outraged, and spoke of ''insurgent farmers who refuse to endure any authority over themselves''. He was, however, a vassal of two liege lords: the Bishop of Prince-Bishopric of Paderborn, Paderborn and Philip I, Landgrave of Hesse, who had been a Lutheran since 1524. This limited his freedom to act. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry The Lion
Henry the Lion (; 1129/1131 – 6 August 1195), also known as Henry III, Duke of Saxony (ruled 1142-1180) and Henry XII, Duke of Bavaria (ruled 1156-1180), was a member of the Welf dynasty. Henry was one of the most powerful German princes of his time. As the Duke of Saxony, Henry had had a decisive part in 1152 in his cousin Frederick Barbarossa's campaign for the throne. Because of this, in the following years, he was intensely promoted by Barbarossa. So, in 1156, he received the Dukedom of Bavaria. In North Germany, Henry could now build a kingly presence. He achieved this in Brunswick by building a new collegiate church, St Blaise, and, in the neighbouring Dankwarderode Castle, he placed a statue of a lion, as a symbol of its place as the capital of his duchies. The aggressive building strategy of the Duke in Saxony and north of the Elbe supplanted the influence of the previous greats of Saxony. Next, Henry repaid Barbarossa’s sponsorship by putting great effort into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Saxony
The Duchy of Saxony () was originally the area settled by the Saxons in the late Early Middle Ages, when they were subdued by Charlemagne during the Saxon Wars from 772 CE and incorporated into the Carolingian Empire (Francia) by 804. Upon the 843 Treaty of Verdun, Saxony was one of the five German stem duchies of East Francia; Duke Henry the Fowler was elected List of German monarchs, German king in 919. Upon the deposition of the House of Welf, Welf duke Henry the Lion in 1180, the ducal title fell to the House of Ascania, while numerous territories split from Saxony, such as the Principality of Anhalt in 1218 and the Welf Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg in 1235. In 1296, the remaining lands were divided between the Ascanian dukes of Saxe-Lauenburg and Duchy of Saxe-Wittenberg, Saxe-Wittenberg, the latter obtaining the title of Electorate of Saxony, Electors of Saxony by the Golden Bull of 1356. Geography The Saxon stem duchy covered the greater part of present-day Northern Germ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernard II, Lord Of Lippe
Bernard II (; 30 April 1224) was Lord of Lippe from 1167 until 1196. He founded the towns of Lippstadt and Lemgo. Marriage and children In 1167, Bernard married Heilwig (1150–1196), likely the daughter of Otto, Count of Are-Hochstaden. They had eleven children who survived into adulthood. Five sons: * Herman II (117525 Apr 1229) * Otto II († 28 Jul 1227); Bishop of Utrecht from 1215 * Bernard IV († 14 Apr 1247); Bishop of Paderborn from 1228 * Dietrich († 28 Jul 1227); killed at the Battle of Ane * Gerhard II (28 August 1258); Archbishop of Bremen from 1219 Six daughters: * Ethelind, Abess of Bassum Bassum (; Northern Low Saxon: ''Bassen'') is a town in the Diepholz (district), district of Diepholz, Lower Saxony, Germany. It is situated approximately 35 km northeast of Diepholz, and 25 km south of Bremen. Geography Subdivision ... from to * Gertrud II, Abbess of the Imperial Abbey at Herford from 1217 to 1239 * Kunigunde, Abbess of Freckenhors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edler
Edler () was until 1919 the lowest rank of nobility in Austria-Hungary and Germany, just beneath a '' Ritter'' (hereditary knight), but above untitled nobles, who used only the nobiliary particle ''von'' before their surname. It was mostly given to civil servants and military officers, as well as those upon whom the lower rank of an Order had been conferred. The noun ''Edler'' comes from the adjective ''edel'' ("noble"), and translated literally means "noble erson. In accordance with the rules of German grammar, the word can also appear as ''Edle'', ''Edlem'', or ''Edlen'' depending on case, gender, and number. Originally, from the Middle Ages, under the feudal system (in Europe and elsewhere), the nobility were generally those who held a fief, often in the form of heritable land worked by vassals. To preserve the feudal naming practice, even in cases where upper-ranking bureaucrats received patents of nobility for long service or merit, as in the 18th, 19th, and early 20th centu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lothair II, Holy Roman Emperor
Lothair III, sometimes numbered Lothair II and also known as Lothair of Supplinburg ( June 1075 – 4 December 1137), was Holy Roman Emperor from 1133 until his death. He was appointed Duke of Saxony in 1106 and elected King of Germany in 1125 before being crowned emperor in Rome. The son of the Saxon count Gebhard of Supplinburg, his reign was troubled by the constant intriguing of the Hohenstaufens, Duke Frederick II of Swabia and Duke Conrad of Franconia. He died while returning from a successful campaign against the Norman Kingdom of Sicily. Rise to power In 1013, a certain Saxon nobleman named ''Liutger'' was mentioned as a count in or of the Harzgau subdivision of Eastphalia. His grandson Count Gebhard, father of Emperor Lothair, possibly acquired the castle of Süpplingenburg about 1060 via his marriage with Hedwig, a daughter of the Bavarian count Frederick of Formbach and his wife Gertrud, herself a descendant of the Saxon margrave Dietrich of Haldensleben who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernard I, Lord Of Lippe
Bernhard I (c. 1090c. 1158) was the first Lord of Lippe in what is now part of Germany. He ruled Lippe from 1123 to 1158. References 1090s births 1150s deaths House of Lippe Lords of Lippe {{Germany-noble-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Rhine-Westphalia
North Rhine-Westphalia or North-Rhine/Westphalia, commonly shortened to NRW, is a States of Germany, state () in Old states of Germany, Western Germany. With more than 18 million inhabitants, it is the List of German states by population, most populous state in Germany. Apart from the city-states (Berlin, Hamburg and Bremen), it is also the List of German states by population density, most densely populated state in Germany. Covering an area of , it is the List of German states by area, fourth-largest German state by size. North Rhine-Westphalia features 30 of the 81 German municipalities with over 100,000 inhabitants, including Cologne (over 1 million), the state capital Düsseldorf (630,000), Dortmund and Essen (about 590,000 inhabitants each) and other cities predominantly located in the Rhine-Ruhr metropolitan area, the largest urban area in Germany and the fourth-largest on the European continent. The location of the Rhine-Ruhr at the heart of the European Blue Banana make ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free State Of Lippe
The Free State of Lippe () was created following the abdication of Prince Leopold IV of the Principality of Lippe on 15 November 1918, following the German Revolution. It was a state in Germany during the Weimar Republic and Nazi Germany. After the end of the Second World War, the Control Commission for Germany – British Element (CCG/BE) abolished the state of Lippe in January 1947 and incorporated it into the new German state of North Rhine-Westphalia that had been created three months earlier. Government The Lippe Constitution was passed on 21 December 1920. It established a state parliament consisting of a ''landtag'' of 21 deputies elected for a term of four years by universal suffrage. The state administration consisted of a collective three-man ''Landespräsidium'' (State Presidency), headed by a chairman, that was responsible to the ''landtag'' and could be removed by a vote of no confidence. Technically, the triumvirate as a whole was the head of state and laws we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |