|
Primary Cell Culture
Primary cell culture is the ''ex vivo'' culture of cells freshly obtained from a multicellular organism, as opposed to the culture of immortalized cell lines. In general, primary cell cultures are considered more representative of ''in vivo'' tissues than cell lines, and this is recognized legally in some countries such as the UK ( Human Tissue Act 2004). However, primary cells require adequate substrate and nutrient conditions to thrive and after a certain number of divisions they acquire a senescent phenotype, leading to irreversible cell cycle arrest. The generation of cell lines stems from these two reasons. Primary cells can become immortalized either spontaneously (e.g. HeLa cells) or by genetic modification (e.g. HEK cells), at which point they become cell lines which can be subcultured indefinitely. Because of their requirements for viability, primary cell cultures did not become widespread until the 2000s. These cultures present several advantages over cell lines, inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organoid
An organoid is a miniaturised and simplified version of an organ produced ''in vitro'' in three dimensions that mimics the key functional, structural, and biological complexity of that organ. It is derived from one or a few cells from a tissue, embryonic stem cells, or induced pluripotent stem cells, which can self-organize in three-dimensional culture owing to their self-renewal and differentiation capacities. The technique for growing organoids has rapidly improved since the early 2010s, and '' The Scientist'' named it one of the biggest scientific advancements of 2013. Scientists and engineers use organoids to study development and disease in the laboratory, for drug discovery and development in industry, personalized diagnostics and medicine, gene and cell therapies, tissue engineering, and regenerative medicine.Verstegen, Monique M. A.; Coppes, Rob P.; Beghin, Anne; De Coppi, Paolo; Gerli, Mattia F. M.; de Graeff, Nienke; Pan, Qiuwei; Saito, Yoshimasa; Shi, Shaojun; Zad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tissue Culture
Tissue culture is the growth of tissue (biology), tissues or cell (biology), cells in an artificial medium separate from the parent organism. This technique is also called micropropagation. This is typically facilitated via use of a liquid, semi-solid, or solid growth medium, such as broth or agar. Tissue culture commonly refers to the culture of animal cells and tissues, with the more specific term plant tissue culture being used for plants. The term "tissue culture" was coined by American pathologist Montrose Thomas Burrows. Historical use In 1885 Wilhelm Roux removed a section of the medullary plate of an embryonic chicken and maintained it in a warm saline solution for several days, establishing the basic principle of tissue culture. In 1907 the zoologist Ross Granville Harrison demonstrated the growth of frog embryonic cells that would give rise to nerve cells in a medium of clotted lymph. In 1913, E. Steinhardt, C. Israeli, and R. A. Lambert grew vaccinia virus in fragme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patient-derived Xenograft
Patient derived xenografts (PDX) are models of cancer where the tissue or cells from a patient's tumor are implanted into an immunodeficient or humanized mouse. It is a form of xenotransplantation. PDX models are used to create an environment that allows for the continued growth of cancer after its removal from a patient. In this way, tumor growth can be monitored in the laboratory, including in response to potential therapeutic options. Cohorts of PDX models can be used to determine the therapeutic efficiency of a therapy against particular types of cancer, or a PDX model from a specific patient can be tested against a range of therapies in a 'personalized oncology' approach. Methods of tumor xenotransplantation Several types of immunodeficient mice can be used to establish PDX models: athymic nude mice, severely compromised immune deficient (SCID) mice, NOD-SCID mice, and recombination-activating gene 2 (Rag2)-knockout mice. The mice used must be immunocompromised to prevent tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell
Induced pluripotent stem cells (also known as iPS cells or iPSCs) are a type of pluripotent stem cell that can be generated directly from a somatic cell. The iPSC technology was pioneered by Shinya Yamanaka and Kazutoshi Takahashi in Kyoto, Japan, who together showed in 2006 that the introduction of four specific genes (named Myc, Oct-4, Oct3/4, Sox2 and Klf4), collectively known as Yamanaka factors, encoding transcription factors could convert somatic cells into pluripotent stem cells. Shinya Yamanaka was awarded the 2012 Nobel Prize along with Sir John Gurdon "for the discovery that mature cells can be reprogrammed to become pluripotent." Pluripotent stem cells hold promise in the field of regenerative medicine. Because they can propagate indefinitely, as well as give rise to every other cell type in the body (such as neurons, heart, pancreatic, and liver cells), they represent a single source of cells that could be used to replace those lost to damage or disease. The most we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3D Cell Culture
A 3D cell culture is an artificially created environment in which biological cells are permitted to grow or interact with their surroundings in all three dimensions. Unlike 2D environments (e.g. a Petri dish), a 3D cell culture allows cells in vitro to grow in all directions, similar to how they would in vivo. These three-dimensional cultures are usually grown in bioreactors, small capsules in which the cells can grow into spheroids, or 3D cell colonies. Approximately 300 spheroids are usually cultured per bioreactor. Background 3D cell cultures have been used in research for several decades. One of the first recorded approaches for their development was at the beginning of the 20th century, with the efforts of Alexis Carrel to develop methods for prolonged in vitro tissue cultures. Early studies in the 80's, led by Mina Bissell from the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, highlighted the importance of 3D techniques for creating accurate in vitro culturing models. This work ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homogeneity And Heterogeneity
Homogeneity and heterogeneity are concepts relating to the uniformity of a substance, process or image. A homogeneous feature is uniform in composition or character (i.e., color, shape, size, weight, height, distribution, texture, language, income, disease, temperature, radioactivity, architectural design, etc.); one that is heterogeneous is distinctly nonuniform in at least one of these qualities. Etymology and spelling The words ''homogeneous'' and ''heterogeneous'' come from Medieval Latin ''homogeneus'' and ''heterogeneus'', from Ancient Greek ὁμογενής (''homogenēs'') and ἑτερογενής (''heterogenēs''), from ὁμός (''homos'', "same") and ἕτερος (''heteros'', "other, another, different") respectively, followed by γένος (''genos'', "kind"); -ous is an adjectival suffix. Alternate spellings omitting the last ''-e-'' (and the associated pronunciations) are common, but mistaken: ''homogenous'' is strictly a biological/pathological term whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathogens And Disease
'' Pathogens and Disease '' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research on all pathogens (eukaryotes, prokaryotes, and viruses, including zoonotic pathogens). It was originally established in 1988 as ''FEMS Microbiology Immunology'' when it split from ''FEMS Microbiology Letters''. It was renamed ''FEMS Immunology and Medical Microbiology'' in 1993, and obtained its current name in 2013. The journal is published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Federation of European Microbiological Societies. The current editors-in-chief are Wilhelmina Huston, Alfredo Garzino-Demo, and Jörn Coers. Abstracting and indexing The journal is indexed and abstracted in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all life, forms of life. Every cell consists of cytoplasm enclosed within a Cell membrane, membrane; many cells contain organelles, each with a specific function. The term comes from the Latin word meaning 'small room'. Most cells are only visible under a light microscope, microscope. Cells Abiogenesis, emerged on Earth about 4 billion years ago. All cells are capable of Self-replication, replication, protein synthesis, and cell motility, motility. Cells are broadly categorized into two types: eukaryotic cells, which possess a Cell nucleus, nucleus, and prokaryotic, prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus but have a nucleoid region. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms such as bacteria, whereas eukaryotes can be either single-celled, such as amoebae, or multicellular organism, multicellular, such as some algae, plants, animals, and fungi. Eukaryotic cells contain organelles including Mitochondrion, mitochondria, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
A tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) is a pharmaceutical drug that inhibits tyrosine kinases. Tyrosine kinases are enzymes responsible for the activation of many proteins by signal transduction cascades. The proteins are activated by adding a phosphate group to the protein (phosphorylation), a step that TKIs inhibit. TKIs are typically used as anticancer drugs. For example, they have substantially improved outcomes in chronic myelogenous leukemia. They have also been used to treat other diseases, such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. They are also called tyrphostins, the short name for "tyrosine phosphorylation inhibitor", originally coined in a 1988 publication, which was the first description of compounds inhibiting the catalytic activity of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). The 1988 study was the first demonstration of a systematic search and discovery of small-molecular-weight inhibitors of tyrosine phosphorylation, which do not inhibit protein kinases that phosphor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mortality Rate
Mortality rate, or death rate, is a measure of the number of deaths (in general, or due to a specific cause) in a particular Statistical population, population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time. Mortality rate is typically expressed in units of deaths per 1,000 individuals per year; thus, a mortality rate of 9.5 (out of 1,000) in a population of 1,000 would mean 9.5 deaths per year in that entire population, or 0.95% out of the total. It is distinct from "morbidity", which is either the prevalence or Incidence (epidemiology), incidence of a disease, and also from the incidence rate (the number of newly appearing cases of the disease per unit of time). An important specific mortality rate measure is the crude death rate, which looks at mortality from all causes in a given time interval for a given population. , for instance, the Central Intelligence Agency, CIA estimates that the crude death rate globally will be 7.7 deaths per 1,000 people in a population p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
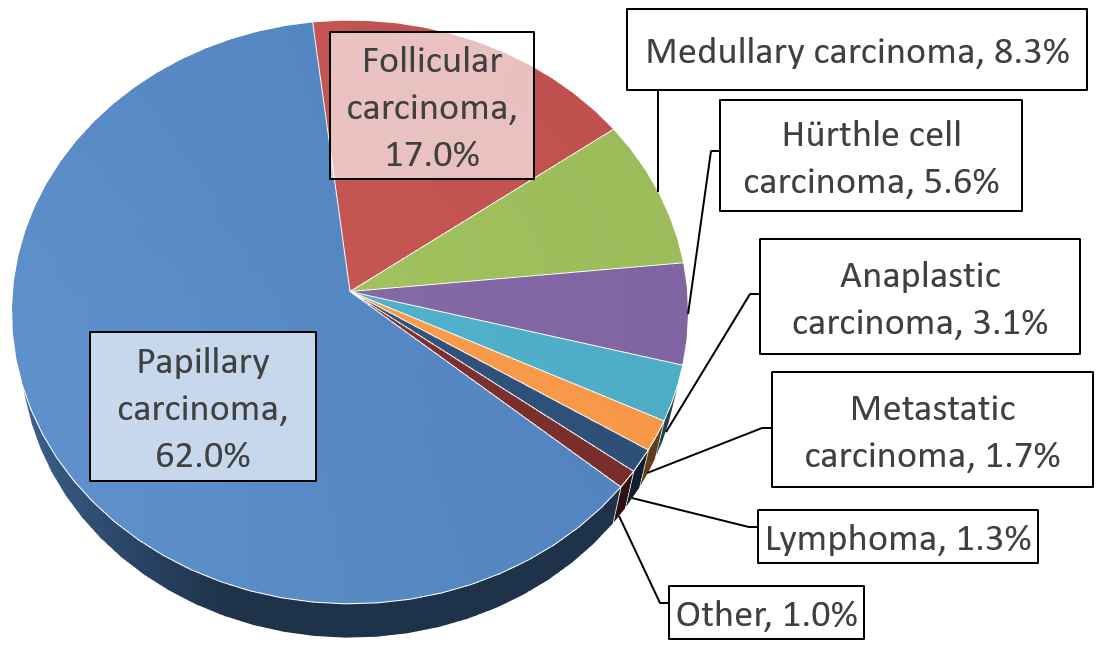
Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cancer is cancer that develops from the tissues of the thyroid gland. It is a disease in which cells grow abnormally and have the potential to spread to other parts of the body. Symptoms can include swelling or a lump in the neck, difficulty swallowing or voice changes including hoarseness, or a feeling of something being in the throat due to mass effect from the tumor. However, most cases are asymptomatic. Cancer can also occur in the thyroid after spread from other locations, in which case it is not classified as thyroid cancer. Risk factors include radiation exposure at a young age, having an enlarged thyroid, family history and obesity Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a disease, in which excess Adipose tissue, body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classifi .... The four main types are papillary thyroid cancer, follicular thyroid canc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocrine Disease
Endocrine diseases are disorders of the endocrine system. The branch of medicine associated with endocrine disorders is known as endocrinology. Types of disease Broadly speaking, endocrine disorders may be subdivided into three groups: # Endocrine gland hypofunction/hyposecretion (leading to hormone deficiency) # Endocrine gland hyperfunction/hypersecretion (leading to hormone excess) # Tumours (benign or malignant) of endocrine glands Endocrine disorders are often quite complex, involving a mixed picture of hyposecretion and hypersecretion because of the feedback mechanisms involved in the endocrine system. For example, most forms of hyperthyroidism are associated with an excess of thyroid hormone and a low level of thyroid stimulating hormone. List of diseases Glucose homeostasis disorders * Diabetes ** Type 1 Diabetes ** Type 2 Diabetes ** Gestational Diabetes ** Mature Onset Diabetes of the Young ** Diabetic myopathy * Hypoglycemia ** Idiopathic hypoglycemia ** Ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |