|
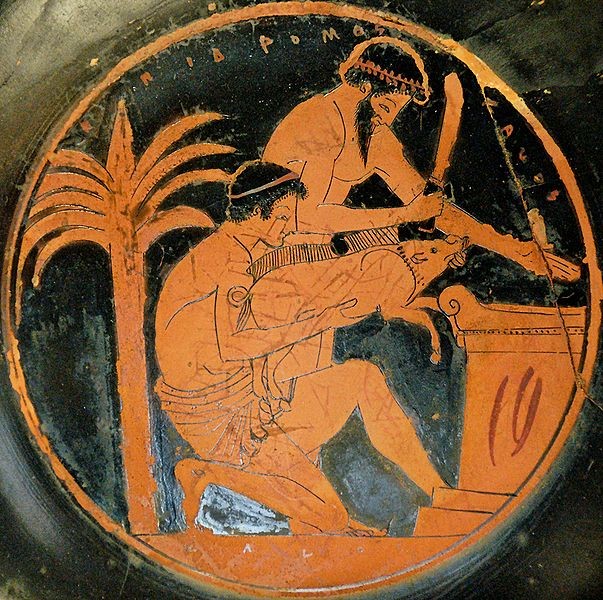
Priesthood (Ancient Israel)
The priesthood of ancient Israel was the class of male individuals, who, according to the Hebrew Bible, were patrilineal descendants from Aaron (the elder brother of Moses) and they were assisted by the tribe of Levi, who served in the Tabernacle, Solomon's Temple and Second Temple until the destruction of Jerusalem in 70 CE. Their temple role included animal sacrifice. The priests (Hebrew ''kohanim'') are viewed as continuing in the Kohen families of rabbinical Judaism. The Levites were not technically priests, they were the priests assistants and are viewed as continuing in the Levite families of rabbinical Judaism. Hebrew Bible The earliest priest mentioned in the Bible, Melchizedek, was a priest of the Most High and a contemporary of Abram. The first priest mentioned of another god is Potipherah priest of On, whose daughter Asenath married Joseph in Egypt. The third priest to be mentioned is Jethro, priest of Midian, and Moses' father in law. The first mention of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach" . '' Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. ; ; or ), also known in Hebrew as (; ), is the canonical collection of scriptures, comprising the Torah (the five Books of Moses), the Nevi'im (the Books of the Prophets), and the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph (son Of Jacob)
Joseph (; ) is an important Hebrew figure in the Bible's Book of Genesis. He was the first of the two sons of Jacob and Rachel (Jacob's twelfth named child and eleventh son). He is the founder of the Tribe of Joseph among the Israelites. His story functions as an explanation for Israel's residence in Egypt. He is the favourite son of the patriarch Jacob, and his envious brothers sell him into slavery in Biblical Egypt, where he eventually ends up incarcerated. After correctly interpreting the dreams of Pharaoh, he rises to second-in-command in Egypt and saves Egypt during a famine. Jacob's family travels to Egypt to escape the famine, and it is through him that they are given leave to settle in the Land of Goshen (the eastern part of the Nile Delta). Scholars hold different opinions about the historical background of the Joseph story, as well as the date and development of its composition. Some scholars suggest that the biblical story of Joseph (Gen 37-50) was a multigenerationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sin Offering
A sin offering (, ''korban ḥatat'', , lit: "purification offering") is a sacrificial offering described and commanded in the Torah (Lev. 4.1-35); it could be fine flour or a proper animal.Leviticus 5:11 A sin offering also occurs in 2 Chronicles 29:21 where seven bulls, seven rams, seven lambs and seven he-goats were sacrificed on the command of King Hezekiah for the kingdom, for the sanctuary, and for Judah. Like all types of sacrifices offered on the altar, the flour had to be unscented and the animal had to be completely unblemished. This offered sacrifice accompanied the important required core means of atonement for the committing of an ''unintentional'' transgression of a prohibition, that either has brought guilt upon the 'community of Israel' or the individual.''Jewish Encyclopedia'' This offering is brought during or after atonement for those transgressions that had been committed inadvertently, or in ignorance: intentional transgressions could only be absolved by othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dough Offering
In Judaism, the dough offering (or separation of ''challah'', ) is an positive commandment requiring the owner of bread dough to give a part of the kneaded dough to a kohen (Jewish priest). The obligation to separate the dough offering (henceforth: challah) from the dough begins the moment the dough is kneaded, but may also be separated after the loaves are baked. This commandment is one of the twenty-four priestly gifts. By biblical law the commandment is only obligatory in the Land of Israel, but rabbinic law applies it also to bread made outside the Land of Israel. The common modern practice in Orthodox Judaism is to burn (although simply throwing away the dough in a double-wrapped container is allowed) the portion to be given the Kohen, although giving the ''challah'' to a Kohen for consumption is permitted—even encouraged—outside Israel (permitted with restrictions, see article below for detail). Hebrew Bible The offering is commanded in : In the above passage "cake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meal Offering
A meal offering, grain offering, or gift offering (, ), is a type of Biblical sacrifice, specifically a sacrifice that did not include sacrificial animals. In older English it is sometimes called an oblation, from Latin. The Hebrew noun () is used 211 times in the Masoretic Text of the Hebrew Bible with the first instances being the offered by both Cain and Abel in Genesis 4:3-5. It is also used of Jacob's "present" to Esau in Genesis 32 and again of the "present" to the Egyptian ruler (who was in fact Joseph, his own son) in Genesis 43. In the King James Version of 1611 this was rendered as "", e.g. in Exodus 29:41, since at the time the King James Version was written, referred to food in general rather than the flesh of animals in particular. In the Hebrew Bible Gift offerings were often made on their own, but also accompanied the burnt offering. Scholars believe that the term "gift offering" originally referred to all voluntary sacrifices, but that it later came to jus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burnt Offering
A holocaust is a religious animal sacrifice that is completely consumed by fire, also known as a burnt offering. The word derives from the ancient Greek ''holokaustos'', the form of sacrifice in which the victim was reduced to ash, as distinguished from an animal sacrifice that resulted in a communal meal. Etymology and usage The word ''holocaust'' derives from the Middle English ''holocaust'', which derived from the Anglo-Norman ''holocauste'' and Late Latin ''holocaustum''. Its original root was the neuter form of the ancient Greek ''holokaustos'' (ὁλόκαυστος), from ὅλος (hólos, “whole”) + καυστός (kaustós, "burnt") or καίω (kaíō, "I burn") with the use of rough breathing to pronounce the leading h. Greek sacrifice ''Holokautein'' (ὁλοκαυτεῖν) is one of the two chief verbs of Greek sacrifice, in which the victim is utterly destroyed and burnt up, as opposed to ''thúesthai'' (θύεσθαι), to share a meal with the god and one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Law Of Moses
The Law of Moses ( ), also called the Mosaic Law, is the law said to have been revealed to Moses by God. The term primarily refers to the Torah or the first five books of the Hebrew Bible. Terminology The Law of Moses or Torah of Moses (Hebrew: , ''Torat Moshe'', Septuagint , ''nómos Mōusē'', or in some translations the "Teachings of Moses") is a biblical term first found in the Book of Joshua , where Joshua writes the Hebrew words of "Torat Moshe " on an altar of stones at Mount Ebal. The text continues: The term occurs 15 times in the Hebrew Bible, a further 7 times in the New Testament, and repeatedly in Second Temple period, intertestamental, rabbinical and patristic literature. The Hebrew word for the first five books of the Hebrew Bible, ''Torah'' (which means "law" and was translated into Greek as "nomos" or "Law") refers to the same five books termed in English "Pentateuch" (from Latinised Greek "five books", implying the five books of Moses). According ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Day Of Atonement
Yom Kippur ( ; , ) is the holiest day of the year in Judaism. It occurs annually on the 10th of Tishrei, corresponding to a date in late September or early October. For traditional Jewish people, it is primarily centered on atonement and repentance. The day's main observances consist of full fasting and asceticism, both accompanied by extended prayer services (usually at synagogue) and sin confessions. Some minor Jewish denominations, such as Reconstructionist Judaism, focus less on sins and more on one's goals and accomplishments and setting yearly intentions. Alongside the related holiday of Rosh Hashanah, Yom Kippur is one of the two components of the High Holy Days of Judaism. It is also the last of the Ten Days of Repentance. Name The formal Hebrew name of the holiday is , 'day fthe atonements'. This name is used in the Bible, Mishnah, and Shulchan Aruch. The word 'atonement' is one of many Biblical Hebrew words which, while using a grammatical plural form, ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
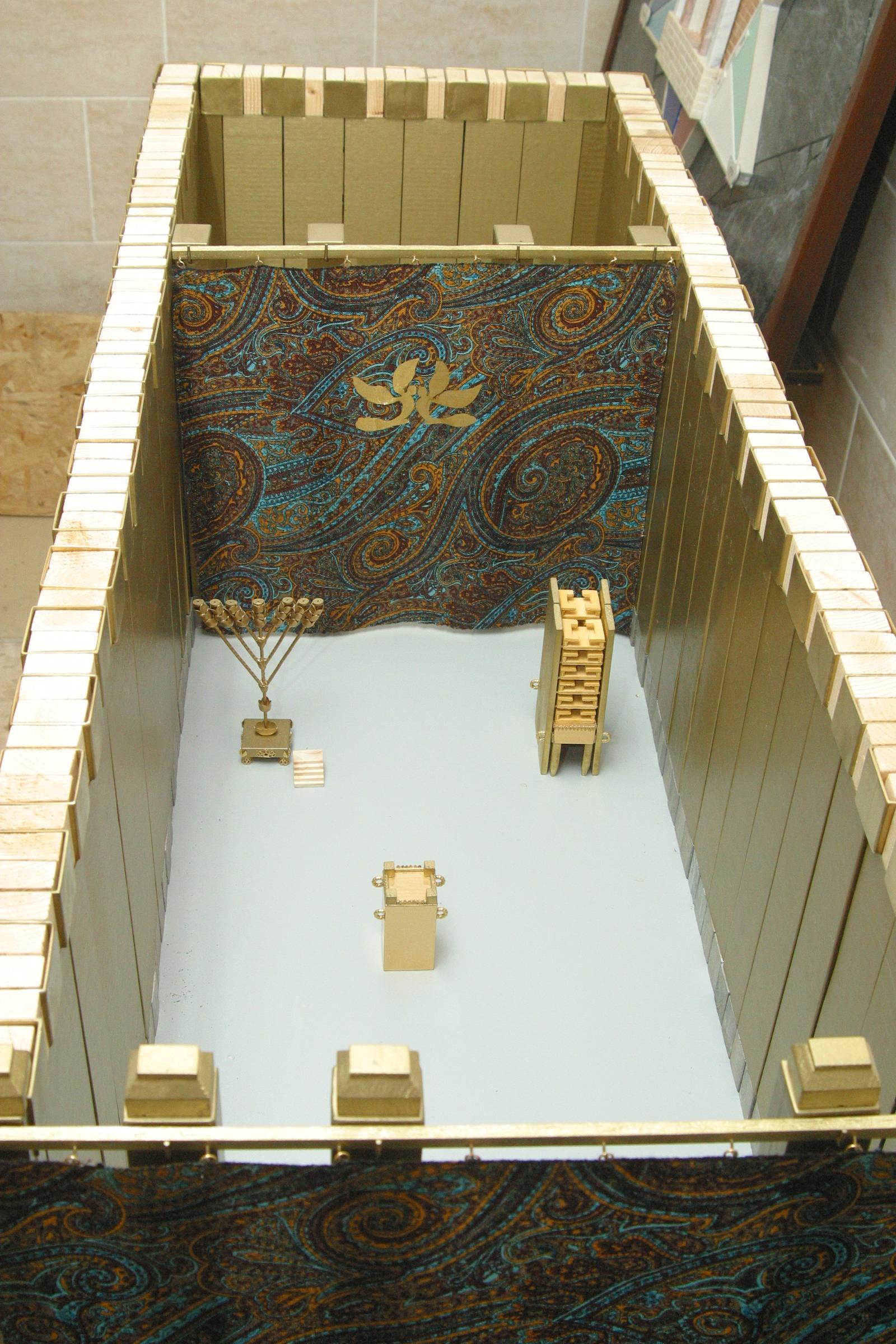
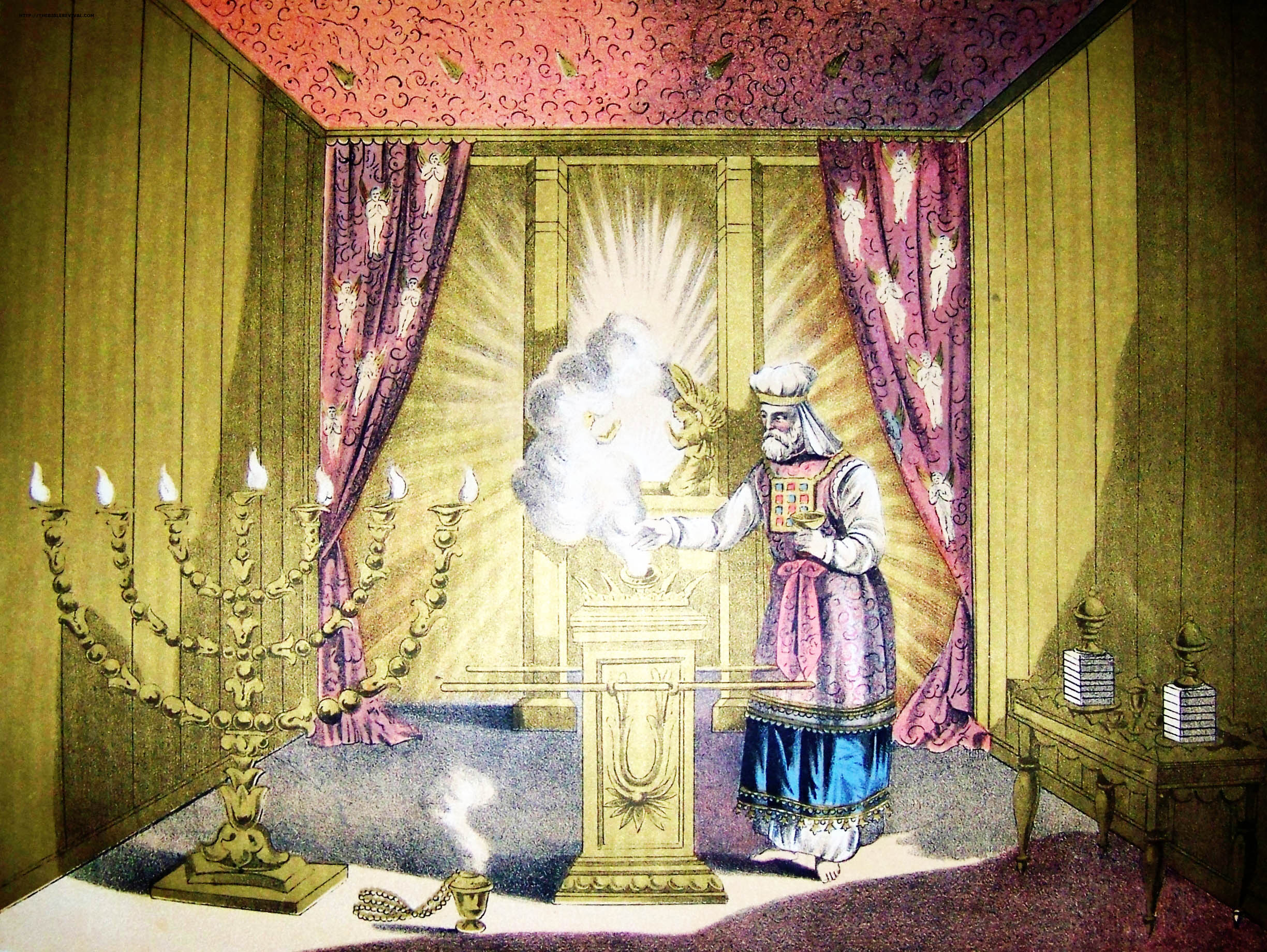
Holy Of Holies
The Holy of Holies ( or ''Kodesh HaKodashim''; also ''hadDəḇīr'', 'the Sanctuary') is a term in the Hebrew Bible that refers to the inner sanctuary of the Tabernacle, where the Shekhinah (God in Judaism, God's presence) appeared. According to Hebrew tradition, the area was defined by four pillars that held up the veil of the covering, under which the Ark of the Covenant was held above the floor. According to the Hebrew Bible, the Ark contained the Ten Commandments, which were given by God to Moses on Mount Sinai (Bible), Mount Sinai. The first Temple in Jerusalem, called Solomon's Temple, was said to have been built by Solomon, King Solomon to keep the Ark. Ancient Judaism, Jewish traditions viewed the Holy of Holies as the spiritual junction of Heaven and Earth, the "axis mundi". As a part of the Jewish Temple in Jerusalem, the Holy of Holies was situated somewhere on Temple Mount; its precise location in the Mount being a matter of dispute, with some classical Jewish sour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Leviticus
The Book of Leviticus (, from , ; , , 'And He called'; ) is the third book of the Torah (the Pentateuch) and of the Old Testament, also known as the Third Book of Moses. Many hypotheses presented by scholars as to its origins agree that it developed over a long period of time, reaching its present form during the Yehud Medinata, Persian Period, from 538 to 332 BC, although this is disputed. Most of its chapters (1–7, 11–27) consist of Yahweh, God's speeches to Moses, which he tells Moses to repeat to the Israelites. This takes place within the story of the Israelites' The Exodus, Exodus after they escaped Egypt and reached Biblical Mount Sinai, Mount Sinai (Exodus 19:1). The Book of Exodus narrates how Moses led the Israelites in building the Tabernacle (Exodus 35–40) with God's instructions (Exodus 25–31). In Leviticus, God tells the Israelites and their priests, Aaron and his sons, how to make offerings in the Tabernacle and how to conduct themselves while camped aro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Priest (Judaism)
In Judaism, the High Priest of Israel (, lit. ‘great priest’; Aramaic: ''Kahana Rabba'') was the head of the Israelite priesthood. He played a unique role in the worship conducted in the Tabernacle and later in the Temple in Jerusalem, as well as in some non-ritual matters. Like all priests, he was required to be descended from Aaron (the first biblical priest). But unlike other priests, the high priest followed more restrictive laws, wore unique priestly garments, and was the only priest allowed to perform certain ceremonies. Titles The high priest is referred to by a number of titles in the Hebrew Bible; the title ''kohen gadol'' did not become dominant until well into the Second Temple period. In addition to the title of "great priest" (''kohen gadol'') which later became the standard Hebrew title, the term "head priest" (''kohen harosh''; ) was used, as was "anointed priest" (''kohen mashiach''; )., , The Torah sometimes uses longer descriptions: "the great priest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King James Version
The King James Version (KJV), also the King James Bible (KJB) and the Authorized Version (AV), is an Early Modern English Bible translations, Early Modern English translation of the Christianity, Christian Bible for the Church of England, which was commissioned in 1604 and published in 1611, by sponsorship of King James VI and I. The List of books of the King James Version, 80 books of the King James Version include 39 books of the Old Testament, 14 books of Biblical apocrypha, Apocrypha, and the 27 books of the New Testament. Noted for its "majesty of style", the King James Version has been described as one of the most important books in English culture and a driving force in the shaping of the English-speaking world. The King James Version remains the preferred translation of many Protestant Christians, and is considered King James Only movement, the only valid one by some Evangelicals. It is considered one of the important literary accomplishments of early modern England ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |