|
Prehistoric Reptile
Reptiles arose about 320 million years ago during the Carboniferous period. Reptiles, in the traditional sense of the term, are defined as animals that have scales or scutes, lay land-based hard-shelled eggs, and possess ectothermic metabolisms. So defined, the group is paraphyletic, excluding endothermic animals like birds that are descended from early traditionally-defined reptiles. A definition in accordance with phylogenetic nomenclature, which rejects paraphyletic groups, includes birds while excluding mammals and their synapsid ancestors. So defined, Reptilia is identical to Sauropsida. Though few reptiles today are apex predators, many examples of apex reptiles have existed in the past. Reptiles have an extremely diverse evolutionary history that has led to biological successes, such as dinosaurs, pterosaurs, plesiosaurs, mosasaurs, and ichthyosaurs. First reptiles Rise from water Reptiles first arose from earlier tetrapods in the swamps of the late Carboniferous ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casineria Kiddi
''Casineria'' is an extinct genus of tetrapod which lived about 340-334 million years ago in the Mississippian (geologic period), Mississippian epoch of the Carboniferous period. Its Generic name (biology), generic name, ''Casineria'', is a latinization of Cheese Bay, the site near Edinburgh, Scotland where the holotype fossil was found. When originally described in 1999, it was identified as a transitional fossil noted for its mix of basal (amphibian-like) and advanced (reptile-like) characteristics, putting it at or very near the origin of the amniotes, the group containing all Mammal, mammals, Bird, birds, modern reptiles, and other descendants of their reptile-like Most recent common ancestor, common ancestor. However, the sole known fossil is lacking key elements such as a skull, making exact analysis difficult. As a result, the classification of ''Casineria'' has been more controversial in analyses conducted since 1999. Other proposed affinities include a placement among the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traditional Reptilia
A tradition is a belief or behavior (folk custom) passed down within a group or society with symbolic meaning or special significance with origins in the past. A component of cultural expressions and folklore, common examples include holidays or impractical but socially meaningful clothes (like lawyers' wigs or military officers' spurs), but the idea has also been applied to social norms such as greetings. Traditions can persist and evolve for thousands of years—the word ''tradition'' itself derives from the Latin ''tradere'' literally meaning to transmit, to hand over, to give for safekeeping. While it is commonly assumed that traditions have an ancient history, many traditions have been invented on purpose, whether that be political or cultural, over short periods of time. Various academic disciplines also use the word in a variety of ways. The phrase "according to tradition", or "by tradition", usually means that whatever information follows is known only by oral tradition, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
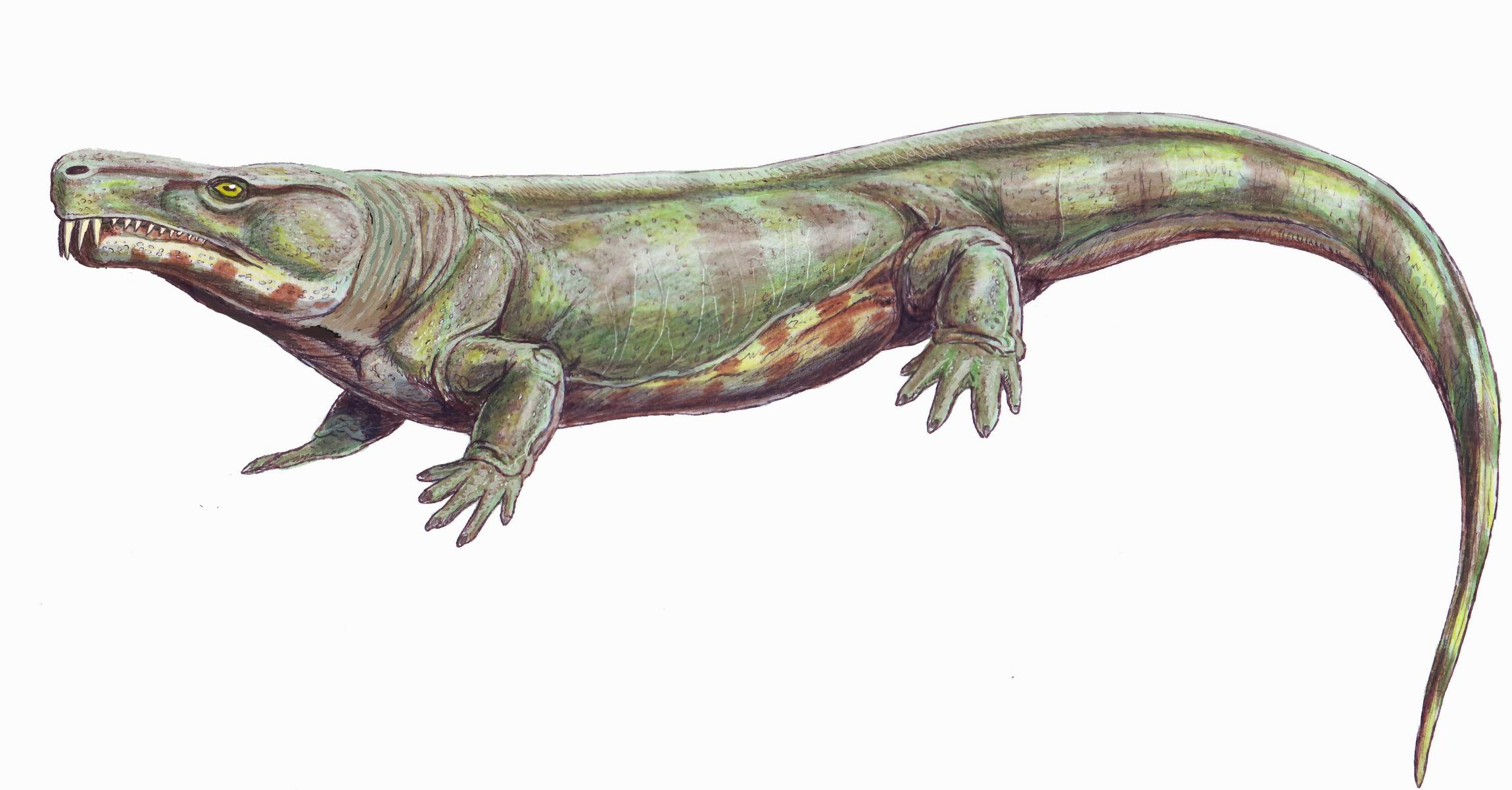
Casineria
''Casineria'' is an extinct genus of tetrapod which lived about 340-334 million years ago in the Mississippian epoch of the Carboniferous period. Its generic name, ''Casineria'', is a latinization of Cheese Bay, the site near Edinburgh, Scotland where the holotype fossil was found. When originally described in 1999, it was identified as a transitional fossil noted for its mix of basal ( amphibian-like) and advanced ( reptile-like) characteristics, putting it at or very near the origin of the amniotes, the group containing all mammals, birds, modern reptiles, and other descendants of their reptile-like common ancestor. However, the sole known fossil is lacking key elements such as a skull, making exact analysis difficult. As a result, the classification of ''Casineria'' has been more controversial in analyses conducted since 1999. Other proposed affinities include a placement among the lepospondyls, seymouriamorphs, " gephyrostegids", or as a synonym of ''Caerorhachis'', anoth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphibian
Amphibians are four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terrestrial, fossorial, arboreal or freshwater aquatic ecosystems. Thus amphibians typically start out as larvae living in water, but some species have developed behavioural adaptations to bypass this. The young generally undergo metamorphosis from larva with gills to an adult air-breathing form with lungs. Amphibians use their skin as a secondary respiratory surface and some small terrestrial salamanders and frogs lack lungs and rely entirely on their skin. They are superficially similar to reptiles like lizards but, along with mammals and birds, reptiles are amniotes and do not require water bodies in which to breed. With their complex reproductive needs and permeable skins, amphibians are often ecological indicators; in recent decades there has been a dramat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amniote
Amniotes are a clade of tetrapod vertebrates that comprises sauropsids (including all reptiles and birds, and extinct parareptiles and non-avian dinosaurs) and synapsids (including pelycosaurs and therapsids such as mammals). They are distinguished from the other tetrapod clade — the amphibians — by the development of three extraembryonic membranes (amnion for embryoic protection, chorion for gas exchange, and allantois for metabolic waste disposal or storage), thicker and more keratinized skin, and costal respiration (breathing by expanding/constricting the rib cage). All three main features listed above, namely the presence of an amniotic buffer, water-impermeable cutes and a robust respiratory system, are very important for amniotes to live on land as true terrestrial animals – the ability to reproduce in locations away from water bodies, better homeostasis in drier environments, and more efficient air respiration to power terrestrial locomotions, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoological Journal Of The Linnean Society
The ''Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering zoology published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Linnean Society. The editor-in-chief is Maarten Christenhusz (Linnean Society). It was established in 1856 as the ''Journal of the Proceedings of the Linnean Society of London. Zoology'' and renamed ''Journal of the Linnean Society of London, Zoology'' in 1866. It obtained its current title in 1969. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 3.286. References External links * Zoology journals Linnean Society of London Monthly journals Academic journals associated with learned and professional societies Publications established in 1856 {{zoo-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labyrinthodontia
"Labyrinthodontia" (Greek, 'maze-toothed') is an informal grouping of extinct predatory amphibians which were major components of ecosystems in the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras (about 390 to 150 million years ago). Traditionally considered a subclass of the class Amphibia, modern classification systems recognize that labyrinthodonts are not a formal natural group ( clade) exclusive of other tetrapods. Instead, they consistute an evolutionary grade (a paraphyletic group), ancestral to living tetrapods such as lissamphibians (modern amphibians) and amniotes (reptiles, mammals, and kin). "Labyrinthodont"-grade vertebrates evolved from lobe-finned fishes in the Devonian, though a formal boundary between fish and amphibian is difficult to define at this point in time. "Labyrinthodont" generally refers to extinct four-limbed tetrapods with a large body size and a crocodile-like lifestyle. The name describes the pattern of infolding of the dentin and enamel of the teeth, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptiliomorpha
Reptiliomorpha (meaning reptile-shaped; in PhyloCode known as ''Pan-Amniota'') is a clade containing the amniotes and those tetrapods that share a more recent common ancestor with amniotes than with living amphibians (lissamphibians). It was defined by Michel Laurin (2001) and Vallin and Laurin (2004) as the largest clade that includes ''Homo sapiens'', but not '' Ascaphus truei'' (tailed frog). Laurin and Reisz (2020) defined Pan-Amniota as the largest total clade containing ''Homo sapiens'', but not '' Pipa pipa'', '' Caecilia tentaculata'', and ''Siren lacertina''. The informal variant of the name, "reptiliomorphs", is also occasionally used to refer to stem-amniotes, i.e. a grade of reptile-like tetrapods that are more closely related to amniotes than they are to lissamphibians, but are not amniotes themselves; the name is used in this meaning e.g. by Ruta, Coates and Quicke (2003). An alternative name, " Anthracosauria", is also commonly used for the group, but is confus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europasaurus Holgeri Scene 2
''Europasaurus'' is a basal macronarian sauropod, a form of quadrupedal herbivorous dinosaur. It lived during the Late Jurassic (middle Kimmeridgian, about 154 million years ago) of northern Germany, and has been identified as an example of insular dwarfism resulting from the isolation of a sauropod population on an island within the Lower Saxony basin. Discovery and naming In 1998, a single sauropod tooth was discovered by private fossil collector Holger Lüdtke in an active quarry at Langenberg (Bad Harzburg), Langenberg Mountain, between the communities of Oker (Goslar), Oker, Harlingerode and Göttingerode in Germany. The Langenberg chalk quarry had been active for more than a century; rocks are quarried using blasting and are mostly processed into fertilisers. The quarry exposes a nearly continuous, thick succession of carbonate rocks belonging to the Süntel Formation, that ranges in age from the early Oxfordian (stage), Oxfordian to late Kimmeridgian stage (geology), stag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hylonomus BW
''Hylonomus'' (; ''hylo-'' "forest" + ''nomos'' "dweller") is an extinct genus of reptile that lived 312 million years ago during the Late Carboniferous period. It is the earliest unquestionable reptile (''Westlothiana'' is older, but in fact it may have been an amphibian, and ''Casineria'' is rather fragmentary). The only species is the type species ''Hylonomus lyelli''. Despite being amongst the oldest known reptiles, it is not the most primitive member of group, being a eureptile more derived than either parareptiles or captorhinids. Description ''Hylonomus'' was long (including the tail). Most of them are 20 cm long and probably would have looked rather similar to modern lizards. It had small sharp teeth and it likely ate small invertebrates such as millipedes or early insects. Fossils of ''Hylonomus'' have been found in the remains of fossilized club moss stumps in the Joggins Formation, Joggins, Nova Scotia, Canada. It is supposed that, after harsh weather, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebellum
The cerebellum (Latin for "little brain") is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as or even larger. In humans, the cerebellum plays an important role in motor control. It may also be involved in some cognitive functions such as attention and language as well as emotional control such as regulating fear and pleasure responses, but its movement-related functions are the most solidly established. The human cerebellum does not initiate movement, but contributes to coordination, precision, and accurate timing: it receives input from sensory systems of the spinal cord and from other parts of the brain, and integrates these inputs to fine-tune motor activity. Cerebellar damage produces disorders in fine movement, equilibrium, posture, and motor learning in humans. Anatomically, the human cerebellum has the appearance of a separate structure attached to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebrum
The cerebrum, telencephalon or endbrain is the largest part of the brain containing the cerebral cortex (of the two cerebral hemispheres), as well as several subcortical structures, including the hippocampus, basal ganglia, and olfactory bulb. In the human brain, the cerebrum is the uppermost region of the central nervous system. The cerebrum develops prenatally from the forebrain (prosencephalon). In mammals, the dorsal telencephalon, or pallium, develops into the cerebral cortex, and the ventral telencephalon, or subpallium, becomes the basal ganglia. The cerebrum is also divided into approximately symmetric left and right cerebral hemispheres. With the assistance of the cerebellum, the cerebrum controls all voluntary actions in the human body. Structure The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain. Depending upon the position of the animal it lies either in front or on top of the brainstem. In humans, the cerebrum is the largest and best-developed of the five majo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)
.jpg)