|
Pre-Arawakan Languages Of The Greater Antilles
Several languages of the Greater Antilles, specifically in Cuba and Hispaniola, appear to have preceded the Arawakan Taíno. Almost nothing is known of them, though a couple recorded words, along with a few toponyms, suggest they were not Arawakan or Cariban, the families of the attested languages of the Antilles. Three languages are recorded: Guanahatabey, Macoris (or Macorix, apparently in two dialects), and Ciguayo. Languages There were three pre-Arawakan populations at the time of the Spanish Conquest, and they were extinct within a century. These were * the Guanahatabey of western Cuba (sometimes confused with the Arawakan Ciboney), * the Macorix (Mazorij) in two populations: the Pedernales Peninsula and northeastern Hispaniola (modern Dominican Republic), and * the Ciguayo (Siwayo) of northeastern Hispaniola ( Samaná Peninsula). They were evidently completely mutually unintelligible with Taíno. Ciguayo and Macorix were apparently moribund when chronicler De las ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciboney People
The Ciboney, or Siboney, were a Taíno people of Cuba, Jamaica, and the Tiburon Peninsula of Haiti. A Western Taíno group living in Cuba during the 15th and 16th centuries, they had a dialect and culture distinct from the Taíno language#Dialects, Classic Taíno in the eastern part of the island, though much of the Ciboney territory was under the control of the eastern chiefs. Confusion in the historical sources led 20th-century scholars to apply the name "Ciboney" to the non-Taíno Guanahatabey of western Cuba and various archaic stage, archaic cultures around the Caribbean, but this is deprecated. History At the time of Spanish colonization of the Americas, Spanish colonization, the Ciboney were the most populous group in Cuba. They inhabited the central part of the island, between western Pinar del Río Province and eastern Oriente Province. Bartolomé de las Casas, who lived among the Ciboney in the early 16th century, related that their dialect and culture was similar to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taíno Language
Taíno is an Arawakan language formerly spoken widely by the Taíno people of the Caribbean. In its revived form, there exist several modern-day Taíno language variants including Hiwatahia-Taino and Tainonaiki. At the time of Spanish contact it was the most common language throughout the Caribbean. Classic Taíno (Taíno proper) was the native language of the Taíno tribes living in the Leeward Islands of the Lesser Antilles, Borikén (now known as Puerto Rico), the Turks and Caicos Islands, most of Ayiti-Kiskeya also known as Hispaniola, and eastern Cuba. The Ciboney dialect is essentially unattested, but colonial sources suggest it was very similar to Classic Taíno, and was spoken in the westernmost areas of Hispaniola, the Bahamas, Jamaica, and most of Cuba. By the late 15th century, Taíno had displaced earlier languages, except in western Cuba and in pockets in Hispaniola. As the Taíno culture declined during Spanish colonization, the language was replaced by Spanish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hokan Languages
The Hokan language family is a hypothetical grouping of a dozen small language families spoken mainly in California, Arizona, and Baja California. Etymology The name ''Hokan'' is loosely based on the word for "two" in the various Hokan languages: ''*xwak'' in Proto-Yuman, (pronounced ) in Seri, in Achumawi, etc. Compare similar construction of the term "Penutian". History of the proposal The "Hokan hypothesis" was first proposed in 1913 by Roland B. Dixon and Alfred L. Kroeber, and further elaborated by Edward Sapir. Initial follow-up research found little additional evidence that these language families were related to each other. But since about 1950, increased efforts to document Hokan languages and to establish sound correspondences in proposed lexical resemblance sets have added weight to the Hokan hypothesis, leading to its acceptance by many specialists in the languages of California, Oregon, and Mesoamerica. However, some skepticism remains among scholars. Lingui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Salvador Island
San Salvador Island, previously Watling's Island, is an islands of the Bahamas, island and districts of The Bahamas, district of The Bahamas, famed for being the probable location of Christopher Columbus's first landing of the Americas on 12 October 1492 during voyages of Columbus, his first voyage. This historical importance, the island's tropical beaches, and its proximity to the United States have made tourism central to the local economy. The island has a population of 824 (2022) and is under the administration of Gilbert C. Kemp. Its largest settlement and seat of local government is Cockburn Town, Bahamas, Cockburn Town. Names ''Watling's Island'' was named for George or John Watling, an English people, Englishman who settled it in the 17th century. The name was used officially from the 1680s until 1926. It is still used unofficially in discussions of the actual location of Columbus's first landfall. ''San Salvador'' derives from the Spanish language, Spanish ("Island ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
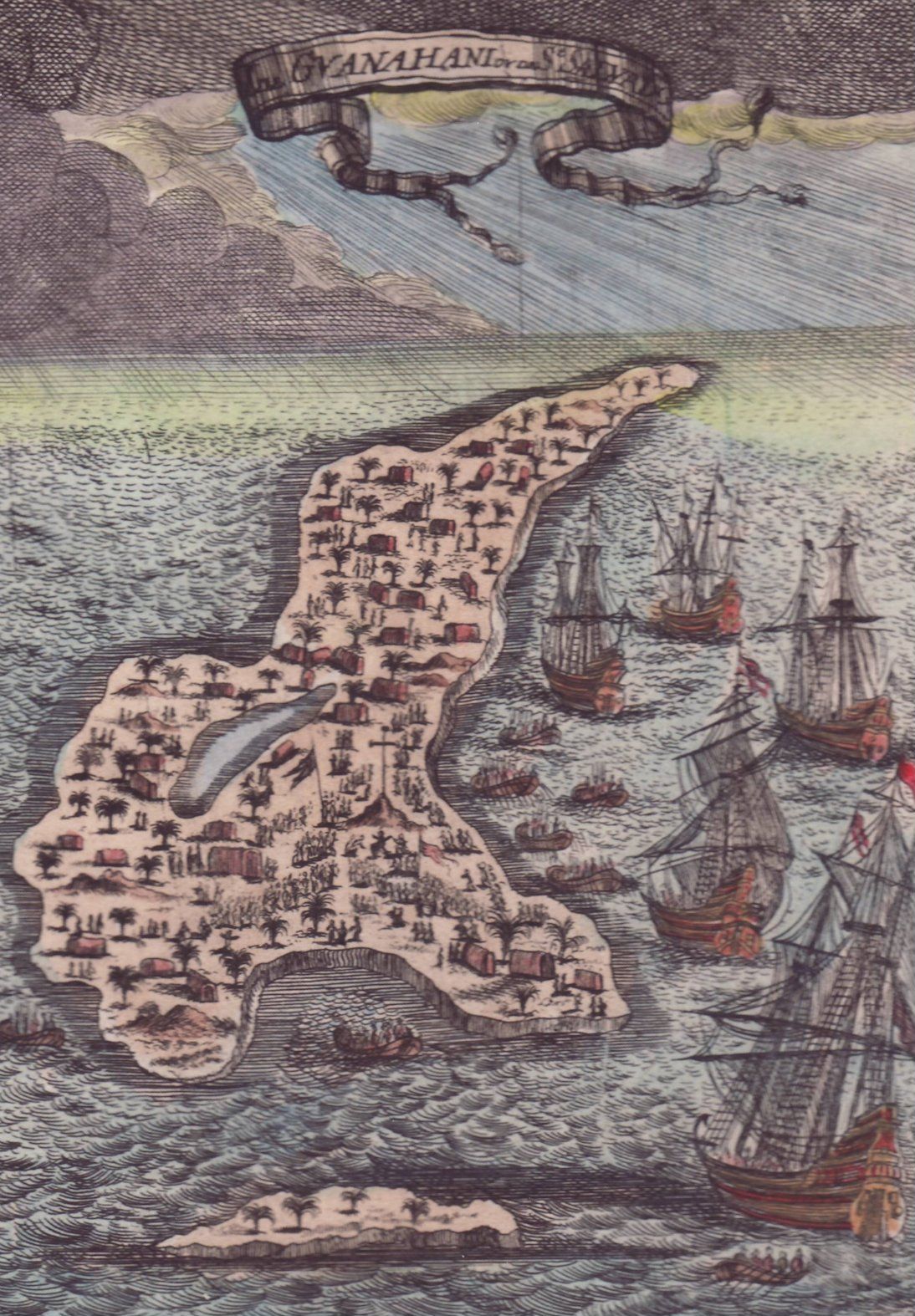
Guanahani
Guanahaní (meaning "small upper waters land") was the Taíno language, Taíno name of an island in the Bahamas that was the first land in the New World sighted and visited by Christopher Columbus' Voyages of Christopher Columbus#First voyage (1492–1493), first voyage, on 12 October 1492. It is a bean-shaped island that Columbus called San Salvador. Guanahaní has traditionally been identified with Watlings Island, which was officially renamed San Salvador Island in 1925 as a result, but modern scholars are divided on the accuracy of this identification and several alternative candidates in and around the southern Bahamas have been proposed as well. Primary sources Letter from Columbus himself Upon his return to Spain in the spring of 1493, Columbus Columbus Letter on the First Voyage, wrote a letter to Luis de Santangel, one of his patrons at the Royal Court of Kingdom of Castile, Castile. The letter was printed widely and translated into many languages, spreading the news of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
League (unit)
A league is a unit of length. It was common in Europe and Latin America, but due to its highly inconsistent definition, it is no longer an official unit in any nation. Derived from an ancient Celtic unit and adopted by the Romans as the , the league became a common unit of measurement throughout western Europe. Since the Middle Ages, many values have been specified in several countries, ranging from 2.2 km (1.4 mi) to 7.9 km (4.9 mi). It may have originally represented, roughly, the distance a Preferred walking speed, person could walk in an hour. Definitions Ancient Rome The league was used in Ancient Rome, defined as 1½ mile#Roman, Roman miles (7,500 Foot (unit)#Historical origin, Roman feet, modern 2.2 km or 1.4 miles). The origin is the ''(also:'' '')'', the league of Gaul. Argentina The Argentine league () is or 6,666 : 1 is . England On land, the league is most commonly defined as three miles (4.83 km), although the length of a mile could vary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moribund Language
An endangered language or moribund language is a language that is at risk of disappearing as its speakers die out or shift to speaking other languages. Language loss occurs when the language has no more native speakers and becomes a " dead language". If no one can speak the language at all, it becomes an "extinct language". A dead language may still be studied through recordings or writings, but it is still dead or extinct unless there are fluent speakers left. Although languages have always become extinct throughout human history, endangered languages are currently dying at an accelerated rate because of globalization, mass migration, cultural replacement, imperialism, neocolonialism and linguicide (language killing). Language shift most commonly occurs when speakers switch to a language associated with social or economic power or one spoken more widely, leading to the gradual decline and eventual death of the endangered language. The process of language shift is often influen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samaná Province
Samaná () is a Provinces of the Dominican Republic, province of the Dominican Republic in the Samaná Peninsula located in the eastern region. Its Capital (political), capital is Samaná (town), Santa Bárbara de Samaná, usually known as Samaná. The province is on the coast of the Atlantic Ocean in the northeastern part of the Dominican Republic. It is known for the mountains of which it is almost entirely formed. Samaná has numerous beaches. Samaná was originally larger covering the area of what is now the María Trinidad Sánchez Province, María Trinidad Sánchez province, before being divided during the Rafael Trujillo, Trujillo era. Samaná was also once known as the Samana Bay Company of Santo Domingo. Geography The Samaná province is occupied by the Sierra de Samaná mountain range, which reaches many of the coastal areas. The highest mountain in this range (and in the province) is located in the eastern portion and is called La Meseta. Samaná has a tropical rainf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciguayo
The Ciguayos (Spanish: Ciguayos) were a group of Indigenous people who inhabited the Samaná Peninsula and its adjoining regions in the present-day Dominican Republic. The Ciguayos appear to have predated the agricultural Taíno who inhabited much of the island. Ciguayo language was spoken on the northeastern coast of the Maguá chiefdom from Nagua southward to at least the Yuna River, and throughout all of the Samaná Province. Since the moment of contact early Spanish writers perceived them as a threat and portrayed them flaunting long hair and brandishing bows with poisoned arrows. Their archery tradition is linked to the Kalinago, or Island Caribs. Their legacy has spawned folktales, and since the 19th century, their memory has been at the center of the Dominican indigenist movement. Society and characteristics They were considered a separate ethnic people that inhabited the Peninsula of Samaná and part of the northern coast toward Nagua in what today is the Dominican ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedernales Province
Pedernales (; ) is the southernmost province of the Dominican Republic, including the offshore island of Isla Beata. It was split from Barahona in 1957. Of its 2,080.95 km2, 1,374 km2 belongs to the Jaragua National Park. A third of its population is of Haitian origin, the highest ratio within the country. The capital of the province, Pedernales, was originally called Juan López, who was a Spanish inhabitant who had settled in the area around the 19th century. The province was called Pedernales after the river located on the border with Haiti, in which flint is abundant. The indigenous people of the Dominican Republic, the Taíno, used them to make sharp tools, such as axes and arrowheads. Geography The province of Pedernales is located in the southwest of the Dominican Republic, sharing its borders with the neighboring Haiti. It is located 330 km (kilometers) from Santo Domingo, the Dominican capital. It is part of the region called Enriquillo, and it is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macorix People
At the time of first contact between Europe and the Americas, the Indigenous peoples of the Caribbean included the Taíno of the northern Lesser Antilles, most of the Greater Antilles and the Bahamas, the Kalinago of the Lesser Antilles, the Ciguayo and Macorix of parts of Hispaniola, and the Guanahatabey of western Cuba. The Kalinago have maintained an identity as an Indigenous people, with a reserved territory in Dominica. Introduction Some scholars consider it important to distinguish the Taíno from the neo-Taíno nations of Cuba, Puerto Rico, and Hispaniola, and the Lucayan of the Bahamas and Jamaica. Linguistically or culturally these differences extended from various cognates or types of canoe: canoa, piragua, cayuco to distinct languages. Languages diverged even over short distances. Previously these groups often had distinctly non-Taíno deities such as the goddess Jagua. Strangely enough the god Teju Jagua is a major demon of Indigenous Paraguayan mythology. Still ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |