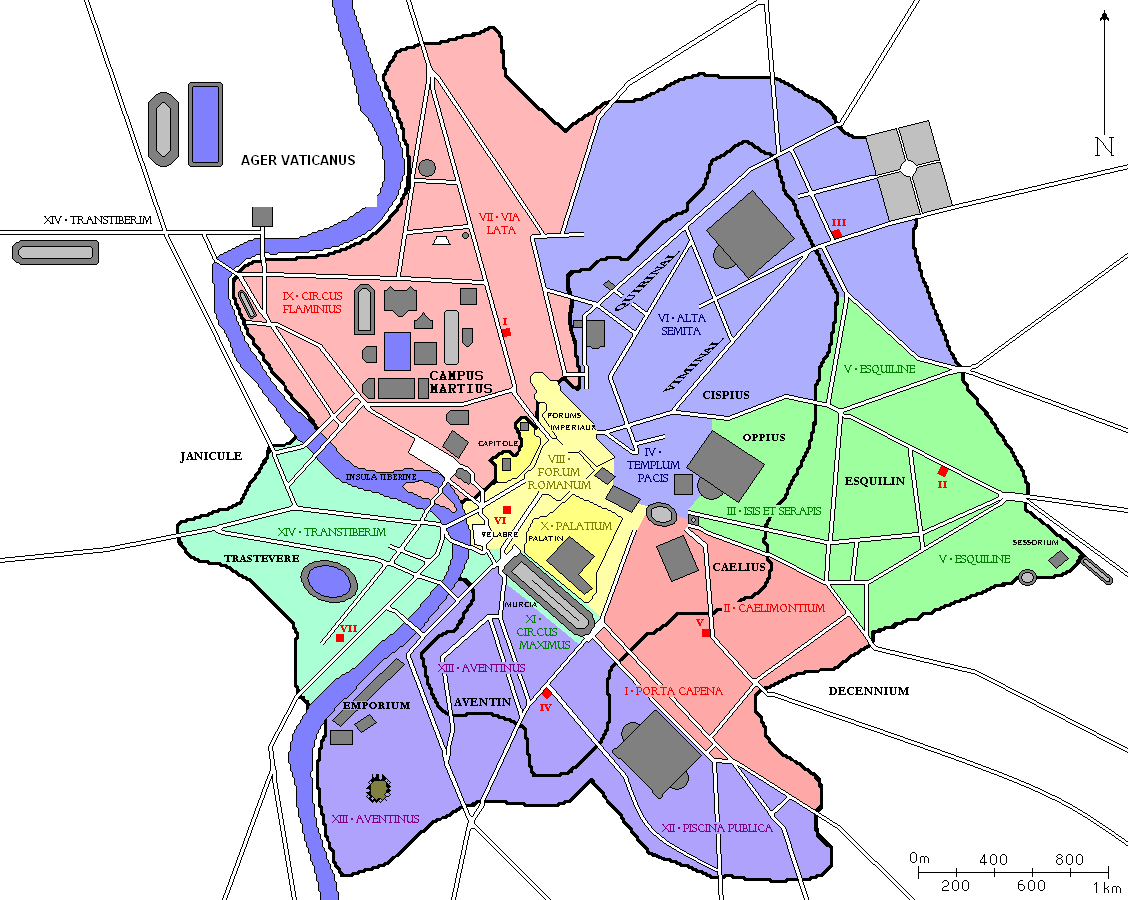
|
Praefectus Vigilum
The ''praefectus vigilum'' (, pl.: ''praefecti vigilum'') was, starting with the reign of the Emperor Augustus, the commander of the city guards in Rome (''cohortes vigilum'' or ''vigiles''), whom were responsible for maintaining peace and order at night--a kind of fire and security police. Although less important than the other prefects, the office was considered a first step in order to reach an important position in the imperial administration. Description Headquarters The offices of the ''praefectus vigilum'' were located in the ''Campus Martius'', perhaps in the quadriportico of the theatre of Balbus (along the '' via Lata''), inside the barracks of the First Cohort of ''Vigiles'' ().Lefebvre (2011), p. 185 The reason to think that is that all the dedications found in the remains of these barracks are inscribed in the name of the prefect.Homo (1971), p. 164 It was in this building that the ''praefectus vigilum'' had his offices and his courtroom and it was from there t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaius Maesius Tertius
Gaius Maesius Tertius (c. 1st century – c. 2nd century) was a Roman civil servant and officer active at the beginning of the 2nd century AD. According to a military diploma issued on 14 October 109 found in Valentia Banasa in the Mauritania Tingitana province in year 109 AD he was ''praefectus'' (commander) of the '' ala I Hamiorum sagittariorum''. In 113 AD he was '' subpraefectus vigilum'' in Rome (the first person known serving under this office).{{CIL, 6, 221 Tertius was inscribed in the Tribe ''Palatina''.Hans-Georg Pflaum Hans-Georg Pflaum (3 June 1902, Berlin – 26 December 1979, Linz) was a German-born French historian. Life Pflaum, who came from a Jewish family of industrialists, at first studied law in Breslau and Heidelberg, afterwards taking a position in ...: ''Les carrières'', Nr. 78, p. 174–175. References 1st-century Romans 2nd-century Romans Ancient Roman equites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Senator
The Roman Senate () was the highest and Roman constitution, constituting assembly of ancient Rome and its aristocracy. With different powers throughout its existence it lasted from the first days of the Rome, city of Rome (traditionally founded in 753 BC) as the Senate of the Roman Kingdom, to the Senate of the Roman Republic and Senate of the Roman Empire and eventually the Byzantine Senate of the Byzantine Empire, Eastern Roman Empire, existing well into the post-classical era and Middle Ages. During the days of the Roman Kingdom, the Senate was generally little more than an advisory council to the king. However, as Rome was an electoral monarchy, the Senate also elected new King of Rome, Roman kings. The last king of Rome, Lucius Tarquinius Superbus, was overthrown following a coup d'état led by Lucius Junius Brutus, who founded the Roman Republic. During the early Republic, the Senate was politically weak, while the various executive Roman magistrates who appointed the se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aedile
Aedile ( , , from , "temple edifice") was an elected office of the Roman Republic. Based in Rome, the aediles were responsible for maintenance of public buildings () and regulation of public festivals. They also had powers to enforce public order and duties to ensure the city of Rome was well supplied and its civil infrastructure well maintained, akin to modern local government. There were two pairs of aediles: the first were the "plebeian aediles" (Latin: ''aediles plebis'') and possession of this office was limited to plebeians; the other two were "curule aediles" (Latin: ''aediles curules''), open to both plebeians and patricians, in alternating years. An ''aedilis curulis'' was classified as a '' magister curulis''. The office of the aedilis was generally held by young men intending to follow the ''cursus honorum'' to high political office, traditionally after their quaestorship but before their praetorship. It was not a compulsory part of the cursus, and hence a former qua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcus Egnatius Rufus
Marcus Egnatius Rufus (died 19 BCE in Rome) was a Ancient Rome, Roman Roman Senate, senator and politician at the time of Augustus. In 22 BCE he served as an aedile and became very popular with the residents of Rome by setting up a private fire brigade. In contrast to earlier enterprises of this kind, which, like the fire brigade of Marcus Licinius Crassus, only worked for payment, Egnatius made the 600 slaves he financed available free of charge to fight fires. Because of the numerous fires in the city he gained great popularity and was elected praetor as early as 21 BCE without observing the usual waiting period.Velleius Paterculus, ''Historia Romana'' 2, 91, 3f. In 19 BCE he stood for election as Roman consul, consul, but the consul Gaius Sentius Saturninus prevented this, probably at the instigation of Augustus. Egnatius was accused of conspiring against Augustus. Seneca the Younger, Seneca includes him in the multiple conspiracy and assassination attempts against Augustus. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcus Licinius Crassus
Marcus Licinius Crassus (; 115–53 BC) was a ancient Rome, Roman general and statesman who played a key role in the transformation of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire. He is often called "the richest man in Rome".Wallechinsky, David & Irving Wallace, Wallace, Irving.Richest People in History Ancient Roman Crassus. Trivia-Library. ''The People's Almanac''. 1975–1981. Web. 23 December 2009."Often named as the richest man ever, a more accurate conversion of sesterce would put his modern figure between $200 million and $20 billion." Peter L. BernsteinThe 20 Richest People Of All Time/ref> Crassus began his public career as a military commander under Sulla, Lucius Cornelius Sulla during his Sulla's civil war, civil war. Following Sulla's assumption of the Roman dictator, dictatorship, Crassus amassed an enormous fortune through property speculation. Crassus rose to political prominence following his victory over the Third Servile War, slave revolt led by Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire following the War of Actium. During this period, Rome's control expanded from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean world. Roman society at the time was primarily a cultural mix of Latins (Italic tribe), Latin and Etruscan civilization, Etruscan societies, as well as of Sabine, Oscan, and Greek cultural elements, which is especially visible in the Ancient Roman religion and List of Roman deities, its pantheon. Its political organisation developed at around the same time as direct democracy in Ancient Greece, with collective and annual magistracies, overseen by Roman Senate, a senate. There were annual elections, but the republican system was an elective olig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostia Antica
Ostia Antica () is an ancient Roman city and the port of Rome located at the mouth of the Tiber. It is near modern Ostia, southwest of Rome. Due to silting and the invasion of sand, the site now lies from the sea. The name ''Ostia'' (the plural of ''ostium'') derives from Latin ''os'' 'mouth'. Ostia is now a large archaeological site noted for the excellent preservation of its ancient buildings, magnificent frescoes and impressive mosaics. The city's decline after antiquity led to harbor deterioration, marshy conditions, and reduced population. Sand dunes covering the site aided its preservation. Its remains provide insights into a city of commercial importance. As in Pompeii, Ostia's ruins provide details about Roman urbanism that are not accessible within the city of Rome itself. History Origins Ostia may have been Rome's first '' colonia''. According to legend, Ancus Marcius, the fourth king of Rome, was the first to destroy Ficana, an ancient town that was only fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claudius
Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; ; 1 August 10 BC – 13 October AD 54), or Claudius, was a Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Nero Claudius Drusus, Drusus and Antonia Minor at Lugdunum in Roman Gaul, where his father was stationed as a military legate. He was the first Roman emperor to be born outside Roman Italy, Italy. As he had a limp and slight deafness due to an illness he suffered when young, he was ostracized by his family and was excluded from public office until his consulship (which was shared with his nephew, Caligula, in 37). Claudius's infirmity probably saved him from the fate of many other nobles during the purges throughout the reigns of Tiberius and Caligula, as potential enemies did not see him as a serious threat. His survival led to him being declared emperor by the Praetorian Guard after Caligula's assassination, at which point he was the last adult male of his family. Despite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sestertius
The ''sestertius'' (: ''sestertii'') or sesterce (: sesterces) was an Ancient Rome, ancient Roman Roman currency, coin. During the Roman Republic it was a small, silver coin issued only on rare occasions. During the Roman Empire it was a large brass coin. The name ''sestertius'' means "two and one half", referring to its nominal value of two and a half ''as (Roman coin), asses'' (a bronze Roman coin, singular ''as''), a value that was useful for commerce because it was one quarter of a denarius, a coin worth ten ''asses''. The name is derived from ''semis'', "half" and ''tertius'', "third", in which "third" refers to the third ''as'': the sestertius was worth two full ''asses'' and half of a third. English-language sources routinely use the original Latin form ''sestertius'', plural ''sestertii''; but older literature frequently uses ''sesterce'', plural ''sesterces'', ''terce'' being the English equivalent of ''tertius''. A modern shorthand for values in sestertii is IIS (Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans-Georg Pflaum
Hans-Georg Pflaum (3 June 1902, Berlin – 26 December 1979, Linz) was a German-born French historian. Life Pflaum, who came from a Jewish family of industrialists, at first studied law in Breslau and Heidelberg, afterwards taking a position in his father's company. He was promoted in 1925 in Breslau. When the company fell victim to the global economic crisis in 1929, Pflaum turned to a career as an academic studying Ancient History and Classical Philology in Berlin, where he studied under Ulrich Wilcken, , Eugen Täubler and Ernst Stein. After the National Socialist German Workers Party took control of the country, he left Germany in 1933 and continued his studies in Paris with Jérôme Carcopino at the Sorbonne. He also studied under the epigraphist Louis Robert. In 1937, Pflaum wrote a dissertation on the Cursus publicus during the Roman Empire and was to become a member of the Centre national de la recherche scientifique (CNRS). After the French defeat in 1940, he had t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centurion
In the Roman army during classical antiquity, a centurion (; , . ; , or ), was a commander, nominally of a century (), a military unit originally consisting of 100 legionaries. The size of the century changed over time; from the 1st century BC through most of the imperial era it was reduced to 80 men. A centurion was promoted for being an exemplary soldier and was then expected to become a strict commander of his subordinates, to lead his troops by example, and coordinate his century's actions. They were also responsible for handling logistics and supplies, as well as any discipline that was required. In a Roman legion, centuries were grouped into cohorts and commanded by a senior centurion. The prestigious first cohort (a formation of five double-strength centuries of 160 men each) was led by the '' primus pilus,'' who commanded the ''primi ordines'' who were the centurions of the first cohort. A centurion's symbol of office was the vine staff, with which they disciplined e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |