|
Powassan Virus
Powassan virus (POWV) is a ''Flavivirus'' transmitted by ticks, found in North America and in the Russian Far East. It is named after the town of Powassan, Ontario, where it was identified in a young boy who eventually died from it. It can cause encephalitis, inflammation of the brain. No approved vaccine or antiviral drug exists. Prevention of tick bites is the best precaution. Classification and occurrence Powassan virus (POWV) is a ''Flavivirus'' named after the town of Powassan, Ontario, Canada, where it was identified in a five-year-old boy, Lincoln Byers, who died from encephalitis in 1958. The ICTV species name for the Powassan Virus is Orthoflavivirus powassanense. The virus exists in North America and causes long-term neurological sequelae. The first human case in the United States was found in 1970 in New Jersey and the first in Russia in 1978. Powassan virus has been noted as the only tick-borne ''Flavivirus'' in North America with human pathogenicity. Powassan virus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deer Tick Virus
Deer tick virus (DTV) is a virus in the genus '' Flavivirus'' spread via ticks that causes encephalitis. Taxonomy DTV closely resembles Powassan virus (to which it has 84% nucleotide sequence identity and 94% amino acid sequence identity). Due to their close similarities, DTV is also called Powassan virus lineage II. The DTV lineage is presumed to be maintained between '' Ixodes scapularis'', or deer ticks, and the white-footed mouse ('' Peromyscus leucopus''). Epidemiology DTV has a strong prevalence in the northeastern and north central part of the United States, although little to no human infections have been reported. Only about 1 to 3% of ''I. scapularis'' ticks in the northern United States are possibly infected with DTV. This infers that the virus is not seriously pathogenic or it does not easily infect humans. Human incidence might be severely underestimated. History In 1997, it was isolated from ''I. scapularis'' ticks collected in Massachusetts and Connecticu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ixodes Cookei
''Ixodes cookei'' is a species of tick in the genus ''Ixodes''. It is normally a parasite of carnivorans, such as raccoons, foxes, and weasels, but has also been recorded on the groundhog (''Marmota monax'') and the marsh rice rat (''Oryzomys palustris''). In the northeastern United States, it is a vector of Powassan virus Powassan virus (POWV) is a ''Flavivirus'' transmitted by ticks, found in North America and in the Russian Far East. It is named after the town of Powassan, Ontario, where it was identified in a young boy who eventually died from it. It can cause ....Reeves et al., 2002, p. 50 See also * List of parasites of the marsh rice rat References Literature cited * * cookei Arachnids of North America Animals described in 1869 Parasitic arthropods of mammals {{Acari-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paresis
In medicine, paresis (), compound word from Greek , (πᾰρᾰ- “beside” + ἵημι “let go, release”), is a condition typified by a weakness of voluntary movement, or by partial loss of voluntary movement or by impaired movement. When used without qualifiers, it usually refers to the limbs, but it can also be used to describe the muscles of the eyes ( ophthalmoparesis), the stomach (gastroparesis), and also the vocal cords ( vocal cord paresis). Neurologists use the term ''paresis'' to describe weakness, and ''plegia'' to describe paralysis in which all voluntary movement is lost. The term ''paresis'' comes from the 'letting go' from παρίημι 'to let go, to let fall'. Types Limbs * Monoparesis – One leg or one arm * Paraparesis – Both legs * Hemiparesis – The loss of function to only one side of the body * Triparesis – Three limbs. This can either mean both legs and one arm, both arms and a leg, or a combination of one arm, one leg, and face * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aphasia
Aphasia, also known as dysphasia, is an impairment in a person's ability to comprehend or formulate language because of dysfunction in specific brain regions. The major causes are stroke and head trauma; prevalence is hard to determine, but aphasia due to stroke is estimated to be 0.1–0.4% in developed countries. Aphasia can also be the result of brain tumors, epilepsy, autoimmune neurological diseases, brain infections, or neurodegenerative diseases (such as dementias). To be diagnosed with aphasia, a person's language must be significantly impaired in one or more of the four aspects of communication. In the case of progressive aphasia, a noticeable decline in language abilities over a short period of time is required. The four aspects of communication include spoken language production, spoken language comprehension, written language production, and written language comprehension. Impairments in any of these aspects can impact functional communication. The difficulties o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meningoencephalitis
Meningoencephalitis (; from ; ; and the medical suffix ''-itis'', "inflammation"), also known as herpes meningoencephalitis, is a medical condition that simultaneously resembles both meningitis, which is an infection or inflammation of the meninges, and encephalitis, which is an infection or inflammation of the brain tissue. Signs and symptoms Signs of meningoencephalitis include unusual behavior, personality changes, nausea, and thinking problems. Symptoms may include headache, fever, pain in neck movement, light sensitivity, and seizure. Causes The organisms which cause meningoencephalitis include bacterial pathogens, protozoans, and viruses. Bacterial Veterinarians have observed meningoencephalitis in animals infected with listeriosis, caused by the pathogenic bacteria '' L. monocytogenes''. Meningitis and encephalitis already present in the brain or spinal cord of an animal may form simultaneously into meningeoencephalitis. The bacteria commonly targets the sensiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serology
Serology is the scientific study of Serum (blood), serum and other body fluids. In practice, the term usually refers to the medical diagnosis, diagnostic identification of Antibody, antibodies in the serum. Such antibodies are typically formed in response to an infection (against a given microorganism), against other foreign proteins (in response, for example, to a Acute hemolytic transfusion reaction, mismatched blood transfusion), or to one's own proteins (in instances of autoimmune disease). In either case, the procedure is simple. Serological tests Serological tests are diagnostic methods that are used to identify antibodies and antigens in a patient's sample. Serological tests may be performed to diagnose infections and autoimmune illnesses, to check if a person has immunity (medical), immunity to certain diseases, and in many other situations, such as determining an individual's blood type. Serological tests may also be used in forensic serology to investigate crime scene evid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis
Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM), or acute demyelinating encephalomyelitis, is a rare autoimmune disease marked by a sudden, widespread attack of inflammation in the brain and spinal cord. As well as causing the brain and spinal cord to become inflamed, ADEM also attacks the nerves of the central nervous system and damages their myelin insulation, which, as a result, destroys the white matter. The cause is often a trigger such as from viral infection or, in extraordinarily rare cases, vaccinations. ADEM's symptoms resemble the symptoms of multiple sclerosis (MS), so the disease itself is sorted into the classification of the multiple sclerosis borderline diseases. However, ADEM has several features that distinguish it from MS. Unlike MS, ADEM occurs usually in children and is marked with rapid fever, although adolescents and adults can get the disease too. ADEM consists of a single flare-up whereas MS is marked with several flare-ups (or relapses), over a long per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaplasmosis
Anaplasmosis is a tick-borne disease affecting ruminants, dogs, and horses, and is caused by ''Anaplasma'' bacteria. Anaplasmosis is an infectious but not contagious disease. Anaplasmosis can be transmitted through mechanical and biological vector processes. Anaplasmosis can also be referred to as "yellow bag" or "yellow fever" because the infected animal can develop a jaundiced look. Other signs of infection include weight loss, diarrhea, paleness of the skin, aggressive behavior, and high fever. Many different tick species can carry the bacteria that cause anaplasmosis. The two major bacterial pathogens are ''Anaplasma marginale'' and ''Anaplasma phagocytophilum''. These microorganisms are Gram-negative, and infect red blood cells. Once the host is infected with anaplasmosis, the immune system will try to fight off and kill the infected red blood cells, but will also kill healthy red blood cells. The ''Anaplasma sparouinense'' species is responsible for a rare zoonosis, the Spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzootic
Enzootic describes the situation where a disease or pathogen is continuously present in at least one species of non-human animal in a particular region. It is the non-human equivalent of endemic. In epizoology, an infection is said to be "''enzootic''" in a population when the infection is maintained in the population without the need for external inputs (''cf''. endemic). See also *Epizootic In epizoology, an epizootic (or epizoötic, from Greek: ''epi-'' "upon" + ''zoon'' "animal") is a disease event in a nonhuman animal population analogous to an epidemic in humans. An epizootic disease (or ) may occur in a specific locale (an ... Biodiversity {{Veterinary-med-stub Pathology Epidemiology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyme Disease
Lyme disease, also known as Lyme borreliosis, is a tick-borne disease caused by species of ''Borrelia'' bacteria, Disease vector, transmitted by blood-feeding ticks in the genus ''Ixodes''. It is the most common disease spread by ticks in the Northern Hemisphere. Infections are most common in the spring and early summer. The most common sign of infection is an expanding red rash, known as erythema migrans (EM), which appears at the site of the tick bite about a week afterwards. The rash is typically neither itchy nor painful. Approximately 70–80% of infected people develop a rash. Other early symptoms may include fever, headaches and fatigue (medical), tiredness. If untreated, symptoms may include Facial nerve paralysis, loss of the ability to move one or both sides of the face, arthritis, joint pains, Meningitis, severe headaches with neck stiffness or heart palpitations. Months to years later, repeated episodes of joint pain and swelling may occur. Occasionally, shootin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
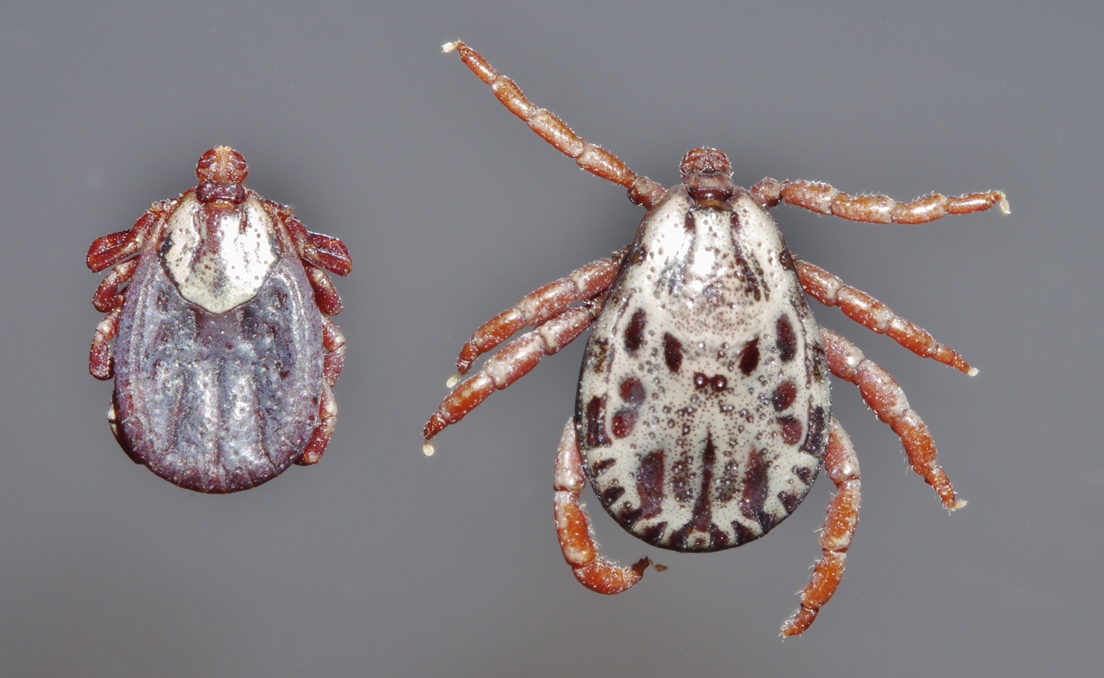
Dermacentor Variabilis
''Dermacentor variabilis'', also known as the American dog tick or wood tick, is a species of tick that is known to carry bacteria responsible for several diseases in humans, including Rocky Mountain spotted fever and tularemia (''Francisella tularensis''). It is one of the best-known Ixodidae, hard ticks. Diseases are spread when it sucks blood from the host. It may take several days for the host to experience symptoms. Though ''D. variabilis'' may be exposed to ''Borrelia burgdorferi'', the causative agent of Lyme disease, these ticks are not competent Vector (epidemiology), vectors for the transmission of this disease. The primary vectors for ''B. burgdorferi'' are the deer ticks ''Ixodes scapularis'' in eastern parts of the United States, ''Ixodes pacificus'' in California and Oregon, and ''Ixodes ricinus'' in Europe. ''D. variabilis'' may also carry ''Anaplasma phagocytophilum'', the causative agent of human granulocytic anaplasmosis, and ''Ehrlichia chaffeensis'', the causat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
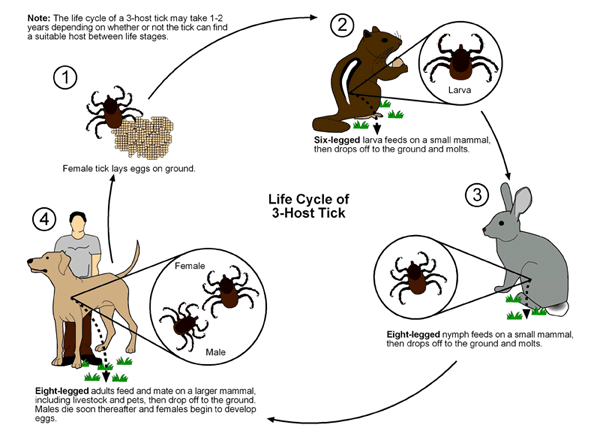
Dermacentor Andersoni
''Dermacentor andersoni'', commonly known as the Rocky Mountain wood tick, is a hard tick, or member of the Ixodidae family, with three life stages including larvae, nymph, and finally adult, or, more entomologically, imago. This tick is generally located in the northwest United States and southwest Canada along the Rocky Mountains. This tick is generally a vector for Colorado tick fever, but can also be a vector for Rocky Mountain spotted fever and tularemia. During the larval and nymphal stages, the tick does not feed on humans, but during the adult stage, it will. Prevention of infections associated with these ticks is based on control of exposure to the vector, including wearing proper clothing when in woods/wet areas, and checking oneself thoroughly after returning home. Adult female ticks can feed for 5 to 15 days, thus removing a tick if present is very important. Follow general tick removal tips. Life cycle ''Dermacentor andersoni'' is a three-host tick with larval, n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |