|
Positivist School (criminology)
The Positivist School was founded by Cesare Lombroso and led by two others: Enrico Ferri (criminologist), Enrico Ferri and Raffaele Garofalo. In criminology, it has attempted to find scientific objectivity for the measurement and quantification of criminal behavior. Its method was developed by observing the characteristics of criminals to observe what may be the root cause of their behavior or actions. Since the Positivist's school of ideas came around, research revolving around its ideas has sought to identify some of the key differences between those who were deemed "criminals" and those who were not, often without considering flaws in the label of what a “criminal” is. As the scientific method became the major paradigm in the search for knowledge, the classical school (criminology), Classical School's social philosophy was replaced by the quest for scientific laws that would be discovered by experts. It is divided into biological, psychological, and social laws. Biologica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cesare Lombroso
Cesare Lombroso ( , ; ; born Ezechia Marco Lombroso; 6 November 1835 – 19 October 1909) was an Italian eugenicist, criminologist, phrenologist, physician, and founder of the Italian school of criminology. He is considered the founder of modern criminology by changing the Western notions of individual responsibility. Lombroso rejected the established classical school (criminology), classical school, which held that crime was a characteristic trait of human nature. Instead, using concepts drawn from physiognomy, degeneration theory, psychiatry, and Social Darwinism, Lombroso's theory of anthropological criminology essentially stated that criminality was inherited, and that someone "born criminal" could be identified by congenital disorder, physical (congenital) defects, which confirmed a criminal as savage or atavism, atavistic. Early life and education Lombroso was born in Verona, Kingdom of Lombardy–Venetia, on 6 November 1835 to a wealthy Jewish family. His father wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a State (polity), state. In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive (government), executive, and judiciary. Government is a means by which organizational policies are enforced, as well as a mechanism for determining policy. In many countries, the government has a kind of constitution, a statement of its governing principles and philosophy. While all types of organizations have governance, the term ''government'' is often used more specifically to refer to the approximately 200 list of sovereign states, independent national governments and government agency, subsidiary organizations. The main types of modern political systems recognized are democracy, democracies, totalitarian regimes, and, sitting between these two, authoritarianism, authoritarian regimes with a variety of hybrid regimes. Modern classification systems also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emotional Intelligence
Emotional intelligence (EI), also known as emotional quotient (EQ), is the ability to perceive, use, understand, manage, and handle emotions. High emotional intelligence includes emotional recognition of emotions of the self and others, using emotional information to guide thinking and behavior, discerning between and labeling of different feelings, and adjusting emotions to adapt to environments. This includes emotional literacy. The term first appeared in 1964, gaining popularity in the 1995 bestselling book '' Emotional Intelligence'' by psychologist and science journalist Daniel Goleman. Some researchers suggest that emotional intelligence can be learned and strengthened, while others claim that it is innate. Various models have been developed to measure EI: The ''trait model'' focuses on self-reporting behavioral dispositions and perceived abilities; the ''ability model'' focuses on the individual's ability to process emotional information and use it to navigate the soc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empirical Evidence
Empirical evidence is evidence obtained through sense experience or experimental procedure. It is of central importance to the sciences and plays a role in various other fields, like epistemology and law. There is no general agreement on how the terms ''evidence'' and ''empirical'' are to be defined. Often different fields work with quite different conceptions. In epistemology, evidence is what Justification (epistemology), justifies beliefs or what determines whether holding a certain belief is rational. This is only possible if the evidence is possessed by the person, which has prompted various epistemologists to conceive evidence as private mental states like experiences or other beliefs. In philosophy of science, on the other hand, evidence is understood as that which ''Scientific method#Confirmation, confirms'' or ''disconfirms'' Hypothesis#Scientific hypothesis, scientific hypotheses and arbitrates between competing theories. For this role, evidence must be public and uncont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature Versus Nurture
Nature versus nurture is a long-standing debate in biology and society about the relative influence on human beings of their genetics, genetic inheritance (nature) and the environmental conditions of their development (nurture). The alliterative expression "nature and nurture" in English has been in use since at least the Elizabethan era, Elizabethan period and goes back to medieval French. The complementary combination of the two concepts is an ancient concept (). Nature is what people think of as pre-wiring and is influenced by genetic inheritance and other biological factors. Nurture is generally taken as the influence of external factors after conception e.g. the product of exposure, experience and learning on an individual. The phrase in its modern sense was popularized by the Victorian era, Victorian polymath Francis Galton, the modern founder of eugenics and behavioral genetics when he was discussing the influence of heredity and Social environment, environment on social adv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome
A chromosome is a package of DNA containing part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome-forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells, the most important of these proteins are the histones. Aided by chaperone proteins, the histones bind to and condense the DNA molecule to maintain its integrity. These eukaryotic chromosomes display a complex three-dimensional structure that has a significant role in transcriptional regulation. Normally, chromosomes are visible under a light microscope only during the metaphase of cell division, where all chromosomes are aligned in the center of the cell in their condensed form. Before this stage occurs, each chromosome is duplicated ( S phase), and the two copies are joined by a centromere—resulting in either an X-shaped structure if the centromere is located equatorially, or a two-armed structure if the centromere is located distally; the jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinians, Augustinian friar working in the 19th century in Brno, was the first to study genetics scientifically. Mendel studied "trait inheritance", patterns in the way traits are handed down from parents to offspring over time. He observed that organisms (pea plants) inherit traits by way of discrete "units of inheritance". This term, still used today, is a somewhat ambiguous definition of what is referred to as a gene. Phenotypic trait, Trait inheritance and Molecular genetics, molecular inheritance mechanisms of genes are still primary principles of genetics in the 21st century, but modern genetics has expanded to study the function and behavior of genes. Gene structure and function, variation, and distribution are studied within the context of the Cell (bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somatotype
Somatotype is a theory proposed in the 1940s by the American psychologist William Herbert Sheldon to categorize the human physique according to the relative contribution of three fundamental elements which he termed ''somatotypes'', classified by him as ''ectomorphic'', ''mesomorphic'', and ''endomorphic''. He created these terms borrowing from the three germ layers of embryonic development: The endoderm (which develops into the digestive tract), the mesoderm (which becomes muscle, heart, and blood vessels) and the ectoderm (which forms the skin and nervous system). Later variations of these categories, developed by his original research assistant Barbara Heath, and later by Lindsay Carter and Rob Rempel, are used by academics today. Constitutional psychology is a theory developed by Sheldon in the 1940s, which attempted to associate his somatotype classifications with human temperament types. The foundation of these ideas originated with Francis Galton and eugenics. Sheldon and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Herbert Sheldon
William Herbert Sheldon, Jr. (November 19, 1898 – September 17, 1977) was an American psychologist, numismatist, and eugenicist. He created the field of somatotype and constitutional psychology that correlate body types with temperament, illustrated by his controversial Ivy League nude posture photos. Early life and education Sheldon was born in Pawtuxet, Rhode Island, on November 19, 1898, to William Herbert Sheldon, Sr., a naturalist and animal breeder, and Mary Abby Greene, a village midwife. His godfather was the noted psychologist and philosopher, William James. He graduated from Warwick Veterans Memorial High School in 1915 and attended Brown University. After graduating, he worked in a range of fields before studying for his master's degree at the University of Colorado. Sheldon attended the University of Chicago and earned his Ph.D. in 1925. He taught psychology at the University of Chicago and at the University of Wisconsin. He attended the University of Chicago Medica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earnest Hooton
Earnest Albert Hooton (November 20, 1887 – May 3, 1954) was an American physical anthropologist known for his work on racial classification and his popular writings such as the book ''Up From The Ape''. Hooton sat on the Committee on the Negro, a group that "focused on the anatomy of blacks and reflected the racism of the time." Biography Earnest Albert Hooton was born in Clemansville, Wisconsin, the third child and only son of an English-born Methodist minister married to a Canadian-born woman of Scotch-Irish ancestry. He was educated at Lawrence University in Appleton, Wisconsin. After earning his BA there in 1907, he won a Rhodes Scholarship to Oxford University, which he deferred in order to continue his studies in the United States. He pursued graduate studies in classics at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, where he received an MA in 1908 and a Ph.D. in 1911 on "The Pre-Hellenistic Stage of the Evolution of the Literary Art at Rome", and then continued on to England ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Buckman Goring
Charles Buckman Goring (1870–1919) was a pioneer in criminology and author of the influential work ''The English Convict: a statistical study''. Life He married Katie Winifred Macdonald, a pianist and suffragette, in Paris in 1905. They had two sons, Charles Donald Austin Goring (known as Donald) who died in a motor vehicle accident in Yemen in 1936 and Marius Goring, the stage and screen actor. He died on 5 May 1919 at his home in Cheetham Hill, Manchester from influenza. He was the Chief Medical Officer at HM Prison Manchester (Strangeways) at the time of his death. He was highly regarded among those who knew him. His colleague Karl Pearson once said: "The creative mind has the potentiality of poet, artist and scientist within its grasp, and Goring's friends were never very certain in which category to place him." ''The English Convict'' Goring's crowning achievement was ''The English Convict: A Statistical Study'', one of the most comprehensive criminological works of it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
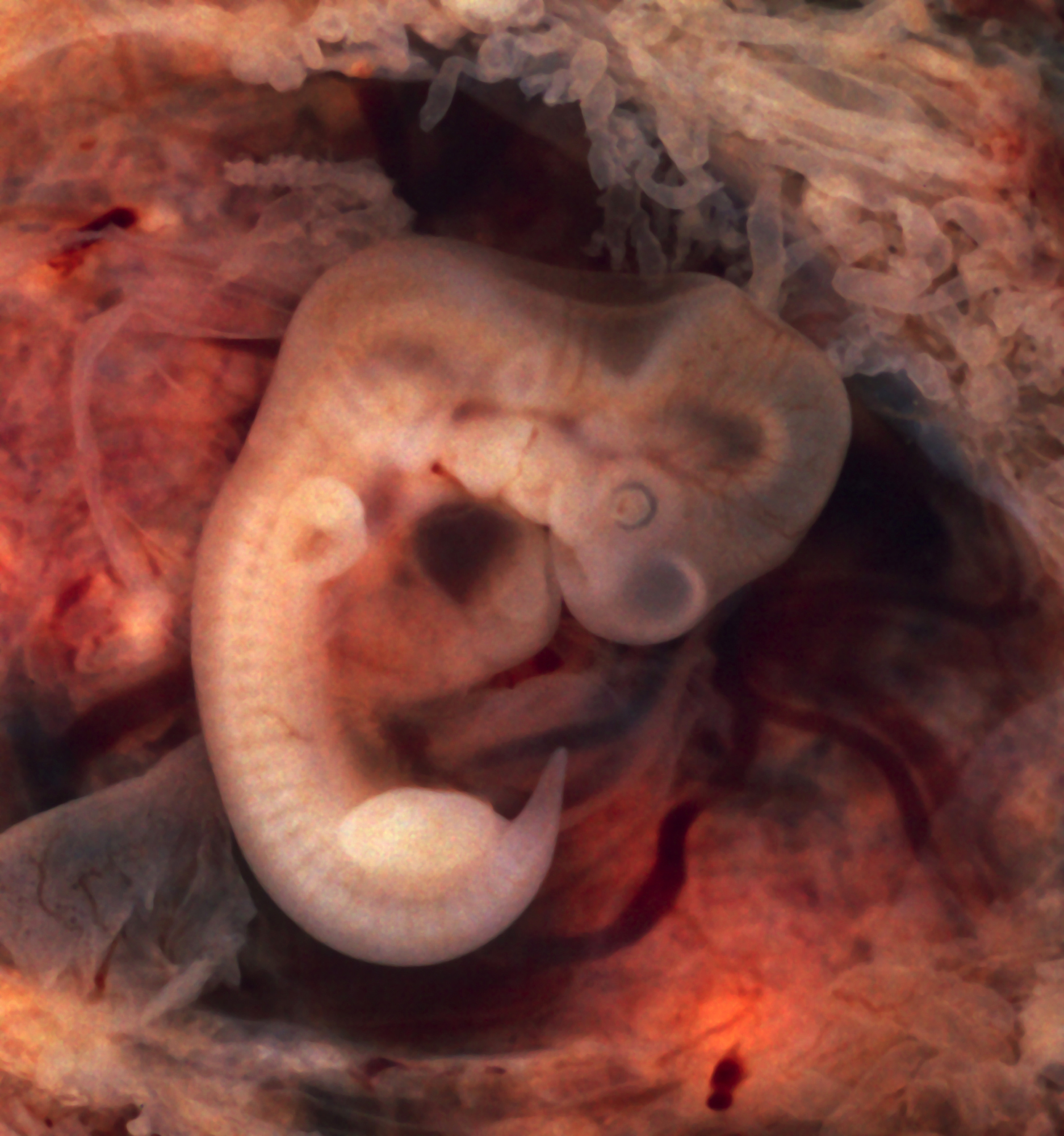
Atavism
In biology, an atavism is a modification of a biological traits structure or behavior whereby an ancestral genetic trait reappears after having been lost through evolutionary change in previous generations. Atavisms can occur in several ways, one of which is when genes for previously existing phenotypic features are preserved in DNA, and these become expressed through a mutation that either knocks out the dominant genes for the new traits or makes the old traits dominate the new one. A number of traits can vary as a result of shortening of the fetal development of a trait (neoteny) or by prolongation of the same. In such a case, a shift in the time a trait is allowed to develop before it is fixed can bring forth an ancestral phenotype. Atavisms are often seen as evidence of evolution. In social sciences, atavism is the tendency of reversion: for example, people in the modern era reverting to the ways of thinking and acting of a former time. The word ''atavism'' is derived fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |