|
Portuguese Conquest Of Hormuz
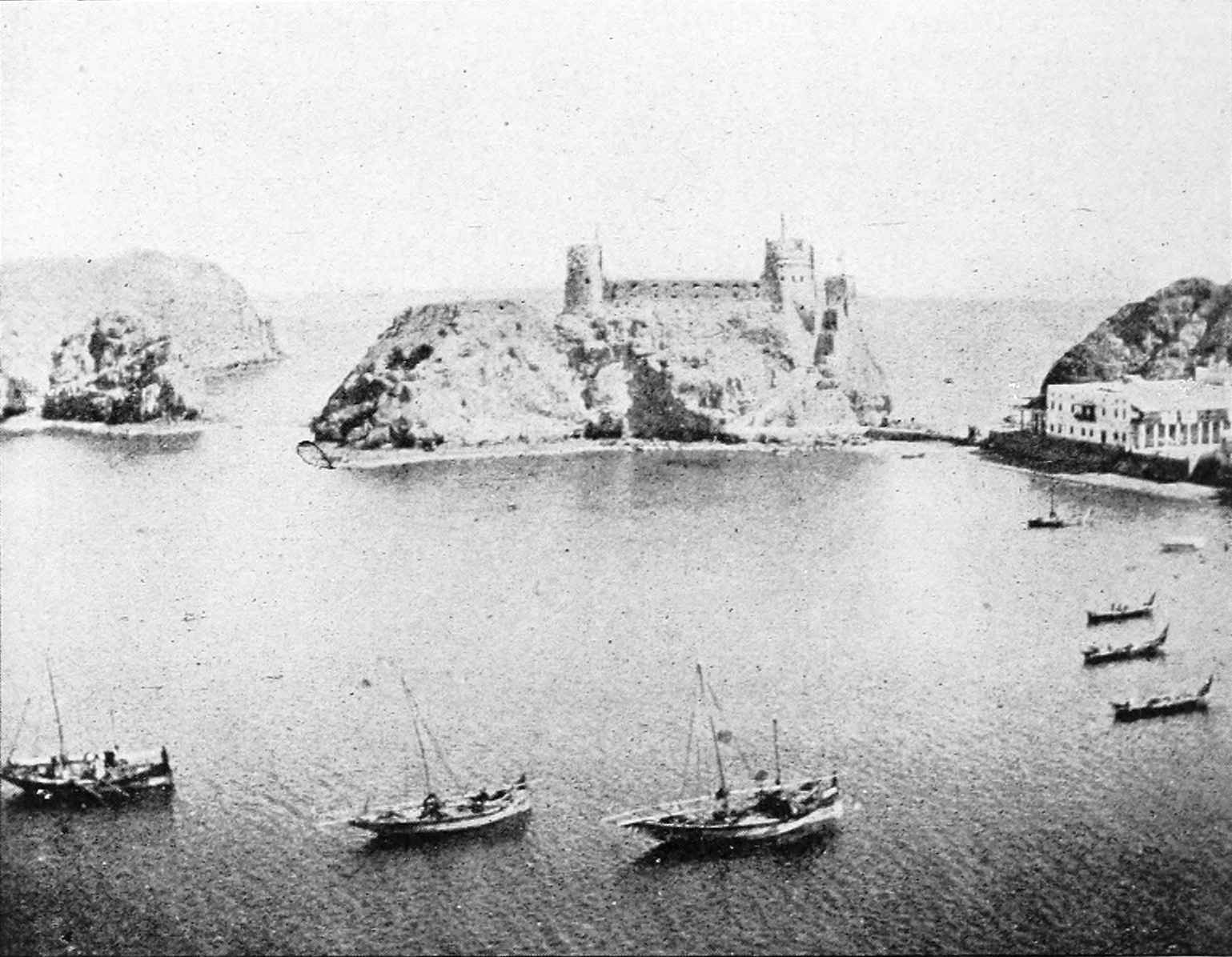
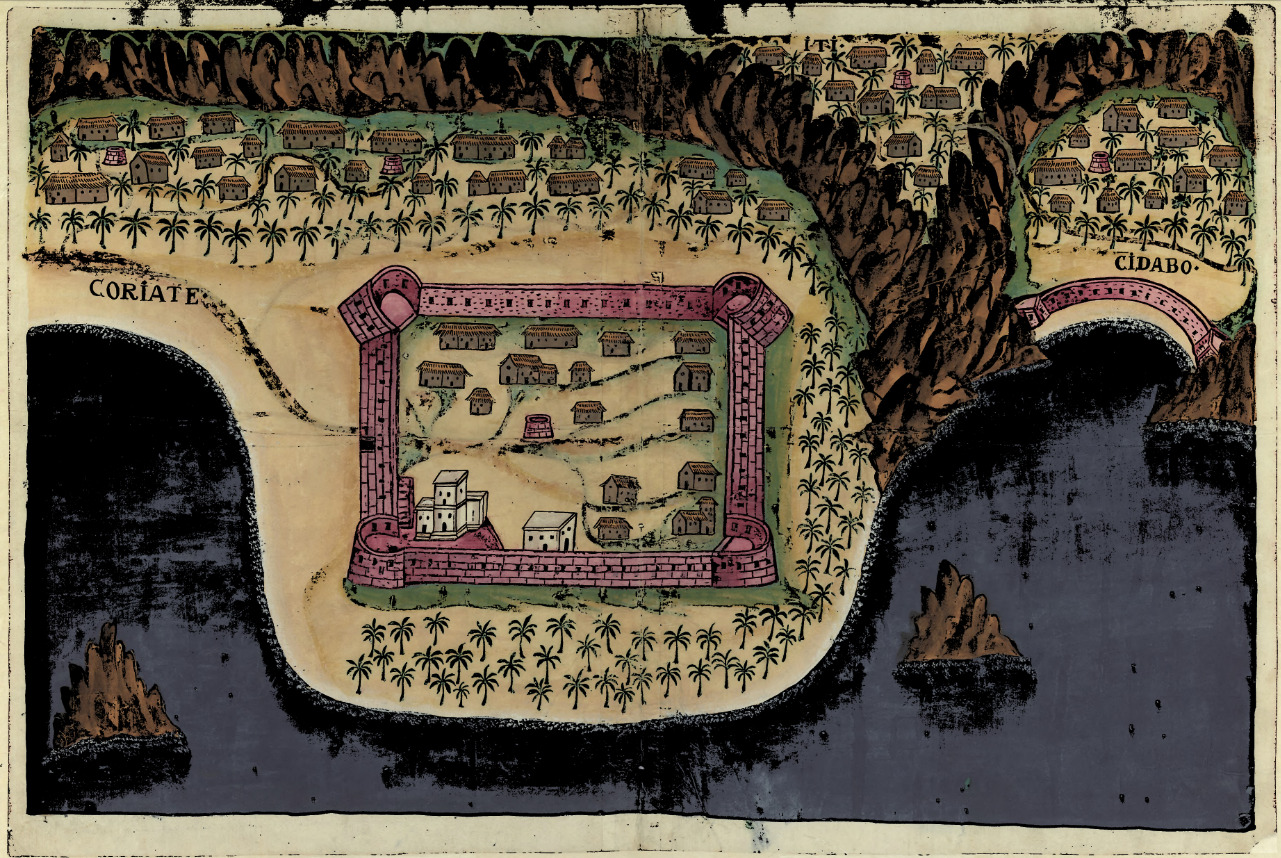
The Portuguese conquest of Hormuz in 1507 occurred when the Portuguese people, Portuguese Afonso de Albuquerque attacked Hormuz Island to establish the Fort of Our Lady of the Conception, Fortress of Hormuz. This conquest gave the Portuguese full control of the trade between India and Europe passing through the Persian Gulf. Background The campaign against Hormuz was a result of a plan by King Manuel I of Portugal, who in 1505 had resolved to thwart Indian Ocean trade, Muslim trade in the Indian Ocean by capturing Aden to block trade through the Red Sea and Alexandria; Hormuz, to block trade through Beirut; and Malacca to control trade with China. The Portuguese had reports indicating that the island of Socotra was inhabited by Nestorian Christians and might prove useful towards this endeavor. Socotra was then a dominion of the Mahra Sultanate, Banu Afrar clan of Qishn, in mainland Arabian Peninsula, Arabia, whom the Portuguese would refer in the 16th century as ''Fartaques'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hormuz Island
Hormuz Island (; ), also spelled Hormoz, Ormoz, Ormuz or Ormus, is an Iranian island in the Persian Gulf. Geography Hormuz Island has an area of . Located in the Strait of Hormuz, off the Iranian coast, the island is part of Hormozgan Province. It is sparsely inhabited, but some development has taken place since the late 20th century. Geology Reddish ochre on the island and its beaches, called Golak by natives, has been exploited for artistic and culinary purposes, and also attracts tourists. Degradation due to overuse of the ochre has resulted in actions by the Department of Environment (Iran), Department of Environment to protect it. The satellite images catching the concentric arrangement of the rocks show that Hormuz Island appears to be a salt diapir, composed of ancient seasalt deposits which, due to lack of salt-dissolving groundwater and rains, and due to their plastic deformabilty, can flow and squeeze just like ice; thus, under the squeezing pressure of other sedim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Sea
The Red Sea is a sea inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. Its connection to the ocean is in the south, through the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait and the Gulf of Aden. To its north lie the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and the Gulf of Suez—leading to the Suez Canal. It is underlain by the Red Sea Rift, which is part of the Great Rift Valley. The Red Sea has a surface area of roughly , is about long, and wide at its widest point. It has an average depth of , and in the central Suakin Trough, it reaches its maximum depth of . Approximately 40% of the Red Sea is quite shallow at less than deep and about 25% is less than deep. The extensive shallow shelves are noted for their marine life and corals. More than 1,000 invertebrate species and 200 types of soft and hard coral live in the sea. The Red Sea is the world's northernmost tropical sea and has been designated a Global 200 ecoregion. Extent The International Hydrographic Organization defines the limi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander The Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II of Macedon, Philip II to the throne in 336 BC at the age of 20 and spent most of his ruling years conducting Wars of Alexander the Great, a lengthy military campaign throughout West Asia, Western Asia, Central Asia, parts of South Asia, and ancient Egypt, Egypt. By the age of 30, he had created one of the List of largest empires, largest empires in history, stretching from History of Greece, Greece to northwestern History of India, India. He was undefeated in battle and is widely considered to be one of history's greatest and most successful military commanders. Until the age of 16, Alexander was tutored by Aristotle. In 335 BC, shortly after his assumption of kingship over Macedon, he Alexander's Balkan campaign, campaigned in the Bal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khor Fakkan
Khor Fakkan () is a city and an exclave of the Emirate of Sharjah, located on the east coast of the United Arab Emirates (UAE), facing the Gulf of Oman, and geographically surrounded by the Emirate of Fujairah. The city, the second largest on the east coast after Fujairah City, is set on the bay of Khor Fakkan, which means "Creek of Two Jaws". It is the site of Khor Fakkan Container Terminal, the only natural deep-sea port in the region and one of the major container ports in the UAE. The Port of Khor Fakkan faces the Emirate of Sharjah’s eastern seaboard, extending connections with Asia and the Far East. This port is one of the Emirate’s three ports. It is also a popular spot among domestic tourists due to its white sand beaches and coral reefs that attract many marine life enthusiasts. Khor Fakkan beach lies to the north of the center of the town. Khor Fakkan is located on the east coast of the UAE, between the Shumayliyah Mountains and the Arabian Sea, with an altitude ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sohar
Sohar () is the capital and largest city of the Al Batinah North Governorate in Oman. An ancient capital of the country that once served as an important Islamic port town on the Gulf of Oman, Sohar has also been credited as the mythical birthplace of Sinbad the Sailor. It was historically known as Mazūn (). At the 2010 census, Sohar's population was 140,006, making it Oman's fifth most-populated settlement. Described as an industrial town, the development of the Sohar Industrial Port during the 2000s has transformed it into a major Omani industrial hub. History As the largest town in the region, it has been argued that Sohar is to be identified with the ancient town called 'Omanah' () mentioned by Pliny the Elder in his '' Natural History''. This settlement is believed to have given Oman its name. According to Al-Tabari, in 893 or 894 C.E., during the Abbasid era, there was a dispute about who should rule Oman amongst local factions. A faction that approached the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eunuch
A eunuch ( , ) is a male who has been castration, castrated. Throughout history, castration often served a specific social function. The earliest records for intentional castration to produce eunuchs are from the Sumerian city of Lagash in the 2nd millennium BCE. Over the millennia since, they have performed a wide variety of functions in many different cultures: courtiers or equivalent Domestic worker, domestics, for espionage or clandestine operations, ''castrato'' singers, Concubinage, concubines or sexual partners, religious specialists, soldiers, royal guards, government officials, and guardians of women or harem servants. Eunuchs would usually be servants or Slavery, slaves who had been castrated to make them less threatening servants of a royal court where physical access to the ruler could wield great influence. Seemingly lowly domestic functions—such as making the ruler's bed, bathing him, cutting his hair, carrying him in his litter (vehicle), litter, or even rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscat
Muscat (, ) is the capital and most populous city in Oman. It is the seat of the Governorate of Muscat. According to the National Centre for Statistics and Information (NCSI), the population of the Muscat Governorate in 2022 was 1.72 million. The metropolitan area includes six provinces, called , and spans approximately . Known since the early 1st century CE as a leading port for trade between the west and the east, Muscat was ruled successively by various indigenous tribes, as well as by foreign powers such as the Persians, the Portuguese Empire and the Ottoman Empire. In the 18th century, Muscat was a regional military power: its influence extended as far as East Africa and Zanzibar. As an important port town in the Gulf of Oman, Muscat attracted foreign traders and settlers such as the Persians, the Balochs and the Sindhis. Beginning in 1970, after the accession of Qaboos bin Said as the Sultan of Oman, Muscat experienced rapid infrastructural development; it developed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qurayyat, Oman
Qurayyat is a small fishing town 83 km southeast of Muscat, Oman, adjacent to the towns of Sur, Diman Wa Tayeen and Aamerat. A popular stopping point on the way to Sur, Qurayyat is in itself also a very popular destination for Muscat. On 28 June 2018, Qurayyat set the record for the highest daily "low" temperature ever recorded: . Climate of Qurayyat Given that the state is coastal, the humidity levels rise up to extremes especially in Summer, while mountains remain relatively lower levels of humidity, Al Jabal Al Aswad (The Black Mountain) is located in the inner parts of the state and it is known for extreme cold weathers in Winter and moderate heat in Summer. Qurayyats Icon Most states in Oman have an icon that generally represents the state (For example, Lemon Tree for Saham), and for Qurayyat it is the Capra, given that the animal's habitat is scattered across the mountains of Qurayyat and the connection between Capra and Qurayyat's people. Landmarks Qurayyat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qalhat
Qalhāt () is a village in Oman, over 20 km north of Sur. The residential area is to the northwest of Wādī Ḥilm (), and the ruins of the ancient city are located to the southeast. The ancient city is referred to as Calatu by Marco Polo and as Calha in the map of Abraham Ortelius. Site description Marco Polo visited Qalhat in the 13th century, referring to it as Calatu. Ibn Battuta visited the city in the 14th century, noting that it had "fine bazaars and one of the most beautiful mosques." He further noted the mosque was built by Bibi Maryam and included walls of qashani. Bibi Maryam continued to rule Qalhat and Hurmuz after the death of her husband Ayaz in 1311 or 1312. Zheng He visited the city in the 15th century, and his crew called it 加剌哈 ( Taihu Wu: ka-la-ha; Hokkien: ka-lat-ha; Cantonese: gaa-laat-haa). Qalhat served as an important stop in the wider Indian Ocean trade network, and was also the second city of the Kingdom of Ormus. By 1507 when it was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oman
Oman, officially the Sultanate of Oman, is a country located on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in West Asia and the Middle East. It shares land borders with Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. Oman’s coastline faces the Arabian Sea to the southeast and the Gulf of Oman on the northeast. The exclaves of Madha and Musandam Governorate, Musandam are surrounded by the United Arab Emirates on their land borders, while Musandam’s coastal boundaries are formed by the Strait of Hormuz and the Gulf of Oman. The capital and largest city is Muscat. With a population of approximately 5.46 million and an area of 309,500 km2 (119,500 sq mi), Oman is the Countries with highest population, 123rd most-populous country. From the 18th century, the Omani Sultanate was Omani Empire, an empire, competing with the Portuguese Empire, Portuguese and British Empire, British empires for influence in the Persian Gulf and the Indian Ocean. At its peak in the 19th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tristão Da Cunha
Tristão da Cunha (sometimes misspelled Tristão d'Acunha; ; c. 1460 – c. 1540) was a Portuguese explorer and naval commander. In 1514, he served as ambassador from King Manuel I of Portugal to Pope Leo X, leading a luxurious embassy presenting in Rome the new conquests of Portugal. He later became a member of the Portuguese privy council. Italian Wars Da Cunha was born in Portugal, c. 1460. He served in the Third Italian War under Castilian general Gonzalo Fernández de Córdoba, participating in the Battle of Cerignola and being entasked with hosting the funeral of the fallen French general, Louis d'Armagnac, Duke of Nemours. He was also in command of Roca Guillerma, between Gaeta and Salerno, where he was briefly captured by the French army in a betrayal of the local nobility. Da Cunha was later freed. After returning to Portugal, he was nominated as first viceroy of Portuguese India in 1504, but could not take up this post owing to a temporary blindness. 1506 voy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula (, , or , , ) or Arabia, is a peninsula in West Asia, situated north-east of Africa on the Arabian plate. At , comparable in size to India, the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world. Geographically, the Arabian Peninsula comprises Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and Yemen, as well as southern Iraq and Jordan. The largest of these is Saudi Arabia. In the Roman era, the Sinai Peninsula was also considered a part of Arabia. The Arabian Peninsula formed as a result of the rifting of the Red Sea between 56 and 23 million years ago, and is bordered by the Red Sea to the west and south-west, the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman to the north-east, the Levant and Mesopotamia to the north and the Arabian Sea and the Indian Ocean to the south-east. The peninsula plays a critical geopolitical role in the Arab world and globally due to its vast reserves of petroleum, oil and natural gas. Before the mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |