|
Porites Lobata
''Porites lobata'', known by the common name lobe coral, is a species of stony coral in the family Poritidae. It is found growing on coral reefs in tropical parts of the Indian and Pacific Oceans. Description ''Porites lobata'' is a hermatypic or reef-building coral. It varies greatly in size and shape depending on its environment. On wave-exposed reef slopes it is encrusting whereas in calm water areas it can grow into large helmet-shaped or hemispherical hummocks up to high and wide. Growth rates are very slow, sometimes being as little as per year, and this means that large corals are very old. The general colour is greenish, yellow or tan because of the zooxanthellae, single-celled microalgae, that live symbiotically within the tissues. These make organic nutrients available to the polyps through photosynthesis. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Dwight Dana
James Dwight Dana Royal Society of London, FRS FRSE (February 12, 1813 – April 14, 1895) was an American geologist, mineralogist, volcanologist, and zoologist. He made pioneering studies of mountain-building, volcano, volcanic activity, and the origin and structure of continents and oceans around the world. His zoological author abbreviation is Dana. Early life and career Dana was born February 12, 1813, in Utica, New York. His father was merchant James Dana (1780–1860) and his mother was Harriet Dwight (1792–1870). Through his mother he was related to the Dwight New England family of missionaries and educators including uncle Harrison Gray Otis Dwight and first cousin Henry Otis Dwight. He showed an early interest in science, which had been fostered by Fay Edgerton, a teacher in the Utica high school, and in 1830 he entered Yale College in order to study under Benjamin Silliman the elder. Graduating in 1833, for the next two years he was teacher of mathematics to midshi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only state not on the North American mainland, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only state in the tropics. Hawaii consists of 137 volcanic islands that comprise almost the entire Hawaiian Islands, Hawaiian archipelago (the exception, which is outside the state, is Midway Atoll). Spanning , the state is Physical geography, physiographically and Ethnology, ethnologically part of the Polynesian subregion of Oceania. Hawaii's ocean coastline is consequently the List of U.S. states and territories by coastline, fourth-longest in the U.S., at about . The eight main islands, from northwest to southeast, are Niihau, Niihau, Kauai, Kauai, Oahu, Oahu, Molokai, Molokai, Lanai, Lānai, Kahoʻolawe, Kahoolawe, Maui, and Hawaii (island), Hawaii, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
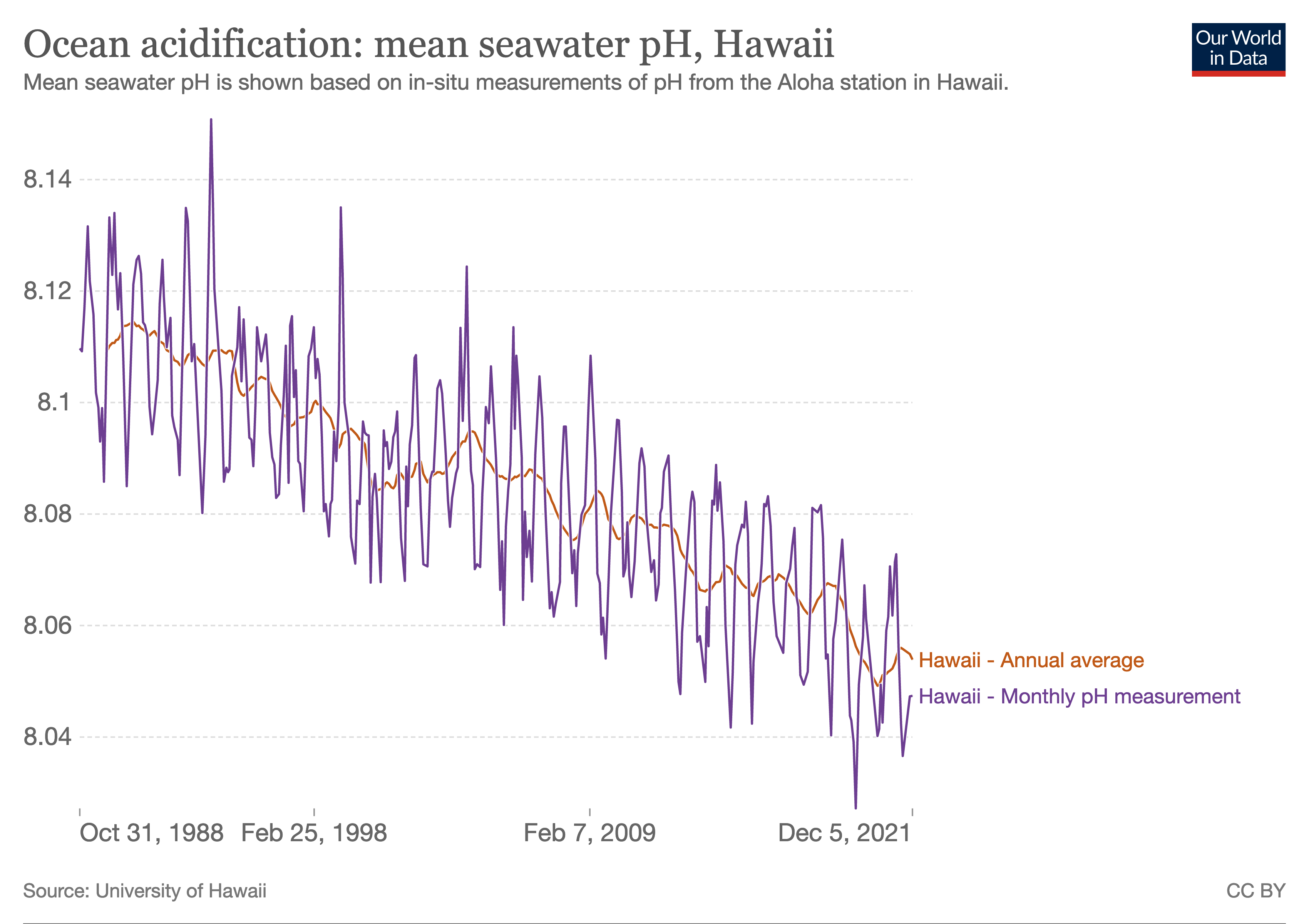
Ocean Acidification
Ocean acidification is the ongoing decrease in the pH of the Earth's ocean. Between 1950 and 2020, the average pH of the ocean surface fell from approximately 8.15 to 8.05. Carbon dioxide emissions from human activities are the primary cause of ocean acidification, with Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric carbon dioxide () levels exceeding 422 ppm (). from the atmosphere is absorbed by the oceans. This chemical reaction produces carbonic acid () which dissociates into a bicarbonate ion () and a hydrogen ion (). The presence of free hydrogen ions () lowers the pH of the ocean, increasing acidity (this does not mean that seawater is acidic yet; it is still alkaline, with a pH higher than 8). Marine biogenic calcification, Marine calcifying organisms, such as Mollusca, mollusks and corals, are especially vulnerable because they rely on calcium carbonate to build shells and skeletons. A change in pH by 0.1 represents a 26% increase in hydrogen ion concentration in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Niño–Southern Oscillation
El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is a global climate phenomenon that emerges from variation in winds and sea surface temperatures over the tropical Pacific Ocean. Those variations have an irregular pattern but do have some semblance of cycles. The occurrence of ENSO is not predictable. It affects the climate of much of the tropics and subtropics, and has links (Teleconnection, teleconnections) to higher-latitude regions of the world. The warming phase of the sea surface temperature is known as "El Niño" and the cooling phase as "La Niña". The Southern Oscillation is the accompanying atmospheric oscillation, which is coupled with the sea temperature change. El Niño is associated with higher than normal air sea level pressure over Indonesia, Australia and across the Indian Ocean to the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic. La Niña has roughly the reverse pattern: high pressure over the central and eastern Pacific and lower pressure through much of the rest of the tropics and subtrop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commensalism
Commensalism is a long-term biological interaction (symbiosis) in which members of one species gain benefits while those of the other species neither benefit nor are harmed. This is in contrast with mutualism, in which both organisms benefit from each other; amensalism, where one is harmed while the other is unaffected; and parasitism, where one is harmed and the other benefits. The commensal (the species that benefits from the association) may obtain nutrients, shelter, support, or locomotion from the host species, which is substantially unaffected. The commensal relation is often between a larger host and a smaller commensal; the host organism is unmodified, whereas the commensal species may show great structural adaptation consistent with its habits, as in the remoras that ride attached to sharks and other fishes. Remoras feed on their hosts' fecal matter, while pilot fish feed on the leftovers of their hosts' meals. Numerous birds perch on bodies of large mammal herbivo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpheus Deuteropus
''Alpheus deuteropus'' or the petroglyph shrimp is a snapper or pistol shrimp in the family Alpheidae. It lives on coral reefs in tropical parts of the Indian and Pacific Oceans and in the Red Sea, as a commensal of corals such as ''Porites lobata''. Its presence among the lobes leaves tunnels, cracks and grooves in the surface.Marine Life Profile: Lobe Coral Waikïkï Aquarium. Retrieved December 20, 2011. Like other snapper shrimp, one of the cheliped
A chela ()also called a claw, nipper, or pinceris a pincer-shaped organ at the end of certain limbs of some arthropods. The name comes from Ancient Greek , through Neo-Latin '. The plural f ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arothron Meleagris
''Arothron meleagris'', commonly known as the guineafowl puffer or golden puffer, is a pufferfish from the Indo-Pacific, and Eastern Pacific. It is occasionally harvested for the aquarium trade. It reaches 50 cm in length. Guineafowl puffers have heavy rounded bodies that are uniformly black with numerous small white spots (black puffer or ''botete negro''), bright yellow spots (golden puffer or ''botete dorado'') or a mixture of the two morphologies with bright yellow spots and black patches. They have large blunt heads with short snouts and are equipped with a set of massive teeth. They have small and similarly shaped anal and dorsal fins that are well back on their body. Their caudal fin base is long and deep and their caudal fin is rounded. Their body is covered with small denticles that resemble coarse sandpaper. When this fish is scared or frightened, they inflate and make themselves larger, exposing the denticles. Botete negro (Arothron meleagris), Cabo Pulmo, Baj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biome
A biome () is a distinct geographical region with specific climate, vegetation, and animal life. It consists of a biological community that has formed in response to its physical environment and regional climate. In 1935, Tansley added the climatic and soil aspects to the idea, calling it ''ecosystem''. The International Biological Program (1964–74) projects popularized the concept of biome. However, in some contexts, the term ''biome'' is used in a different manner. In German literature, particularly in the Walter terminology, the term is used similarly as '' biotope'' (a concrete geographical unit), while the biome definition used in this article is used as an international, non-regional, terminology—irrespectively of the continent in which an area is present, it takes the same biome name—and corresponds to his "zonobiome", "orobiome" and "pedobiome" (biomes determined by climate zone, altitude or soil). In the Brazilian literature, the term ''biome'' is sometimes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stone Triggerfish
The stone triggerfish (''Pseudobalistes naufragium'') is the largest species of triggerfish. Distribution It is found at reefs and over sandy bottoms in the eastern Pacific, ranging from Baja California Baja California, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California, is a state in Mexico. It is the northwesternmost of the 32 federal entities of Mexico. Before becoming a state in 1952, the area was known as the North Territory of B ... (Mexico) to Chile. Description It can reach in length, but is more common at about half that size. Covered entirely with platelike scales aside from one scaleless area behind the jaws, the stone triggerfish has 16 strong protruding teeth, with 8 held in each jaw. Diet ''Pseudobalistes naufragium'' feeds on small crustaceans, mollusks, and sea urchins. Gallery File:Pseudobalistes naufragium, Coiba N.P. Isla Cocos Sur imported from iNaturalist photo 30859189.jpg File:Pseudobalistes naufragium, Juluapan imported from iNa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithophaga
''Lithophaga'', the date mussels, are a genus of medium-sized marine bivalve molluscs in the family Mytilidae. Some of the earliest fossil ''Lithophaga'' shells have been found in Mesozoic rocks from the Alps and from Vancouver Island.Ludvigsen, Rolf & Beard, Graham. 1997. West Coast Fossils: A Guide to the Ancient Life of Vancouver Island. pg. 102Kleemann, K.H., 1994. Mytilid bivalve ''Lithophaga'' in Upper Triassic coral ''Pamiroseris'' from Zlambach Beds compared with Cretaceous ''Lithophaga alpina''. Facies 30, 151–154. The shells of species in this genus are long and narrow with parallel sides. The animals bore into stone or coral rock with the help of pallial gland secretions,"integument (mollusks)."Encyclopædia Britannica. 2009. Encyclopædia Britannica 2006 Ultimate Reference Suite DVD hence the systematic name ''Lithophaga'', which means "stone-eater". Their club-shaped borings are given the trace fossil name ''Gastrochaenolites''. Species Species within the genus ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zooplankton
Zooplankton are the heterotrophic component of the planktonic community (the " zoo-" prefix comes from ), having to consume other organisms to thrive. Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents. Consequently, they drift or are carried along by currents in the ocean, or by currents in seas, lakes or rivers. Zooplankton can be contrasted with phytoplankton (cyanobacteria and microalgae), which are the plant-like component of the plankton community (the " phyto-" prefix comes from , although taxonomically ''not'' plants). Zooplankton are heterotrophic (other-feeding), whereas phytoplankton are autotrophic (self-feeding), often generating biological energy and macromolecules through chlorophyllic carbon fixation using sunlightin other words, zooplankton cannot manufacture their own food, while phytoplankton can. As a result, zooplankton must acquire nutrients by feeding on other organisms such as phytoplankton, which are generally smaller t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planula
A planula is the free-swimming, flattened, ciliated, bilaterally symmetric larval form of various cnidarian species and also in some species of Ctenophores, which are not related to cnidarians at all. Some groups of Nemerteans also produce larvae that are very similar to the planula, which are called planuliform larva. In a few cnidarian clades, like Aplanulata and the parasitic Myxozoa, the planula larval stage has been lost. Development The planula forms either from the fertilized egg of a medusa, as is the case in scyphozoans and some hydrozoans, or from a polyp, as in the case of anthozoans. Depending on the species, the planula either metamorphoses directly into a free-swimming, miniature version of the mobile adult form, or navigates through the water until it reaches a hard substrate (many may prefer specific substrates) where it anchors and grows into a polyp. The miniature-adult types include many open-ocean scyphozoans. The attaching types include all anthozoans w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |