|
Porcine Circovirus 2
Porcine circovirus (PCV) is a group of four single-stranded DNA viruses that are non-enveloped with an unsegmented circular genome. They are members of the genus ''Circovirus'' that can infect pigs. The viral capsid is icosahedral and approximately 17 nm in diameter. PCVs are the smallest viruses replicating autonomously in eukaryotic cells. They replicate in the nucleus of infected cells, using the host polymerase for genome amplification. PCV-2 causes Porcine circovirus associated disease or postweaning multisystemic wasting syndrome (PMWS). An effective vaccination is now available. Fort Dodge Animal Health (Wyeth) launched the first USDA approved vaccine in 2006, containing an inactivated virus (ATCvet code: ). Classification Three strains of PCV are known as of 2018: * PCV-1 (first identified in 1974) readily infects, but is not known to cause disease in swine. * PCV-2 (first isolated in 1997) causes PMWS, which over time results in significant depletion of lymph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virion
A virion (plural, ''viria'' or ''virions'') is an inert virus particle capable of invading a Cell (biology), cell. Upon entering the cell, the virion disassembles and the genetic material from the virus takes control of the cell infrastructure, thus enabling the virus to Replication (virus), replicate. The genetic material (''Viral core, core'', either DNA or RNA, along with occasionally present virus core protein) inside the virion is usually enclosed in a protection shell, known as the capsid. While the terms "virus" and "virion" are occasionally confused, recently "virion" is used solely to describe the virus structure outside of cells, while the terms "virus/viral" are broader and also include biological properties such as the infectivity of a virion. Components A virion consists of one or more nucleic acid genome molecules (single-stranded or double-stranded RNA or DNA) and coatings (a capsid and possibly a viral envelope). The virion may contain other proteins (for examp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytokine
Cytokines () are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are produced by a broad range of cells, including immune cells like macrophages, B cell, B lymphocytes, T cell, T lymphocytes and mast cells, as well as Endothelium, endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and various stromal cells; a given cytokine may be produced by more than one type of cell. Due to their size, cytokines cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm and therefore typically exert their functions by interacting with specific cytokine receptor, cytokine receptors on the target cell surface. Cytokines are especially important in the immune system; cytokines modulate the balance between humoral immunity, humoral and cell-mediated immunity, cell-based immune responses, and they regulate the maturation, growth, and responsiveness of particular cell populations. Some cytokines enhance or inhibit the action of other cytokines in complex way ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrophages
Macrophages (; abbreviated MPhi, φ, MΦ or MP) are a type of white blood cell of the innate immune system that engulf and digest pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that are specific to healthy body cells on their surface. This self-protection method can be contrasted with that employed by Natural killer cell, Natural Killer cells. This process of engulfment and digestion is called phagocytosis; it acts to defend the host against infection and injury. Macrophages are found in essentially all tissues, where they patrol for potential pathogens by amoeboid movement. They take various forms (with various names) throughout the body (e.g., histiocytes, Kupffer cells, alveolar macrophages, microglia, and others), but all are part of the mononuclear phagocyte system. Besides phagocytosis, they play a critical role in nonspecific defense (innate immunity) and also help initiate specific defense mechanisms (adapti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiomyocytes
Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle or myocardium) is one of three types of vertebrate muscle tissues, the others being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. It is an involuntary, striated muscle that constitutes the main tissue of the wall of the heart. The cardiac muscle (myocardium) forms a thick middle layer between the outer layer of the heart wall (the pericardium) and the inner layer (the endocardium), with blood supplied via the coronary circulation. It is composed of individual cardiac muscle cells joined by intercalated discs, and encased by collagen fibers and other substances that form the extracellular matrix. Cardiac muscle contracts in a similar manner to skeletal muscle, although with some important differences. Electrical stimulation in the form of a cardiac action potential triggers the release of calcium from the cell's internal calcium store, the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The rise in calcium causes the cell's myofilaments to slide past each other in a pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatocytes
A hepatocyte is a cell of the main parenchymal tissue of the liver. Hepatocytes make up 80% of the liver's mass. These cells are involved in: * Protein synthesis * Protein storage * Transformation of carbohydrates * Synthesis of cholesterol, bile salts and phospholipids * Detoxification, modification, and excretion of exogenous and endogenous substances * Initiation of formation and secretion of bile Structure The typical hepatocyte is cubical with sides of 20-30 μm, (in comparison, a human hair has a diameter of 17 to 180 μm).The diameter of human hair ranges from 17 to 181 μm. The typical volume of a hepatocyte is 3.4 x 10−9 cm3. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum is abundant in hepatocytes, in contrast to most other cell types. Microanatomy Hepatocytes display an eosinophilic cytoplasm, reflecting numerous mitochondria, and basophilic stippling due to large amounts of rough endoplasmic reticulum and free ribosomes. Brown lipofuscin granules are also observed (with i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
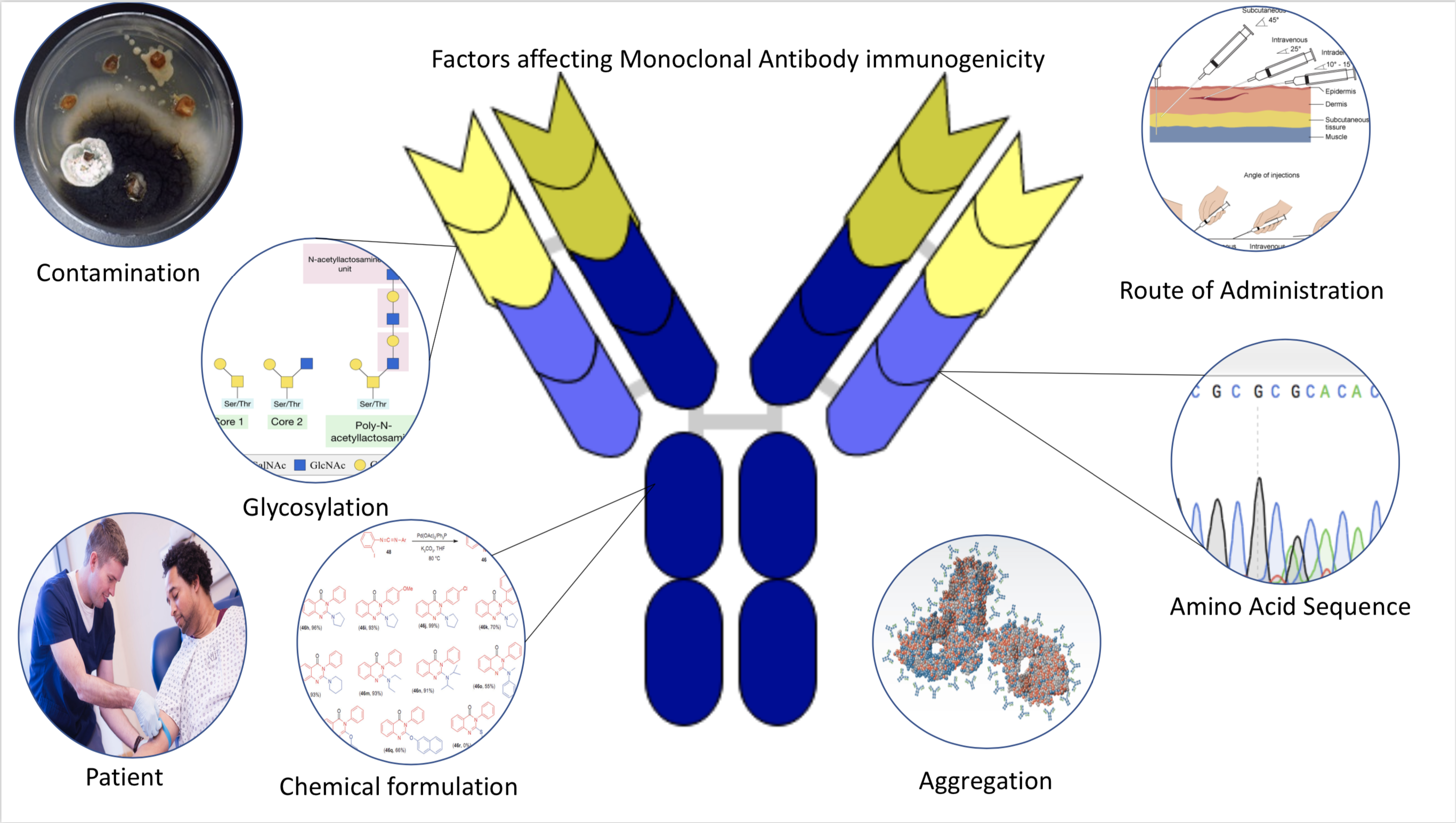
Immunogenicity
Immunogenicity is the ability of a foreign substance, such as an antigen, to provoke an immune response in the body of a human or other animal. It may be wanted or unwanted: * Wanted immunogenicity typically relates to vaccines, where the injection of an antigen (the vaccine) provokes an immune response against the pathogen, protecting the organism from future exposure. Immunogenicity is a central aspect of vaccine development. * Unwanted immunogenicity is an immune response by an organism against a therapeutic antigen. This reaction leads to production of anti-drug-antibodies (ADAs), inactivating the therapeutic effects of the treatment and potentially inducing adverse effects. A challenge in biotherapy is predicting the immunogenic potential of novel protein therapeutics. For example, immunogenicity data from high-income countries are not always transferable to low-income and middle-income countries. Another challenge is considering how the immunogenicity of vaccines changes wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exon
An exon is any part of a gene that will form a part of the final mature RNA produced by that gene after introns have been removed by RNA splicing. The term ''exon'' refers to both the DNA sequence within a gene and to the corresponding sequence in RNA transcripts. In RNA splicing, introns are removed and exons are covalently joined to one another as part of generating the mature RNA. Just as the entire set of genes for a species constitutes the genome, the entire set of exons constitutes the exome. History The term ''exon'' is a shortening of the phrase ''expressed region'' and was coined by American biochemist Walter Gilbert in 1978: "The notion of the cistron... must be replaced by that of a transcription unit containing regions which will be lost from the mature messengerwhich I suggest we call introns (for intragenic regions)alternating with regions which will be expressedexons." This definition was originally made for protein-coding transcripts that are spliced before b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capsomere
The capsomere is a subunit of the capsid, an outer covering of protein that protects the genetic material of a virus. Capsomeres self-assemble to form the capsid. Subunits called protomers aggregate to form capsomeres. Various arrangements of capsomeres are: 1) Icosahedral, 2) Helical, and 3) Complex. 1) Icosahedral- An icosahedron is a polyhedron with 12 vertices and 20 faces. Two types of capsomeres constitute the icosahedral capsid: pentagonal (pentons) at the vertices and hexagonal ( hexons) at the faces. There are always twelve pentons, but the number of hexons varies among virus groups. In electron micrographs, capsomeres are recognized as regularly spaced rings with a central hole. 2) Helical- The protomers are not grouped in capsomeres, but are bound to each other so as to form a ribbon-like structure. This structure folds into a helix because the protomers are thicker at one end than at the other. The diameter of the helical capsid is determined by characteristics of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rolling Circle Replication
Rolling circle replication (RCR) is a process of unidirectional nucleic acid replication that can rapidly synthesize multiple copies of circular molecules of DNA or RNA, such as plasmids, the genomes of bacteriophages, and the circular RNA genome of viroids. Some eukaryotic viruses also replicate their DNA or RNA via the rolling circle mechanism. As a simplified version of natural rolling circle DNA replication, replication, an isothermal DNA amplification technique, rolling circle amplification was developed. The RCA mechanism is widely used in molecular biology and biomedical nanotechnology, especially in the field of Biosensor, biosensing (as a method of signal amplification). Circular DNA replication Rolling circle DNA replication is initiated by an initiator protein encoded by the plasmid or bacteriophage DNA, which nicks one strand of the double-stranded, circular DNA molecule at a site called the double-strand origin, or DSO. The initiator protein remains bound to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Polymerase
A DNA polymerase is a member of a family of enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of DNA molecules from nucleoside triphosphates, the molecular precursors of DNA. These enzymes are essential for DNA replication and usually work in groups to create two identical DNA duplexes from a single original DNA duplex. During this process, DNA polymerase "reads" the existing DNA strands to create two new strands that match the existing ones. These enzymes catalysis, catalyze the chemical reaction : deoxynucleoside triphosphate + DNAn pyrophosphate + DNAn+1. DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the Directionality (molecular biology), three prime (3')-end of a DNA strand, one nucleotide at a time. Every time a Cell division, cell divides, DNA polymerases are required to duplicate the cell's DNA, so that a copy of the original DNA molecule can be passed to each daughter cell. In this way, genetic information is passed down from generation to generation. Before replication can take place, an enzy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA Polymerase
In molecular biology, RNA polymerase (abbreviated RNAP or RNApol), or more specifically DNA-directed/dependent RNA polymerase (DdRP), is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactions that synthesize RNA from a DNA template. Using the enzyme helicase, RNAP locally opens the double-stranded DNA so that one strand of the exposed nucleotides can be used as a template for the synthesis of RNA, a process called transcription. A transcription factor and its associated transcription mediator complex must be attached to a DNA binding site called a promoter region before RNAP can initiate the DNA unwinding at that position. RNAP not only initiates RNA transcription, it also guides the nucleotides into position, facilitates attachment and elongation, has intrinsic proofreading and replacement capabilities, and termination recognition capability. In eukaryotes, RNAP can build chains as long as 2.4 million nucleotides. RNAP produces RNA that, functionally, is either for protei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primer (molecular Biology)
A primer is a short, single-stranded nucleic acid used by all living organisms in the initiation of DNA synthesis. A synthetic primer is a type of oligo, short for oligonucleotide. DNA polymerases (responsible for DNA replication) are only capable of adding nucleotides to the 3’-end of an existing nucleic acid, requiring a primer be bound to the template before DNA polymerase can begin a complementary strand. DNA polymerase adds nucleotides after binding to the RNA primer and synthesizes the whole strand. Later, the RNA strands must be removed accurately and replaced with DNA nucleotides. This forms a gap region known as a nick that is filled in using a ligase. The removal process of the RNA primer requires several enzymes, such as Fen1, Lig1, and others that work in coordination with DNA polymerase, to ensure the removal of the RNA nucleotides and the addition of DNA nucleotides. Living organisms use solely RNA primers, while laboratory techniques in biochemistry and mole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |