|
Polycarboxylic Acid
Polycarboxylates are organic compounds with several carboxylic acid groups. Butane-1,2,3,4-tetracarboxylate is one example. Often, polycarboxylate refers to linear polymers with a high molecular mass (Mr ≤ 100 000) and with many carboxylate groups. They are polymers of acrylic acid or copolymers of acrylic acid and maleic acid. The polymer is used as the sodium salt (see: sodium polyacrylate). Use Polycarboxylates are used as builders in detergents. Their high chelating power, even at low concentrations, lowers deposits on the laundry and inhibits the growth of calcite crystals. As applied to concrete, PCE-based superplasticizers can reduce water content by up to 40% at low dosages of around 0.12% to 0.22% without compromising fluidity. Polycarboxylate superplasticizers accelerate the early strength development of concrete and mortar. They also help with slump retention, ensuring concrete consistency and workability. With a higher slump rating, concrete can be more fluid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soap Scum
Soap scum or lime soap is the white solid composed of calcium stearate, magnesium stearate, and similar alkaline earth metal derivatives of fatty acids. These materials result from the addition of soap and other anionic surfactants to hard water. Hard water contains calcium and magnesium ions, which react with the surfactant anion to give these metallic or lime soaps. :2 C17H35COO−Na+ + Ca2+ → (C17H35COO)2Ca + 2 Na+ In this reaction, the sodium cation in soap is replaced by calcium to form calcium stearate. Lime soaps build deposits on fibres, washing machines, and sinks. Synthetic surfactants are less susceptible to the effects of hard water. Most detergents contain builders that prevent the formation of lime soaps. See also * Water softening Water softening is the removal of calcium, magnesium, and certain other metal cations in hard water. The resulting soft water requires less soap for the same cleaning effort, as soap is not wasted bonding with calcium io ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tricarboxylic Acid
A tricarboxylic acid is an organic carboxylic acid that contain three carboxyl functional groups (−COOH). A well-known example is citric acid. Promient examples Some prominent substituted tricarboxylic acids Citric acid, is used in the citric acid cyclealso known as the ''tricarboxylic acid'' (''TCA'') ''cycle'' or ''Krebs cycle''which is fundamental to all aerobic organisms. Nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA) is a chelating agent for Ca2+, Co2+, Cu2+, and Fe3+. See also * Citric acid cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle) * Dicarboxylic acid In organic chemistry, a dicarboxylic acid is an organic compound containing two carboxyl groups (). The general molecular formula for dicarboxylic acids can be written as , where R can be aliphatic or aromatic.Boy Cornils, Peter Lappe "Dicarbox ... * Mellitic acid References Literature *{{cite journal , title = The Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle, an Ancient Metabolic Network with a Novel Twist. , author = Ryan J. Mailloux, Robin Bériaul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eutrophication
Eutrophication is a general term describing a process in which nutrients accumulate in a body of water, resulting in an increased growth of organisms that may deplete the oxygen in the water; ie. the process of too many plants growing on the surface of a river, lake, etc., often because chemicals that are used to help crops grow have been carried there by rain. Eutrophication may occur naturally or as a result of human actions. Manmade, or cultural, eutrophication occurs when sewage, Industrial wastewater treatment, industrial wastewater, fertilizer runoff, and other nutrient sources are released into the environment. Such nutrient pollution usually causes algal blooms and bacterial growth, resulting in the depletion of dissolved oxygen in water and causing substantial environmental degradation. Many policies have been introduced to combat eutrophication, including the United Nations Development Program (UNDP)'s sustainability development goals. Approaches for prevention and re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biodegradability
Biodegradation is the breakdown of organic matter by microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi. It is generally assumed to be a natural process, which differentiates it from composting. Composting is a human-driven process in which biodegradation occurs under a specific set of circumstances. The process of biodegradation is threefold: first an object undergoes biodeterioration, which is the mechanical weakening of its structure; then follows biofragmentation, which is the breakdown of materials by microorganisms; and finally assimilation, which is the incorporation of the old material into new cells. In practice, almost all chemical compounds and materials are subject to biodegradation, the key element being time. Things like vegetables may degrade within days, while glass and some plastics take many millennia to decompose. A standard for biodegradability used by the European Union is that greater than 90% of the original material must be converted into , water and minerals b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
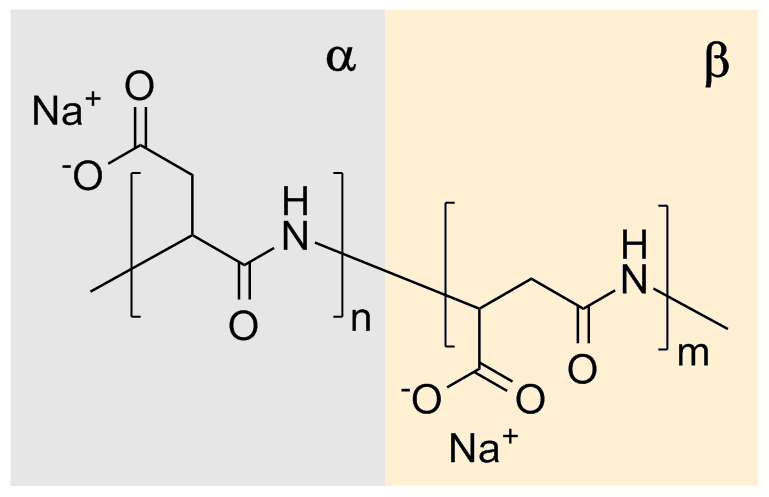
Polyglutamic Acid
Polyglutamic acid (PGA) is a polymer of the amino acid glutamic acid (GA). Depending on where the individual monomers connect, PGA can be gamma PGA (poly-γ-glutamic acid, γ-PGA), the form where the peptide bonds are between the amino group of GA and the carboxyl group at the end of the GA side chain, or alpha PGA, the form where the alpha-carboxyl is used to form the peptide bond. Gamma PGA is formed by bacterial fermentation. It is a major constituent of the Japanese food nattō and has a wide range of uses. Alpha PGA has been investigated as a drug delivery system. Structure Both form of PGA are linked together by peptide bonds. Because the glutamic acid has a chiral center, both forms of PGA can be made from L-glutamic acid, D-glutamic acid, or a mixture of both. In practical use, alpha PGA is composed mostly of L-glutamic acid, while gamma PGA tends to have a mixture of both. Properties Gamma PGA is non-immunogenic and biodegradable. It hydrolyzes in hot water. Both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyaspartic Acid
Polyaspartic acid (PASA) is a biodegradable, water-soluble condensation polymer based on the amino acid aspartic acid. It is a biodegradable replacement for water softeners and related applications. PASA can be chemically crosslinked with a wide variety of methods to yield PASA hydrogels. The resulting hydrogels are pH-sensitive such that under acidic conditions, they shrink, while the swelling capacity increases under alkaline conditions. Sodium polyaspartate is a sodium salt of polyaspartic acid. In nature, PASA has been found in as fragments of larger proteins with length up to 50 amino acids, but as of 2004 had not been isolated as a pure homo polymeric material from any natural source. The first isolation of synthetic oligomeric sodium polyaspartate, obtained by thermal polycondensation of aspartic acid, was reported by Hugo Schiff in late 19th century. Later it was proposed that thermal polymerization process leads through polysuccinimide intermediate. Polyaspartic acid i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aminopolycarboxylic Acid
left, 120px, a metal complex with the EDTA anion 120px, Aspartic acid is an aminodicarboxylic acid and precursor to other ligands. An aminopolycarboxylic acid (sometimes abbreviated APCA) is a chemical compound containing one or more nitrogen atoms connected through carbon atoms to two or more carboxyl groups. Aminopolycarboxylates that have lost acidic protons form strong complexes with metal ions. This property makes aminopolycarboxylic acids useful complexone in a wide variety of chemical, medical, and environmental applications. Structure The parent of this family of ligands is the amino acid glycine, H2NCH2COOH, in which the amino group, NH2, is separated from the carboxyl group, COOH by a single methylene group, CH2. When the carboxyl group is deprotonated the glycinate ion can function as a bidentate ligand, binding the metal centre through the nitrogen and one of two carboxylate oxygen atoms, to form chelate complexes of metal ions. Replacement of a hydrogen atom on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wastewater
Wastewater (or waste water) is water generated after the use of freshwater, raw water, drinking water or saline water in a variety of deliberate applications or processes. Another definition of wastewater is "Used water from any combination of domestic, industrial, commercial or agricultural activities, surface runoff / storm water, and any sewer inflow or sewer infiltration". In everyday usage, wastewater is commonly a synonym for sewage (also called domestic wastewater or municipal wastewater), which is wastewater that is produced by a community of people. As a generic term, wastewater may also describe water containing contaminants accumulated in other settings, such as: * Industrial wastewater: waterborne waste generated from a variety of industrial processes, such as manufacturing operations, mineral extraction, power generation, or water and wastewater treatment. * Cooling water, is released with potential thermal pollution after use to condense steam or reduce machinery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sewage Treatment Plant
Sewage treatment is a type of wastewater treatment which aims to remove contaminants from sewage to produce an effluent that is suitable to discharge to the surrounding environment or an intended reuse application, thereby preventing water pollution from raw sewage discharges. Sewage contains wastewater from households and businesses and possibly pre-treated industrial wastewater. There are a large number of sewage treatment processes to choose from. These can range from decentralized systems (including on-site treatment systems) to large centralized systems involving a network of pipes and pump stations (called sewerage) which convey the sewage to a treatment plant. For cities that have a combined sewer, the sewers will also carry urban runoff (stormwater) to the sewage treatment plant. Sewage treatment often involves two main stages, called primary and secondary treatment, while advanced treatment also incorporates a tertiary treatment stage with polishing processes and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecotoxicity
Ecotoxicity, the subject of study in the field of ecotoxicology (a portmanteau of ecology and toxicology), refers to the biological, chemical or physical stressors that affect ecosystems. Such stressors can occur in the natural environment at densities, concentrations, or levels high enough to disrupt natural biochemical and physiological behavior and interactions. This ultimately affects all living organisms that comprise an ecosystem. Ecotoxicology has been defined as a branch of toxicology that focuses on the study of toxic effects, caused by natural or synthetic pollutants. These pollutants affect animals (including humans), vegetation, and microbes, in an intrinsic way. Acute vs. chronic ecotoxicity In Barrie Peake's paper, ''Impact of Pharmaceuticals on the Environment'', ecotoxicity is defined based on the level of exposure to hazardous substances. Peake identifies two categories: acute and chronic ecotoxicity (Peake, 2016). Acute ecotoxicity refers to harmful effects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biodegradable
Biodegradation is the breakdown of organic matter by microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi. It is generally assumed to be a natural process, which differentiates it from composting. Composting is a human-driven process in which biodegradation occurs under a specific set of circumstances. The process of biodegradation is threefold: first an object undergoes biodeterioration, which is the mechanical weakening of its structure; then follows biofragmentation, which is the breakdown of materials by microorganisms; and finally assimilation, which is the incorporation of the old material into new cells. In practice, almost all chemical compounds and materials are subject to biodegradation, the key element being time. Things like vegetables may degrade within days, while glass and some plastics take many millennia to decompose. A standard for biodegradability used by the European Union is that greater than 90% of the original material must be converted into , water and minerals b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |