|
Polikarpov SPB (D)
The Polikarpov SPB (D) (''Skorostnoy Pikiruyushchy Bombardirovshchik (Dalnost)''—High Speed Dive Bomber (Distance)) was a Soviet twin-engined dive bomber designed before World War II. A single prototype and five pre-production aircraft were built, but two crashed and the program was cancelled in favor of the Petlyakov Pe-2. Development The SPB (D) closely resembled the Polikarpov VIT-2, which had been recommended for production as a dive bomber, but the former actually was an entirely new design. It was smaller than the VIT-2 and had a monocoque fuselage. The main gears of the conventional undercarriage retracted aft into the rear of the engine nacelles and the tail wheel retracted into the rear fuselage. Two liquid-cooled Klimov M-105 V12 engines were slung underneath the wings. It retained its predecessor's prominent canopy and nose glazing, but reduced the armament to a single ShKAS machine gun for the bombardier/navigator while the rear gunner had a retractable Berezin UB ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dive Bomber
A dive bomber is a bomber aircraft that Dive (aviation), dives directly at its targets in order to provide greater accuracy for the Aerial bomb, bomb it drops. Diving towards the target simplifies the bomb's trajectory and allows the pilot to keep visual contact throughout the bomb run. This allows attacks on point targets and ships, which were difficult to attack with conventional level bombers, even ''en masse''. After World War II, the rise of precision-guided munitions and improved Anti-aircraft warfare, anti-aircraft defences—both fixed gunnery positions and fighter interception—led to a fundamental change in dive bombing. New weapons, such as rockets, allowed for better accuracy from smaller dive angles and from greater distances. They could be fitted to almost any aircraft, including fighter aircraft, fighters, improving their effectiveness without the inherent vulnerabilities of dive bombers, which needed air superiority to operate effectively. Method A dive bom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tupolev SB
The Tupolev ANT-40, also known by its service name Tupolev SB (russian: Скоростной бомбардировщик – ''Skorostnoi Bombardirovschik'' – high speed bomber) and development co-name TsAGI-40, was a high speed twin-engined three-seat monoplane bomber, first flown in 1934. The Tupolev design was advanced but lacked refinement, much to the dismay of crews, maintenance personnel, and Stalin, who pointed out that "there are no trivialities in aviation". Numerically the most important bomber in the world in the late 1930s, the SB was the first modern stressed skin aircraft produced in quantity in the Soviet Union and probably the most formidable bomber of the mid-1930s. It was produced in the Soviet Union and was also built under license in Czechoslovakia. Many versions saw extensive action in Spain, the Republic of China, Mongolia, Finland and at the beginning of World War II against Germany in 1941. It was also used in various duties in civil variants, as tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft First Flown In 1940
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air. It counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines. Common examples of aircraft include airplanes, helicopters, airships (including blimps), gliders, paramotors, and hot air balloons. The human activity that surrounds aircraft is called ''aviation''. The science of aviation, including designing and building aircraft, is called ''aeronautics.'' Crewed aircraft are flown by an onboard pilot, but unmanned aerial vehicles may be remotely controlled or self-controlled by onboard computers. Aircraft may be classified by different criteria, such as lift type, aircraft propulsion, usage and others. History Flying model craft and stories of manned flight go back many centuries; however, the first manned ascent — and safe descent — in modern times took place by larger hot-air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abandoned Military Aircraft Projects Of The Soviet Union
Abandon, abandoned, or abandonment may refer to: Common uses * Abandonment (emotional), a subjective emotional state in which people feel undesired, left behind, insecure, or discarded * Abandonment (legal), a legal term regarding property ** Child abandonment, the extralegal abandonment of children ** Lost, mislaid, and abandoned property, legal status of property after abandonment and rediscovery * Abandonment (mysticism) Art, entertainment, and media Film * ''Abandon'' (film), a 2002 film starring Katie Holmes * ''Abandoned'' (1949 film), starring Dennis O'Keefe * ''Abandoned'' (1955 film), the English language title of the Italian war film ''Gli Sbandati'' * ''Abandoned'' (2001 film), a Hungarian film * ''Abandoned'' (2010 film), starring Brittany Murphy * ''Abandoned'' (2015 film), a television movie about the shipwreck of the ''Rose-Noëlle'' in 1989 * ''Abandoned'' (2022 film), starring Emma Roberts * ''The Abandoned'' (1945 film), a 1945 Mexican film * ''The A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1940s Soviet Attack Aircraft
Year 194 (Roman numerals, CXCIV) was a common year starting on Tuesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Septimius and Septimius (or, less frequently, year 947 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 194 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Emperor Septimius Severus and Clodius Albinus, Decimus Clodius Septimius Albinus Caesar become Roman Consuls. * Battle of Issus (194), Battle of Issus: Septimius Severus marches with his army (12 Roman legion, legions) to Cilicia, and defeats Pescennius Niger, Roman governor of Syria. Pescennius retreats to Antioch, and is executed by Severus' troops. * Septimius Severus besieges Byzantium (194–196); the Defensive wall, city walls suffer extensive damage. Asia * Battle of Yan Province: Warlords Cao Cao ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polikarpov Aircraft
Polikarpov Design Bureau was a Soviet OKB (design bureau) for aircraft, led by Nikolai Nikolaevich Polikarpov. Dux Factory was acquired by the USSR and became part of Polikarpov. After the death of Polikarpov on 30 July 1944 at the age of 52, his OKB was absorbed into Lavochkin, but with some of its engineers going to Mikoyan-Gurevich and its production facilities going to Sukhoi. For a long time the Polikarpov OKB headquarters were located at Aircraft plant #1 (formerly Dux Factory) in Moscow, where its purpose-built building still stands. Designs Polikarpov designs: Bombers * TB-2 twin-engined biplane bomber prototype, 1930 * SPB (D) twin-engined dive bomber developed from the VIT-2, 1940 * NB (T) medium bomber prototype, 1944 Fighters * I-1 (IL-400) monoplane fighter prototype, 1923 * DI-1 (2I-N1) twin-seat biplane fighter prototype, 1926 * I-3 biplane fighter, 1928 * DI-2 two-seat biplane fighter developed from the I-3, 1929 * I-6 biplane fighter prototype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vadim Shavrov
Vadim (Cyrillic: Вадим) is a Russian, Ukrainian, Romanian, Slovene masculine given name derived either from the Persian ''badian'' (anise or aniseed), or from the Ruthenian word ''volod'' (russian: волод), meaning ''to rule'' or ''vaditi'' (russian: вадити), meaning ''to blame''. Its long version, Vadimir, is now obsolete. Dictionary of Russian Names This given name is highly popular in Russia (as Vadim), Ukraine (as ), [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bill Gunston
Bill Gunston (1 March 1927 – 1 June 2013) was a British aviation and military author. He flew with Britain's Royal Air Force from 1945 to 1948, and after pilot training became a flying instructor. He spent most of his adult life doing research and writing on aircraft and aviation. He was the author of over 350 books and articles. His work included many books published by Salamander Books. Early life Born William Tudor Gunston in London on 1 March 1927,"William Tudor Gunston." '' Contemporary Authors Online.'' Detroit: Gale, 2001. ''Biography in Context''. Web. 21 February 2013. Gunston was educated at Pinner County Grammar School. In his spare time, he was Flight Sergeant in the school Air Training Corps squadron and, for several months, the London Philharmonic Orchestra's librarian. Royal Air Force Gunston joined the Royal Air Force in 1945 and went to University College, Durham on an RAF cadetship. In 1946 he moved to No 4 Flying Training School in Bulawayo, Southern Rhod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
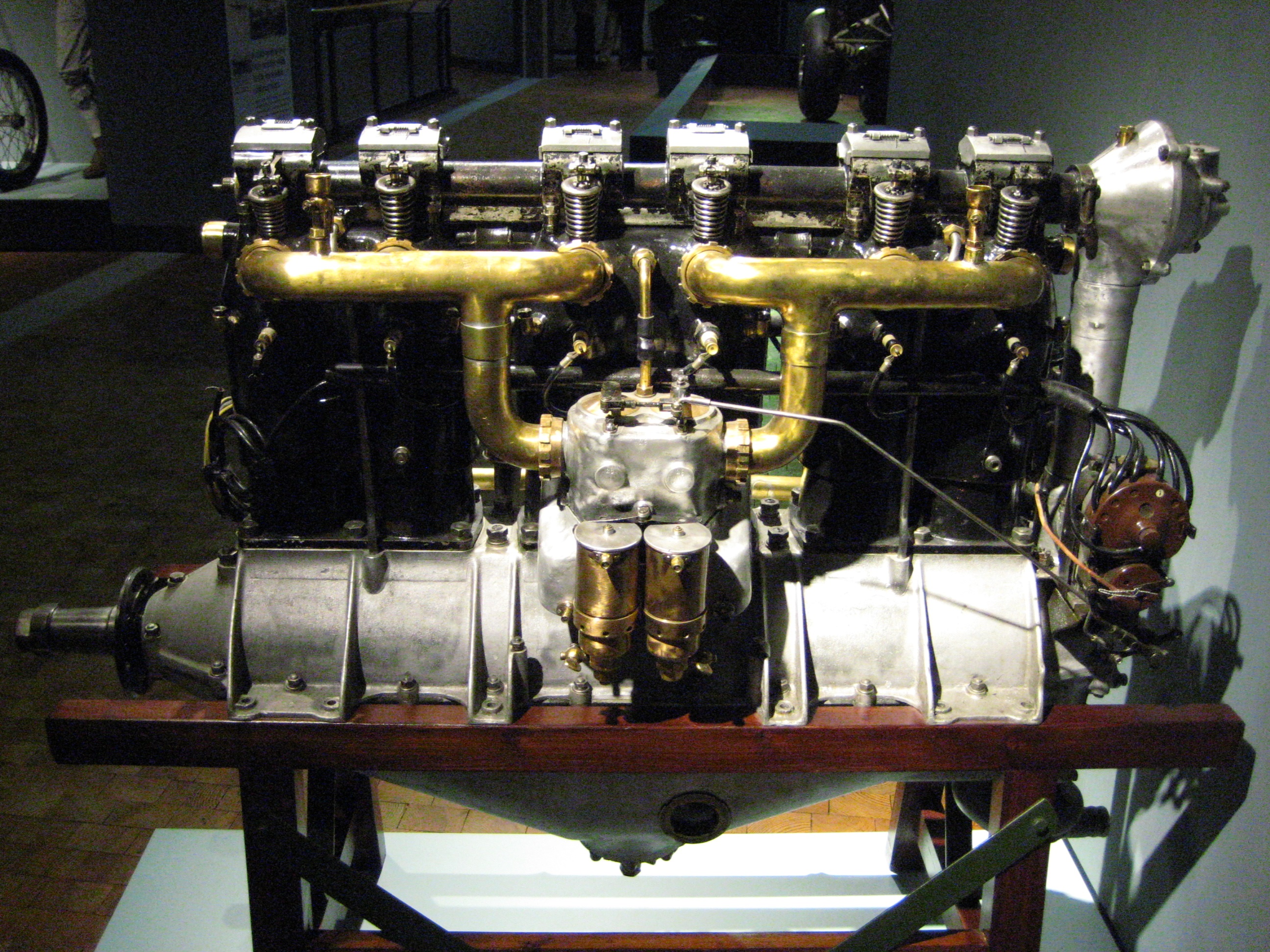
Inline Engine (aviation)
In aviation, an inline engine is a reciprocating engine with banks of cylinders, one behind another, rather than rows of cylinders, with each bank having any number of cylinders, although more than six is uncommon. The major reciprocating-engine alternative configuration is the radial engine, where the cylinders are placed in a circular or "star" arrangement. The term "inline" is used somewhat differently for aircraft engines than automotive engines. For automotive engines, the term ‘inline’ refers only to straight engines (those with a single bank of cylinders). But for aircraft, ‘inline’ can also refer to engines which are not of the straight configuration, such as V, H, or horizontally opposed. Inline engine configurations ; Straight: Engines with a single bank of cylinders which can be arranged at any angle but typically upright or inverted, (e.g. upright ADC Cirrus, inverted de Havilland Gipsy Major). ; V:Engines with two banks of cylinders with less than 180° b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petlyakov VI-100
The Petlyakov VI-100 (''Visotnyi Istrebitel'' – high altitude fighter) was a fighter/dive bomber aircraft designed and built in the USSR from 1938. Development The VI-100 was first conceived in 1938 by a team led by Vladimir Petlyakov at STO-100, it was an aerodynamically-clean all-metal monoplane with turbo-supercharged engines. Constructed using light alloy stressed skin the VI-100 had electrical servo-motors in the flying controls and automatic adjustment of the gunsight with angle of attack, as well as pressure cabins for pilot and radio-operator/gunner, and an extensive 28V DC electrical system. Originally intended to carry a 3in calibre gun with 24 rounds in a drum, the large calibre gun was replaced by racks under centre-section to carry 100(220 lb),200(440 lb) or 500 kg(1,100 lb) bombs as well as two ShVAK and two ShKAS The ShKAS (Shpitalny-Komaritski Aviatsionny Skorostrelny, Shpitalny-Komaritski rapid fire for aircraft; Russian: ШКАС - Шп ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trim Tab
Trim tabs are small surfaces connected to the trailing edge of a larger control surface on a boat or aircraft, used to control the trim of the controls, i.e. to counteract hydro- or aerodynamic forces and stabilise the boat or aircraft in a particular desired attitude without the need for the operator to constantly apply a control force. This is done by adjusting the angle of the tab relative to the larger surface. Changing the setting of a trim tab adjusts the neutral or resting position of a control surface (such as an elevator or rudder). As the desired position of a control surface changes (corresponding mainly to different speeds), an adjustable trim tab will allow the operator to reduce the manual force required to maintain that position—to zero, if used correctly. Thus the trim tab acts as a servo tab. Because the center of pressure of the trim tab is farther away from the axis of rotation of the control surface than the center of pressure of the control surface, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TsAGI
The Central Aerohydrodynamic Institute (also (Zhukovsky) Central Institute of Aerodynamics, russian: Центра́льный аэрогидродинами́ческий институ́т, ЦАГИ, Tsentral'nyy Aerogidrodinamicheskiy Institut, TsAGI) was founded in Moscow by Russian aviation pioneer Nikolai Yegorovich Zhukovsky on December 1, 1918. History From 1925 and up to the 1930s, TsAGI developed and hosted Tupolev's AGOS (''Aviatziya, Gidroaviatziya i Opytnoye Stroitelstvo'', the "Aviation, Hydroaviation, and Experimental Construction"), the first aircraft design bureau in Soviet Union, and at the time the main one. In 1930, two other major aircraft design bureaus in the country were the Ilyushin's TsKB (''Tsentralnoye Konstruksionnoye Byuro'' means "Central Design Bureau") and an independent, short-lived Kalinin's team in Kharkiv. In 1935 TsAGI was partly relocated to the former dacha settlement ''Otdykh'' (literally, "Relaxation") converted to the new urban-type s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |