|
Pokanoket People
The Pokanoket (also spelled PakanokickKathleen J. Bragdon, ''Native People of Southern New England, 1500–1650'', page 21) are a group of Wampanoag people and the village governed by Massasoit (c. 1581–1661), chief sachem of the Wampanoag people. The village was located on what is now called Mount Hope in Bristol, Rhode Island. Later the term Pokanoket broadened to refer to the peoples and lands governed by Massasoit and his successors, which were part of the Wampanoag people in what is now Rhode Island and Massachusetts. Name Pokanoket is also spelled Pauquunaukit, and translates as "land at the clearing" from the Massachusett. History At the time of the pilgrims' arrival in Plymouth, the realm of Pokanoket included parts of Rhode Island and much of southeastern Massachusetts. European accounts of Pokanoket social life noted the political authority of the Massasoit (Great Leader). The realm of the Pokanoket was extensive and known to the Pilgrims before they arrived at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massasoit
Massasoit Sachem ( ) or Ousamequin (1661)"Native People" (page), "Massasoit (Ousamequin) Sachem" (section),''MayflowerFamilies.com'', web pag was the sachem or leader of the Wampanoag confederacy. ''Massasoit'' means ''Great Sachem''. Although Massasoit was only his title, English colonists mistook it as his name and it stuck. Massasoit's people had been seriously weakened by a series of epidemics and were vulnerable to attacks by the Narragansetts, and he formed an alliance with the colonists at Plymouth Colony for defense against them. It was through his assistance that the Plymouth Colony avoided starvation during the early years. English at Plymouth At the time of the pilgrims' arrival in Plymouth, the realm of the Wampanoag, also known as the Pokanokets, included parts of Rhode Island and much of southeastern Massachusetts. Massasoit lived in Sowams, a village at Pokanoket in Warren, Rhode Island. He held the allegiance of lesser Pokanoket sachems. In 1621, he sent Squa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wamsutta
Wamsutta ( 16341662), known to the New England colonists as Alexander, was the eldest son of Massasoit (meaning Great Leader) Ousa Mequin of the Pokanoket within the Wampanoag nation, and the brother of Metacomet (or Metacom). Life Wamsutta was born circa 1634. He was the eldest son of Massasoit Ousa Mequin, leader of the Pokanoket, and he married Weetamoo. Upon Massasoit's death, Wamsutta became the leader of the Pokanoket, overseeing tribes in territory covering parts of present-day Massachusetts and Rhode Island. Wamsutta, whom the English called Alexander, agreed to uphold the peace established by his father. Facing a decline in the fur trade, he sought to maintain the Pokanoket's influence by selling land to colonists. The English accused him of conspiring with the Narragansetts to stage an attack. In 1662, the Plymouth Court summoned Wamsutta for unauthorized land negotiations and detained him. Following his interrogation, Wamsutta fell ill and died under uncertain circum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Acknowledgment
A land acknowledgement (or territorial acknowledgement) is a formal statement that acknowledges the indigenous peoples of the land. It may be in written form, or be spoken at the beginning of public events. The custom of land acknowledgement is present in Canada, Australia, and New Zealand, and more recently in the United States. History The modern practice of land acknowledgements began in Australia in the late 1970s, taking the form of the Welcome to Country ceremony, and was at first primarily associated with Indigenous Australian political movements and the arts. This ceremony, and the closely related Acknowledgement of Country, became more popular during the 1990s, having been promoted by the Council for Aboriginal Reconciliation and taken up in the aftermath of the ''Mabo'' decision recognizing Aboriginal title. By the early 2000s, land acknowledgements had become commonplace in Australia. They became common in Canada subsequent to the release of the Truth and Reconciliatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warren, Rhode Island
Warren is a town in Bristol County, Rhode Island, United States. The population was 11,147 at the 2020 census. History Warren was the site of the Pokanoket Indian settlement of Sowams located on a peninsula within the Pokanoket region. The region consisted of over 60 settlements under the authority of Chief Massasoit (sometimes called Osamequin) who controlled the land from Plymouth to the eastern shores of Narragansett Bay. English colonists Edward Winslow and Stephen Hopkins (Mayflower passenger), Stephen Hopkins from Plymouth Colony first visited there in July, 1621. Winslow and John Hampden saved Massasoit's life two years later and gained an important ally and lifelong friend. The colonists set up a trading post by 1632 on the banks of the Kickemuit River where they traded English goods for furs and other items. Roger Williams was banished from Salem, Massachusetts, in January, 1636, and fled to Sowams, becoming ill on the way. He was sheltered by Massasoit in Sowams un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State-recognized
State-recognized tribes in the United States are Native American tribes or heritage groups that do not meet the criteria for federally recognized Indian tribes but have been recognized by state government through laws, governor's executive orders, or state commissions legally granted the power to recognize tribes for varying purposes. State recognition does not dictate whether or not they are recognized as Native American tribes by continually existing tribal nations. Individual states confer state-recognition "for their various internal state government purposes." Members of a state-recognized tribe are still subject to state law and government, and the tribe does not have sovereign control over its affairs. State recognition confers few benefits under federal law. It is not the same as federal recognition, which is the federal government's acknowledgment of a tribe as a dependent sovereign nation. Some states have provided laws related to state recognition that provide some pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federally Recognized
This is a list of federally recognized tribes in the contiguous United States. There are also federally recognized Alaska Native tribes. , 574 Indian tribes are legally recognized by the Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA) of the United States.Federal Acknowledgment of the Pamunkey Indian Tribe Of these, 228 are located in Alaska, and 109 are located in California. Of the 574 federally recognized tribes, 346 are located in the contiguous United States. Description [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pocasset Wampanoag Tribe Of The Pokanoket Nation
The Pocasset Wampanoag Tribe of the Pokanoket Nation is one of several cultural heritage organizations of individuals who identify as descendants of the Wampanoag people in Rhode Island. They formed a nonprofit organization, the Pocasset Pokanoket Land Trust, Inc., in 2017. The Pocasset Wampanoag Tribe of the Pokanoket Nation is an unrecognized organization. Despite having the word "nation" in their name, this organization is neither a federally recognized tribe nor a state-recognized tribe. They should not be confused with other unrecognized tribes, such as the Pocasset Wampanoag Tribe of Massachusetts and Rhode Island; the Pokanoket/Wampanoag Federation, based in Warwick, Rhode Island; the Pocasset Wampanoag Indian Tribe in Cheshire, Connecticut; or the Pokanoket Nation, based in Millbury, Massachusetts, and Bristol, Rhode Island. The Mashpee Wampanoag Tribe, one of the only two federally recognized Wampanoag tribes, states they are the descendants of the historical Pokanok ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unrecognized Tribe
These organizations, located within the United States, self-identify as Native American tribes, heritage groups, or descendant communities, but they are not federally recognized or state-recognized as Native American tribes. The U.S. Governmental Accountability Office states: "Non-federally recognized tribes fall into two distinct categories: (1) state-recognized tribes that are not also federally recognized and (2) other groups that self-identify as Indian tribes but are neither federally nor state recognized." The following list includes the latter. For organizations that are recognized by the government of the United States as Native American tribes and tribal nations, see List of federally recognized tribes in the contiguous United States and List of Alaska Native tribal entities. For groups that are recognized by state governments as Native American tribes, see State-recognized tribes in the United States. Many of these organizations are not accepted as being Native Ame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federally Recognized Tribe
A federally recognized tribe is a Native American tribe recognized by the United States Bureau of Indian Affairs as holding a government-to-government relationship with the US federal government. In the United States, the Native American tribe is a fundamental unit of sovereign tribal government. As the Department of the Interior explains, "federally recognized tribes are recognized as possessing certain inherent rights of self-government (i.e., tribal sovereignty)...." The constitution grants to the U.S. Congress the right to interact with tribes. In the 1831 Supreme Court of the United States case '' Cherokee Nation v. Georgia'' Chief Justice of the United States John Marshall wrote that a Native American government is a " domestic dependent nation'" whose relationship to the United States is like that of a "ward to its guardian". The case was a landmark decision which led to the United States recognizing over 574 federally recognized tribal governments and 326 India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mashpee Wampanoag Tribe
The Mashpee Wampanoag Tribe (formerly Mashpee Wampanoag Indian Tribal Council, Inc.) is one of two federally recognized tribes of Wampanoag people in Massachusetts. Recognized in 2007, they are headquartered in Mashpee, Massachusetts, Mashpee on Cape Cod. The other Wampanoag tribe is the Wampanoag Tribe of Gay Head (Aquinnah) on Martha's Vineyard. The tribe has its own health services, police force, Judiciary, court system, and education departments. In March 2024, the Mashpee Wampanoag Tribe had approximately 3,200 enrolled citizens. Their 170 acres in Mashpee, as well as an additional 150 acres in Taunton, Massachusetts, were taken into trust on their behalf by the United States Department of the Interior, US Department of Interior in 2015, establishing these parcels as reservation land. History The historic Algonquian languages, Algonquian-speaking Wampanoag are one of 69 tribes of the original Wampanoag Nation; they are the Native people encountered by the English settler, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
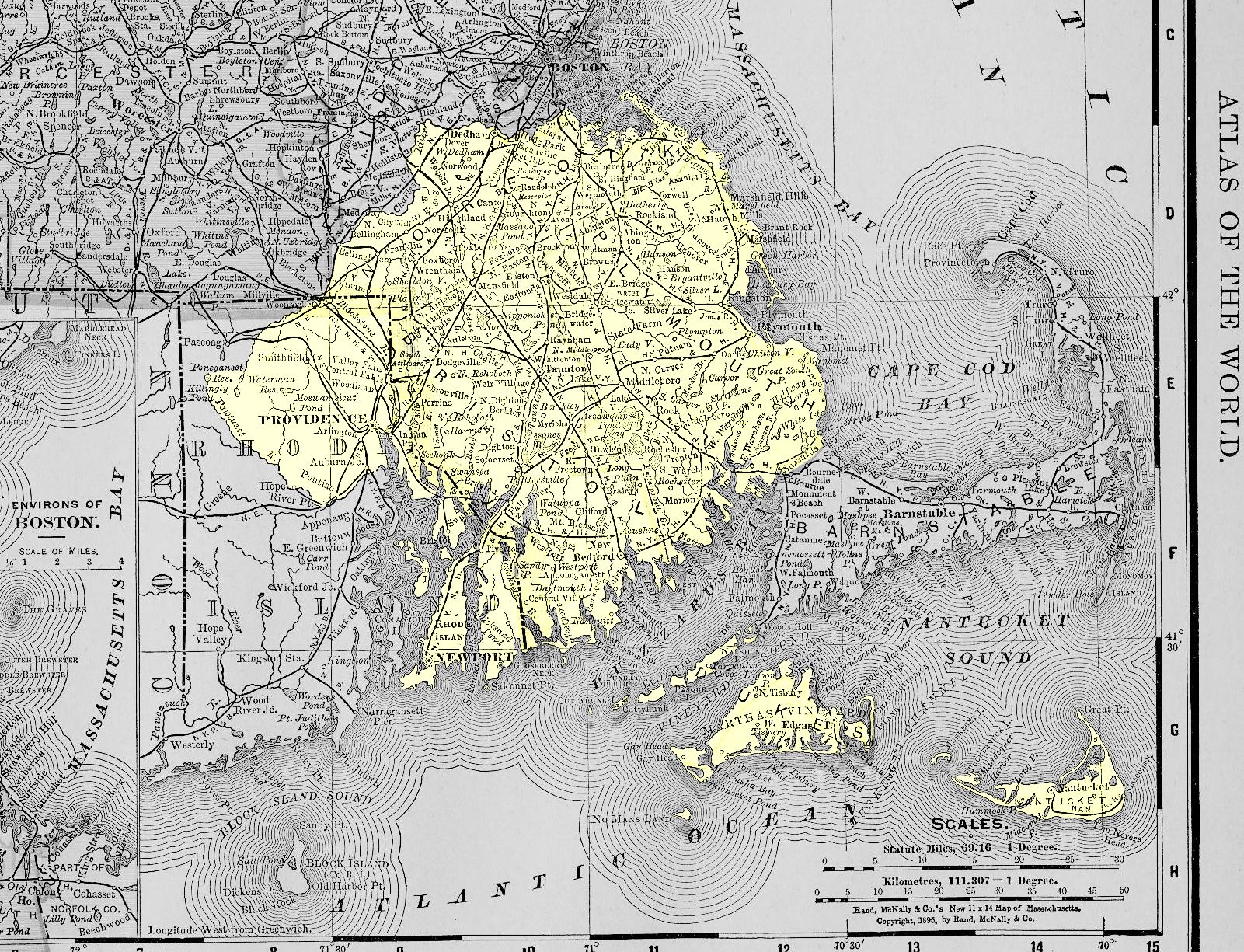
Territories And Boundaries Of Pokanoket Tribe
A territory is an area of land, sea, or space, belonging or connected to a particular country, person, or animal. In international politics, a territory is usually a geographic area which has not been granted the powers of self-government, i.e. an area that is under the jurisdiction of a sovereign state. As a subdivision, a territory in most countries is an organized division of an area that is controlled by a country but is not formally developed into, or incorporated into, a political unit of that country, which political units are of equal status to one another and are often referred to by words such as "provinces", "regions", or "states". In its narrower sense, it is "a geographic region, such as a colonial possession, that is dependent on an external government." Etymology The origins of the word "territory" begin with the Proto-Indo-European root ''ters'' ('to dry'). From this emerged the Latin word ''terra'' ('earth, land') and later the Latin word ''territorium'' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massachusett
The Massachusett are a Native American tribe from the region in and around present-day Greater Boston in the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. The name comes from the Massachusett language term for "At the Great Hill," referring to the Blue Hills overlooking Boston Harbor from the south. As some of the first people to make contact with European explorers in New England, the Massachusett and fellow coastal peoples were severely decimated from an outbreak of leptospirosis circa 1619, which had mortality rates as high as 90 percent in these areas. This was followed by devastating impacts of virgin soil epidemics such as smallpox, influenza, scarlet fever and others to which the Indigenous people lacked natural immunity. Their territories, on the more fertile and flat coastlines, with access to coastal resources, were mostly taken over by English colonists, as the Massachusett were too few in number to put up any effective resistance. Missionary John Eliot converted the majority of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |