|
Poema De Yuçuf
The ''Poema de Yuçuf'' or ''Poema de Yusuf'' is an anonymous poem written in Aragonese language, Aragonese in the Aljamiado Arabic script from the fourteenth century. It was written in a strophe, strophic form called "cuaderna vía" by a Morisco poet. The text was discovered incomplete, but 380 verses have been preserved. Manuscripts and origins The poem has been passed on two codices. The most complete is Manuscript B, written, according to Ramón Menéndez PidalRamón Menéndez Pidal, ''Poema de Yuçuf: Materiales para su estudio'', Granada, Universidad de Granada, 1952, págs. 62-63 ''apud'' Antonio Pérez Lasheras, ''La literatura del reino de Aragón hasta el siglo XVI'', Zaragoza, Ibercaja-Institución «Fernando el Católico» (Biblioteca Aragonesa de Cultura, 15), 2003, pág. 143. . in a very Hispanicization, hispanicised Aragonese, while Manuscript A uses phonetic, morphosyntactic, and lexical features more typical of Aragonese. According to Menéndez Pidal, the poem date ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golden Legend
The ''Golden Legend'' ( or ''Legenda sanctorum'') is a collection of 153 hagiographies by Jacobus de Voragine that was widely read in Europe during the Late Middle Ages. More than a thousand manuscripts of the text have survived.Hilary Maddocks, "Pictures for aristocrats: the manuscripts of the ''Légende dorée'', in Margaret M. Manion, Bernard James Muir, eds. ''Medieval texts and images: studies of manuscripts from the Middle Ages'' 1991:2; a study of the systemization of the Latin manuscripts of the ''Legenda aurea'' is B. Fleith, "Le classement des quelque 1000 manuscrits de la Legenda aurea latine en vue de l'éstablissement d'une histoire de la tradition" in Brenda Dunn-Lardeau, ed. ''Legenda Aurea: sept siècles de diffusion'', 1986:19–24 It was probably compiled around 1259 to 1266, although the text was added to over the centuries. Initially entitled ''Legenda sanctorum'' (''Readings of the Saints''), it gained its popularity under the title by which it is best ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
14th-century Books
The 14th century lasted from 1 January 1301 (represented by the Roman numerals MCCCI) to 31 December 1400 (MCD). It is estimated that the century witnessed the death of more than 45 million lives from political and natural disasters in both Europe and the Mongol Empire. West Africa experienced economic growth and prosperity. In Europe, the Black Death claimed 25 million lives wiping out one third of the European population while the Kingdom of England and the Kingdom of France fought in the protracted Hundred Years' War after the death of King Charles IV of France led to a claim to the French throne by King Edward III of England. This period is considered the height of chivalry and marks the beginning of strong separate identities for both England and France as well as the foundation of the Italian Renaissance and the Ottoman Empire. In Asia, Tamerlane (Timur), established the Timurid Empire, history's third largest empire to have been ever established by a single conqueror. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aragonese-language Literature
Aragonese literature of Spain includes Aragonese-language poetry, prose and novels. Middle Ages The Glosas Emilianenses (11th century) are the first written testimony in Basque and Aragonese languages. This is known from their finding but it is said that they are written in Spanish. This text has a lot of Aragonese-language features like the article ''o'', ''a''; the diphthongization of ''duenno'', ''nuestro'', ''sieculo'', ''get'' (''ye'') and vocabulary such as ''honore'' and ''aiutorio''. From the 11th century all Aragonese documents were written in Latin with Romance features, but it is not until the second part of the 13th century that there is generalization of the use of Aragonese language in all documents, a later date than in Castile or Occitania. From this century there are a lot of works written in Aragonese mixed with Spanish such as ''Razón feita d'amor'', ''Lo Libre dels Tres Reys d'Orient'' or ''Bida de Santa María Egipciaca''. There are still some Aragone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Poems
Spanish might refer to: * Items from or related to Spain: **Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain **Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many countries in the Americas **Spanish cuisine ** Spanish history **Spanish culture **Languages of Spain, the various languages in Spain Other places * Spanish, Ontario, Canada * Spanish River (other), the name of several rivers * Spanish Town, Jamaica Other uses * John J. Spanish (1922–2019), American politician * "Spanish" (song), a single by Craig David, 2003 See also * * * Español (other) * Spain (other) * España (other) * Espanola (other) * Hispania, the Roman and Greek name for the Iberian Peninsula * Hispanic, the people, nations, and cultures that have a historical link to Spain * Hispanic (other) * Hispanism * Spain (other) * National and regional identity in Spain * Culture of Spain The culture of Spain is influenced by its Western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
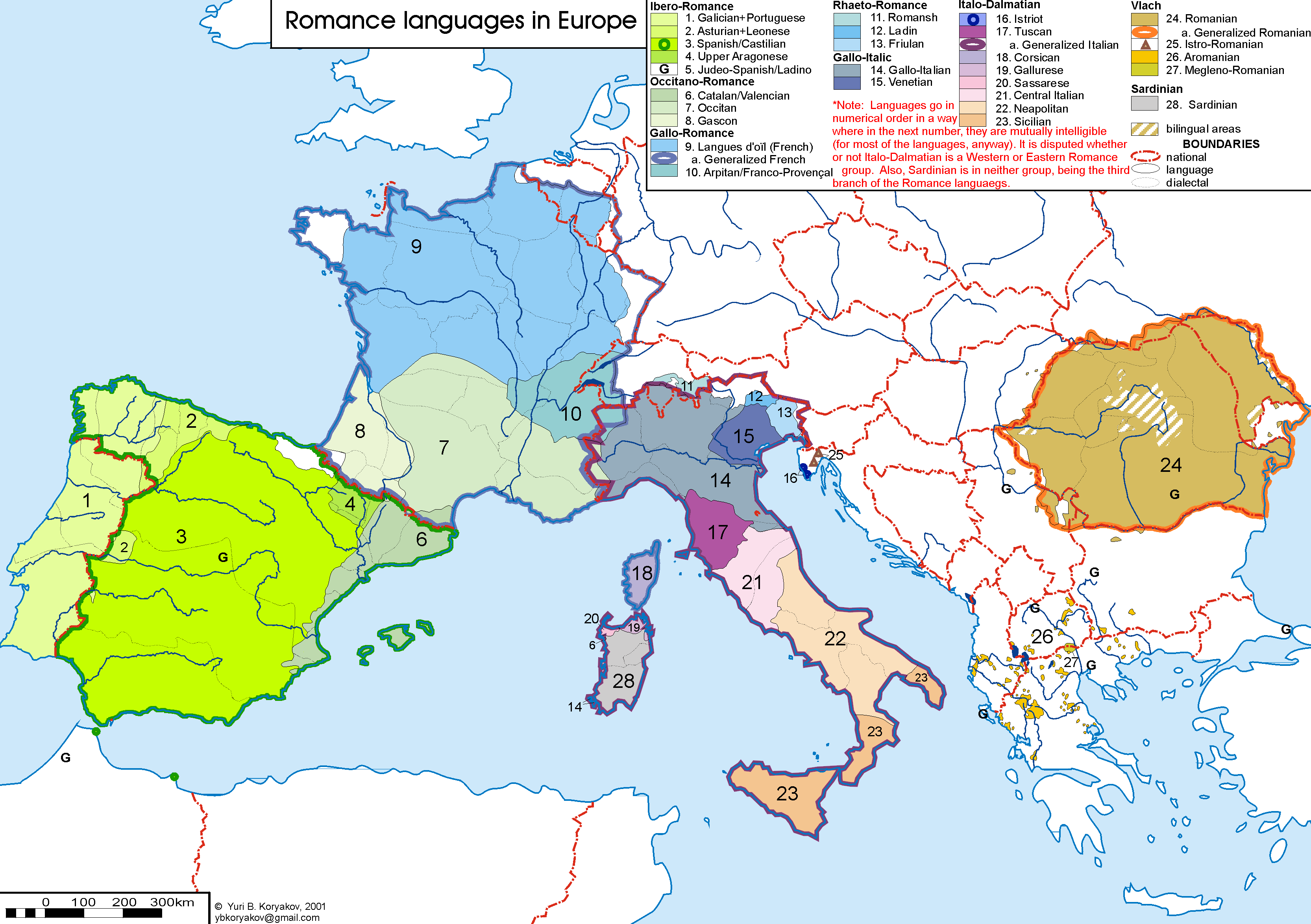
Romance Languages
The Romance languages, also known as the Latin or Neo-Latin languages, are the languages that are Language family, directly descended from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. The five list of languages by number of native speakers, most widely spoken Romance languages by number of native speakers are: * Spanish language, Spanish (489 million): official language in Spain, Mexico, Equatorial Guinea, the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic, SADR, Cuba, Dominican Republic, Puerto Rico and most of Central America, Central and South America * French language, French (310 million): official in 26 countries * Portuguese language, Portuguese (240 million): official in Portugal, Brazil, Portuguese-speaking African countries, Portuguese-speaking Africa, Timor-Leste and Macau * Italian language, Italian (67 million): official in Italy, Vatican City, San Marino, Switzerland; mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anagnorisis
Anagnorisis (; ) is a moment in a play or other work when a character makes a critical discovery. Anagnorisis originally meant recognition in its Greek context, not only of a person but also of what that person stood for. Anagnorisis was the hero's sudden awareness of a real situation, the realization of things as they stood, and finally, the hero's insight into a relationship with an often antagonistic character in Aristotelian tragedy. Tragedy In his '' Poetics,'' Aristotle discussed peripeteia. In this work, he defined anagnorisis as "a change from ignorance to knowledge, producing love or hate between the persons destined by the poet for good or bad fortune" (1452a). Anagnorisis is often discussed along with Aristotle's concept of catharsis. In the Aristotelian definition of tragedy, it was the discovery of one's own identity or true character (e.g. Cordelia, Edgar, Edmund, etc. in Shakespeare's ''King Lear'') or of someone else's identity or true nature (e.g. Lear's chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potiphar
Potiphar ( ; ; ) is a figure in the Hebrew Bible and the Quran. His name possibly indicates the same figure as Potiphera (). Potiphar is the captain of the guard for a pharaoh who is said to have purchased Joseph as a slave and, impressed by his intelligence, makes him the master of his household. Potiphar's wife, who was known for her infidelities, took a liking to Joseph and attempted to seduce him. When Joseph refused her advances and ran off, leaving his outer vestment in her hands, she retaliated by falsely accusing him of trying to rape her, and Potiphar had Joseph imprisoned. What happened to Potiphar after that is unclear; some sources identify him as Potipherah, an Egyptian priest whose daughter, Asenath, marries Joseph. The false accusation by Potiphar's wife plays an important role in Joseph's narrative because had he not been imprisoned, he would not have met the fellow prisoner who introduced him to Pharaoh. Likewise, the fate of Potiphar's wife is unclear but some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zuleika (tradition)
Zuleikha is a figure in the Hebrew Bible and the Quran. She was the wife of Potiphar, the captain of Pharaoh's guard in the time of Jacob and his twelve sons. According to the Book of Genesis, she falsely accused Joseph of attempted rape after he rejected her sexual advances, resulting in his imprisonment. In Genesis she is given no name, but in later medieval Jewish sources and Islamic tradition, she is identified as Zuleikha ( ''zoo-LAY-kah''; ; ). The story of Yusuf and Zulaikha is a popular one in Islamic literature. In Genesis The BibleGenesis 39:5–20 narrates her treatment of Joseph, slave to her husband Potiphar: In Quran Potiphar's wife, as well as Potiphar himself, are not explicitly named in the Quran, though it alludes to a governor (Arabic: العزيز al-azīz) and his wife. The book narrates her treatment of Yusuf as follows: Interpretation In Jewish sources The Sefer haYashar adds more lurid details to Potiphar's wife's character. She tried ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midrash
''Midrash'' (;"midrash" . ''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. ; or ''midrashot'') is an expansive Judaism, Jewish Bible, Biblical exegesis using a rabbinic mode of interpretation prominent in the Talmud. The word itself means "textual interpretation", "study", or "exegesis", derived from the root verb (), which means "resort to, seek, seek with care, enquire, require". Midrash and rabbinic readings "discern value in texts, words, and letters, as potential revelatory spaces", writes the Hebrew scholar Wilda Gafney. "They reimagine dominant narratival readings while crafting new ones to stand alongside—not replace—former readings. Midrash also asks questions of the text; sometimes it provides answers, sometimes it leaves the reader to answer the questions". Vanessa Lovelace defines midrash as "a Jewish mode of int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sefer HaYashar (midrash)
Sefer haYashar () is a medieval Hebrew language, Hebrew ''midrash'', also known as the Toledot Adam and Divrei haYamim heArukh. The Hebrew title "Sefer haYashar" might be translated as the "Book of Righteousness" (or literally "Book of the Straight") but it is known in English translation mostly as The Book of Jasher following English tradition. Its author is unknown. Other books of the same name The book is named after the Sefer HaYashar (Biblical references), Book of Jasher mentioned in Book of Joshua, Joshua and Books of Samuel, 2 Samuel. Although it is presented as the original "Book of Jasher" in translations such as that of Moses Samuel (1840), it is not accepted as such in rabbinical Judaism. It should not be confused with the very different ''Book of Jasher (Pseudo-Jasher)'' printed by Jacob Ilive in 1751, which was purported to have been translated by the English monk Alcuin. Additionally, an ethical text was written under the same name (not purporting to be the bibli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacobus De Voragine
Jacobus de Voragine, OP (13/16 July 1298) was an Italian chronicler and archbishop of Genoa. He was the author, or more accurately the compiler, of the '' Golden Legend'', a collection of the legendary lives of the greater saints of the medieval church that was one of the most popular religious works of the Middle Ages. Biography Jacobus was born either in Varazze or in Genoa, where a family originally from Varazze and bearing that name is attested at the time. He entered the Dominican order in 1244, and became the prior at Como, Bologna and Asti in succession. Besides preaching with success in many parts of Italy, he also taught in the schools of his own fraternity. He was provincial of Lombardy from 1267 till 1286, when he was removed at the meeting of the order in Paris. He also represented his own province at the councils of Lucca (1288) and Ferrara (1290). On the last occasion he was one of the four delegates charged with signifying Pope Nicholas IV's desire for the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |