|
Ploërmel Astronomical Clock
The Ploërmel Astronomical Clock is a 19th-century astronomical clock in Ploërmel in Brittany, in north-west France. History and description The clock was built and operational by 1855. It was constructed by Brother Bernardin (1812−1876) of the Community of Brothers of The Mother House of the Brothers of Ploërmel. The clock was originally inside the monastic building, it is now displayed in a glazed kiosk in the interior court of the cloisters. It comprises an astronomical clock and an orrery displaying all the planets known at that time. The Earth is especially well represented with its correct inclination and the moon encircling it Astronomical clock The clock has ten dials which show: *Dial 1. Solar time *Dial 2. Calendar *Dial 3. Position of the Moon, the months of the year, seasons and signs of the zodiac *Dial 4. The equation of time (the difference between mean time and real time) *Dials 5 and 6. The standard time to the nearest minute for the whole world. *Dial 7. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is often called Earth's "twin" or "sister" planet for having almost the same size and mass, and the closest orbit to Earth's. While both are rocky planets, Venus has an atmosphere much thicker and denser than Earth and any other rocky body in the Solar System. Its atmosphere is composed of mostly carbon dioxide (), with a global sulfuric acid cloud cover and no liquid water. At the mean surface level the atmosphere reaches a temperature of and a pressure 92 times greater than Earth's at sea level, turning the lowest layer of the atmosphere into a supercritical fluid. Venus is the third brightest object in Earth's sky, after the Moon and the Sun, and, like Mercury, appears always relatively close to the Sun, either as a "morning star" or an "evening star", resulting from orbiting closer ( inferior) to the Sun than Earth. The orbits of Venus and Earth make the two planets approach each other in synodic periods of 1.6 years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Clocks In France
Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxies, meteoroids, asteroids, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole. Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences. The early civilizations in recorded history made methodical observations of the night sky. These include the Egyptians, Babylonians, Greeks, Indians, Chinese, Maya, and many ancient indigenous peoples of the Americas. In the past, astronomy included disciplines as diverse as astrometry, celestial navigation, observat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
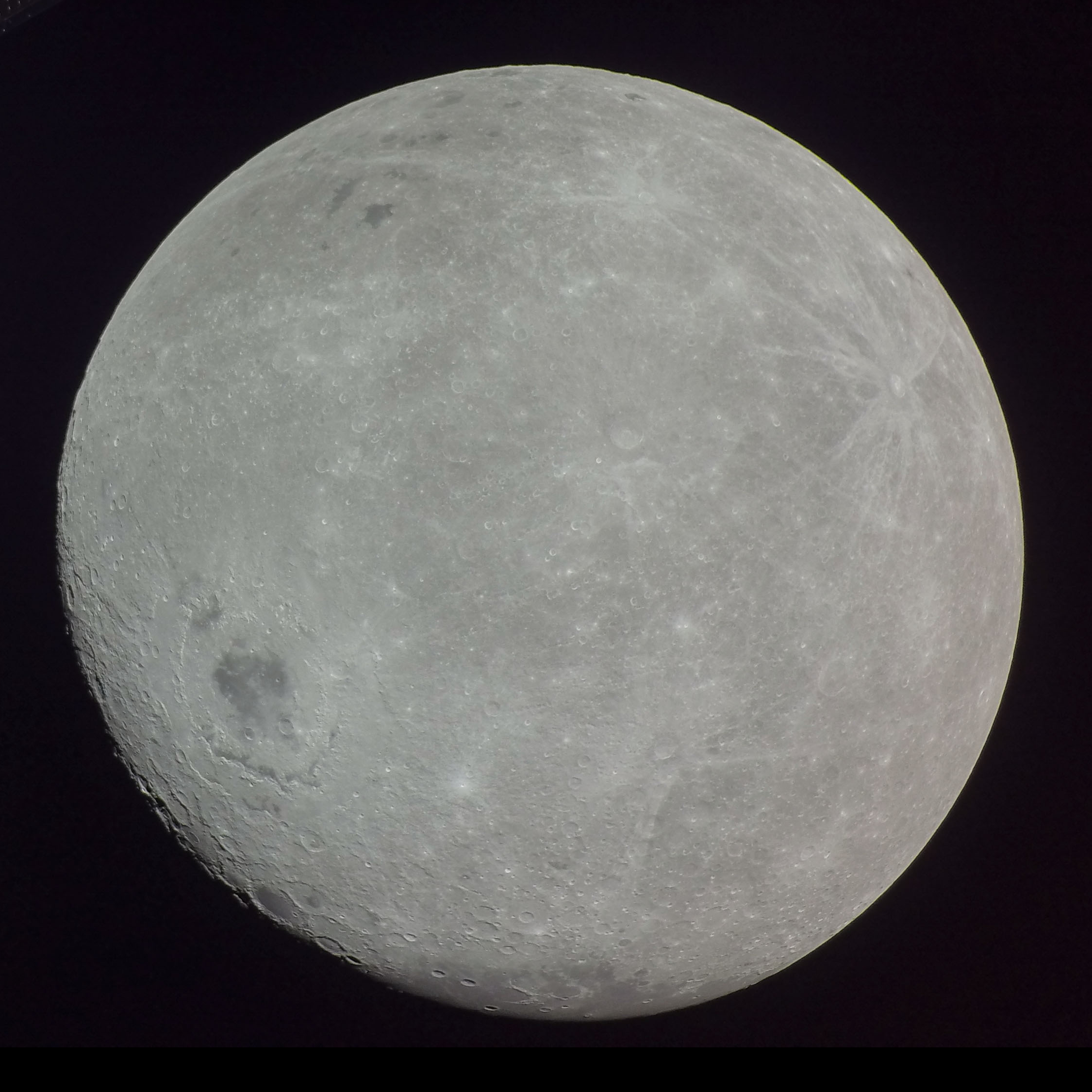
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It Orbit of the Moon, orbits around Earth at Lunar distance, an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth diameter, Earth's diameter). The Moon rotation, rotates, with a rotation period (lunar day) that is synchronized to its orbital period (Lunar month#Synodic month, lunar month) of 29.5 Earth days. This is the product of Earth's gravitation having tidal forces, tidally pulled on the Moon until one part of it stopped rotating away from the near side of the Moon, near side, making always the same lunar surface face Earth. Conversley, the gravitational pull of the Moon, on Earth, is the main driver of Earth's tides. In geophysical definition of planet, geophysical terms, the Moon is a planetary-mass object or satellite planet. Its mass is 1.2% that of the Earth, and its diameter is , roughly one-quarter of Earth's (about as wide as the contiguous United States). Within the Solar System, it is the List of Solar System objects by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. It is a gaseous cyan-coloured ice giant. Most of the planet is made of water, ammonia, and methane in a Supercritical fluid, supercritical phase of matter, which astronomy calls "ice" or Volatile (astrogeology), volatiles. Atmosphere of Uranus, The planet's atmosphere has a complex layered cloud structure and has the lowest minimum temperature () of all the Solar System's planets. It has a marked axial tilt of 82.23° with a Retrograde and prograde motion, retrograde rotation period of 17 hours and 14 minutes. This means that in an 84-Earth-year orbital period around the Sun, its poles get around 42 years of continuous sunlight, followed by 42 years of continuous darkness. Uranus has the third-largest diameter and fourth-largest mass among the Solar System's planets. Based on current models, inside its volatile Mantle (geology), mantle layer is a rocky core, and surrounding it is a thick hydrogen and helium atmosphere. Trace amount ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant, with an average radius of about 9 times that of Earth. It has an eighth the average density of Earth, but is over 95 times more massive. Even though Saturn is almost as big as Jupiter, Saturn has less than a third its mass. Saturn orbits the Sun at a distance of , with an orbital period of 29.45 years. Saturn's interior is thought to be composed of a rocky core, surrounded by a deep layer of metallic hydrogen, an intermediate layer of liquid hydrogen and liquid helium, and an outer layer of gas. Saturn has a pale yellow hue, due to ammonia crystals in its upper atmosphere. An electrical current in the metallic hydrogen layer is thought to give rise to Saturn's planetary magnetic field, which is weaker than Earth's, but has a magnetic moment 580 times that of Earth because of Saturn's greater size. Saturn's magnetic field strength is about a twen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a Jupiter mass, mass more than 2.5 times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined and slightly less than one-thousandth the mass of the Sun. Its diameter is 11 times that of Earth and a tenth that of the Sun. Jupiter orbits the Sun at a distance of , with an orbital period of . It is the List of brightest natural objects in the sky, third-brightest natural object in the Earth's night sky, after the Moon and Venus, and has been observed since prehistoric times. Its name derives from that of Jupiter (god), Jupiter, the chief deity of ancient Roman religion. Jupiter was the first of the Sun's planets to form, and its inward migration during the primordial phase of the Solar System affected much of the formation history of the other planets. Jupiter's atmosphere consists of 76% hydrogen and 24% helium by mass, with a denser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
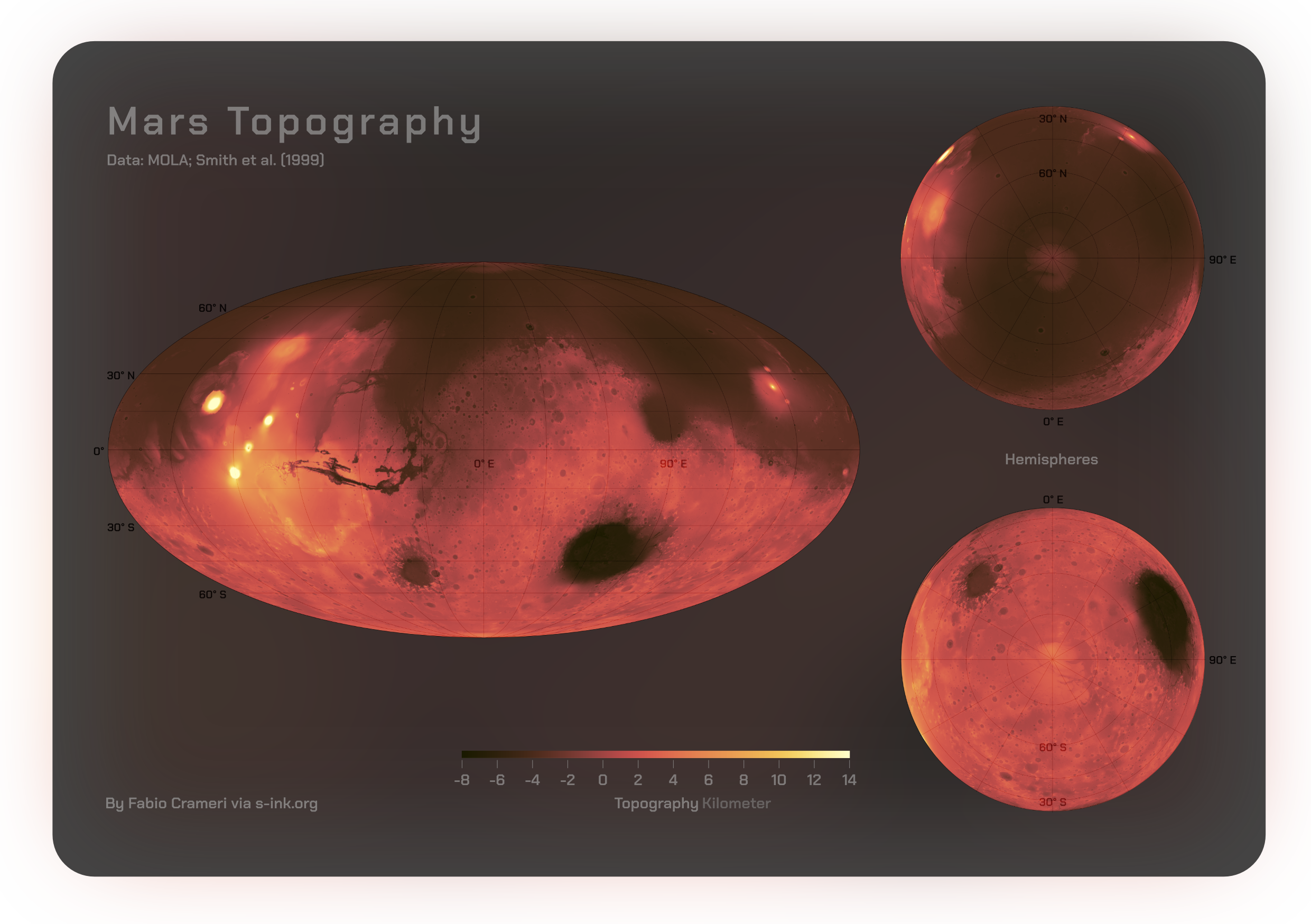
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmospheric pressure is a few thousandths of Earth's, atmospheric temperature ranges from and cosmic radiation is high. Mars retains some water, in the ground as well as thinly in the atmosphere, forming cirrus clouds, frost, larger polar regions of permafrost and ice caps (with seasonal snow), but no liquid surface water. Its surface gravity is roughly a third of Earth's or double that of the Moon. It is half as wide as Earth or twice the Moon, with a diameter of , and has a surface area the size of all the dry land of Earth. Fine dust is prevalent across the surface and the atmosphere, being picked up and spread at the low Martian gravity even by the weak wind of the tenuous atmosphere. The terrain of Mars roughly follows a north-south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all of Earth's water is contained in its global ocean, covering Water distribution on Earth, 70.8% of Earth's crust. The remaining 29.2% of Earth's crust is land, most of which is located in the form of continental landmasses within Earth's land hemisphere. Most of Earth's land is at least somewhat humid and covered by vegetation, while large Ice sheet, sheets of ice at Polar regions of Earth, Earth's polar polar desert, deserts retain more water than Earth's groundwater, lakes, rivers, and Water vapor#In Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric water combined. Earth's crust consists of slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's outer core, Earth has a liquid outer core that generates a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercury (planet)
Mercury is the first planet from the Sun. It is a rocky planet with a trace atmosphere. While it is the List of Solar System objects by size, smallest and least massive planet of the Solar System, its surface gravity is slightly higher than that of Mars. The surface of Mercury is similar to Earth's Moon, heavily Impact crater, cratered, with expansive rupes system, generated from thrust faults, and bright ray systems, formed by ejecta. Its largest crater, Caloris Planitia, has a diameter of , which is about one-third the diameter of the planet (). Being the most inferior planet, inferior orbiting planet it appears in Earth's sky, always close to the Sun, either as a "morning star" or an "evening star". It stays most of the time the closest to all other planets and is the planet with the highest delta-v needed to travel to from all other planets of the Solar System. Mercury's sidereal year (88.0 Earth days) and sidereal day (58.65 Earth days) are in a 3:2 ratio. This relation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Clock
An astronomical clock, horologium, or orloj is a clock with special mechanisms and dials to display astronomical information, such as the relative positions of the Sun, Moon, zodiacal constellations, and sometimes major planets. Definition The term is loosely used to refer to any clock that shows, in addition to the time of day, astronomical information. This could include the location of the Sun and Moon in the sky, the age and Lunar phases, the position of the Sun on the ecliptic and the current zodiac sign, the sidereal time, and other astronomical data such as the Moon's nodes for indicating eclipses), or a rotating star map. The term should not be confused with an ''astronomical regulator'', a high precision but otherwise ordinary pendulum clock used in observatories. Astronomical clocks usually represent the Solar System using the geocentric model. The center of the dial is often marked with a disc or sphere representing the Earth, located at the center of the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orrery
An orrery is a mechanical Solar System model, model of the Solar System that illustrates or predicts the relative positions and motions of the planets and natural satellite, moons, usually according to the heliocentric model. It may also represent the relative sizes of these bodies; however, since accurate scaling is often not practical due to the actual large ratio differences, it may use a scaled-down approximation. Ancient Greek astronomy, The Greeks had working planetarium, planetaria, but the first modern example was produced by John Rowley. He named it "orrery" for his patron Charles Boyle, 4th Earl of Orrery (in County Cork, Ireland). The plaque on it reads "Orrery invented by Graham 1700 improved by Rowley and presented by him to John [sic] Earl of Orrery after whom it was named at the suggestion of Richard Steele." Orreries are typically driven by a clockwork mechanism with a globe representing the Sun at the centre, and with a planet at the end of each of a series of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |