|
Plectroglyphidodon Dickii
''Plectroglyphidodon dickii'', common name blackbar devil, Dick's damsel or narrowbar damselfish, is a species of damselfish in the family Pomacentridae. This species was formerly classified as ''Dascyllus aruanus'', but recently the populations of western Indian Ocean and Pacific Ocean have been split off. Etymology The genus epithet ''Plectroglyphidodon'' derives from the Greek words (meaning = ''anything to strike with, spur''), plus the suffixes (mening ''carved'') and (meaning ''teeth''). Distribution This species is present in the Indo-Pacific, from East Africa to the Line Islands and Tuamotu, north to Japan, south to Australia and east to French Polynesia. Habitat These tropical marine reef-associated damselfishes occur in shallow coral reefs, especially with branching corals, in areas of high wave action, in clear waters lagoons and seaward reefs, at depths of 1 to 15 m. They are commonly present with Pocillopora or Acropora corals. Description ''Plectroglyphidodo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
François Liénard De La Mivoye
François Liénard de la Mivoye (born 29 July 1782, Visakhapatnam, died 6 November 1862, Paris) was a Francophone Mauritian naturalist, ichthyologist, zoologist and mariner. He lived most of his life in Mauritius and, in 1829, was a founder member and treasurer of the ''société d'histoire natural locale'' alongside Charles Telfair, Wenceslas Bojer, Jacques Delisse and Julien Desjardins. In 1841 this became the ''Société Royale des arts et des Sciences de l'île Maurice''. The Society regularly sent fish specimens to Georges Cuvier in Paris and these were described in his 22 volume ''Histoire naturelle des poissons'', this was completed after Cuvier’s death by Achille Valenciennes. Liénard was responsible for describing a number of species including the now extinct Rodrigues giant day gecko (''Phesulma gigas''), Liénard being the last known person to see this species. Liénard is commemorated in the specific name of the predatory sea snail ''Conus lienardi''. He is also c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign ''Sovereign'' is a title which can be applied to the highest leader in various categories. The word is borrowed from Old French , which is ultimately derived from the Latin , meaning 'above'. The roles of a sovereign vary from monarch, ruler or ... country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by area in Oceania and the world's sixth-largest country. Australia is the oldest, flattest, and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils. It is a megadiverse country, and its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes and climates, with deserts in the centre, tropical Forests of Australia, rainforests in the north-east, and List of mountains in Australia, mountain ranges in the south-east. The ancestors of Aboriginal Australians began arriving from south east Asia approx ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oviparous
Oviparous animals are animals that lay their eggs, with little or no other embryonic development within the mother. This is the reproductive method of most fish, amphibians, most reptiles, and all pterosaurs, dinosaurs (including birds), and monotremes. In traditional usage, most insects (one being '' Culex pipiens'', or the common house mosquito), molluscs, and arachnids are also described as oviparous. Modes of reproduction The traditional modes of reproduction include oviparity, taken to be the ancestral condition, traditionally where either unfertilised oocytes or fertilised eggs are spawned, and viviparity traditionally including any mechanism where young are born live, or where the development of the young is supported by either parent in or on any part of their body. However, the biologist Thierry Lodé recently divided the traditional category of oviparous reproduction into two modes that he named ovuliparity and (true) oviparity respectively. He distinguis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operculum (fish)
The operculum is a series of bones found in bony fish and chimaeras that serves as a facial support structure and a protective covering for the gills; it is also used for respiration and feeding. Anatomy The opercular series contains four bone segments known as the preoperculum, suboperculum, interoperculum and operculum. The preoperculum is a crescent-shaped structure that has a series of ridges directed posterodorsally to the organisms canal pores. The preoperculum can be located through an exposed condyle that is present immediately under its ventral margin; it also borders the operculum, suboperculum, and interoperculum posteriorly. The suboperculum is rectangular in shape in most bony fishy and is located ventral to the preoperculum and operculum components. It is the thinnest bone segment out of the opercular series and is located directly above the gills. The interoperculum is triangular shaped and borders the suboperculum posterodorsally and the preoperculum anterodors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acropora
''Acropora'' is a genus of small polyp stony coral in the phylum Cnidaria. Some of its species are known as table coral, elkhorn coral, and staghorn coral. Over 149 species are described. ''Acropora'' species are some of the major reef corals responsible for building the immense calcium carbonate substructure that supports the thin living skin of a reef. Anatomy and distribution Depending on the species and location, ''Acropora'' species may grow as plates or slender or broad branches. Like other corals, ''Acropora'' corals are colonies of individual polyps, which are about 2 mm across and share tissue and a nerve net. The polyps can withdraw back into the coral in response to movement or disturbance by potential predators, but when undisturbed, they protrude slightly. The polyps typically extend further at night to help capture plankton and organic matter from the water. The species are distributed in the Indo-Pacific (over 100 species) and Caribbean (3 species). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pocillopora
''Pocillopora'' is a genus of stony corals in the family Pocilloporidae occurring in the Pacific and Indian Oceans.Veron, J.E.N. (2000) Corals of the World. Australian Institute of Marine Science, Townville, Australia. They are commonly called cauliflower corals and brush corals. Description Cauliflower corals are widespread and can be identified by the presence of wart-like growths on their surface. The colonies can be dome shaped or branching and are very variable in colour and shape depending on the species and the environmental conditions. Species situated on shallow reefs pounded by the sea tend to be stunted whilst those in deep calm water are often thin and open. Each individual polyp has tentacles but these are normally extended only at night. Biology The polyps are hermaphrodite, possessing four sets of male and four sets of female gonads. Pocillopora can reproduce asexually via fragmentation. They also reproduce sexually and the larvae develop inside the polyps rather ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pomacanthidae - Plectroglyphidodon Dickii
Marine angelfish are perciform fish of the family Pomacanthidae. They are found on shallow reefs in the tropical Atlantic, Indian, and mostly western Pacific Oceans. The family contains seven genera and about 86 species. They should not be confused with the freshwater angelfish, tropical cichlids of the Amazon Basin. Description With their bright colours and deep, laterally compressed bodies, marine angelfishes are some of the more conspicuous residents of the reef. They most closely resemble the butterflyfishes, a related family of similarly showy reef fish. Marine angelfish are distinguished from butterflyfish by the presence of strong preopercle spines (part of the gill covers) in the former. This feature also explains the family name Pomacanthidae; from the Greek πομα, ''poma'' meaning "cover" and ακάνθα, ''akantha'' meaning "thorn". Many species of marine angelfishes have streamer-like extensions of the soft dorsal and anal fins. The fish have small mouths, relat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Polynesia
)Territorial motto: ( en, "Great Tahiti of the Golden Haze") , anthem = , song_type = Regional anthem , song = "Ia Ora 'O Tahiti Nui" , image_map = French Polynesia on the globe (French Polynesia centered).svg , map_alt = Location of French Polynesia , map_caption = Location of French Polynesia (circled in red) , mapsize = 290px , subdivision_type = Sovereign state , subdivision_name = , established_title = Protectorate proclaimed , established_date = 9 September 1842 , established_title2 = Territorial status , established_date2 = 27 October 1946 , established_title3 = Collectivity status , established_date3 = 28 March 2003 , established_title4 = Country status (nominal title) , established_date4 = 27 February 2004 , official_languages = French , regional_languages = , capital = Papeete , coordinates = , largest_city = Fa'a'ā , demonym = French Polynesian , ethnic_groups = 66.5% unmixed Polynesians7.1% mixed Polynesians9.3% Demis11 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north toward the East China Sea, Philippine Sea, and Taiwan in the south. Japan is a part of the Ring of Fire, and spans an archipelago of 6852 islands covering ; the five main islands are Hokkaido, Honshu (the "mainland"), Shikoku, Kyushu, and Okinawa. Tokyo is the nation's capital and largest city, followed by Yokohama, Osaka, Nagoya, Sapporo, Fukuoka, Kobe, and Kyoto. Japan is the eleventh most populous country in the world, as well as one of the most densely populated and urbanized. About three-fourths of the country's terrain is mountainous, concentrating its population of 123.2 million on narrow coastal plains. Japan is divided into 47 administrative prefectures and eight traditional regions. The Greater Tokyo Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudolf Kner
Rudolf Ignaz Kner (24 August 1810 – 27 October 1869) was an Austrian geologist, paleontologist, zoologist and ichthyologist. He also wrote some poems which were published by his brother-in-law K.A. Kaltenbrunner. Biography Kner was born in Linz where his father Johann Evangelist Georg Kner (1763-1845) was a tax officer. His mother Barbara (1770-1825), daughter of forester Johann von Adlersburg was earlier married to apothecary Felix Gulielmo until his death. Barbara had a daughter Marie Gulielmo from her earlier marriage before having Rudolf and his sister Pauline. Pauline Anna Barbara Kner (1809-1843) married the Austrian poet Karl Adam Kaltenbrunner (1804-1867) in 1834. Rudolf studied in the secondary school in Linz from 1818 and the high school from 1821. During this period he was encouraged in the natural sciences with a gift of minerals from his uncle Hallstatt Maximilian Kner (1755–1821). From 1823 he went to the Stiftsgymnasium Kremsmünster. His godfather, Igna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuamotu
The Tuamotu Archipelago or the Tuamotu Islands (french: Îles Tuamotu, officially ) are a French Polynesian chain of just under 80 islands and atolls in the southern Pacific Ocean. They constitute the largest chain of atolls in the world, extending (from northwest to southeast) over an area roughly the size of Western Europe. Their combined land area is . This archipelago's major islands are Anaa, Fakarava, Hao and Makemo. The Tuamotus have approximately 16,000 inhabitants. The islands were initially settled by Polynesians, and modern Tuamotuans have inherited from them a shared culture and the Tuamotuan language. The Tuamotus are a French overseas collectivity. History The early history of the Tuamotu islands is generally unknown. Archaeological findings suggest that the western Tuamotus were settled from the Society Islands as early as 900 CE or as late as 1200 CE. DNA evidence suggests that they were settled about 1110 CE. On the islands of Rangiroa, Manihi and M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
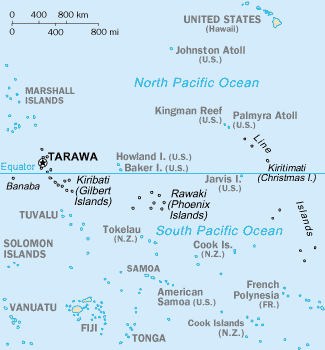
Line Islands
The Line Islands, Teraina Islands or Equatorial Islands (in Gilbertese, ''Aono Raina'') are a chain of 11 atolls (with partly or fully enclosed lagoons) and coral islands (with a surrounding reef) in the central Pacific Ocean, south of the Hawaiian Islands. The island chain stretches northwest to southeast across , making it one of the longest island chains in the world. It lies at the geographic center of the Pacific Ocean (), near Starbuck Island. One of the atolls in the group, Kiritimati, has the largest land area of any atoll in the world. Of the 11 atolls, all of which were formed by volcanic activity, only the Kiritimati and Tabuaeran atolls and Teraina island have a permanent population (one of the reefs, Filippo Reef, is shown on some maps, but its existence is doubted). Eight of the atolls are parts of Kiribati. The remaining three— Jarvis Island, Kingman Reef (which is largely submerged), and Palmyra Atoll—are territories of the United States grouped with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_(48272091136).jpg)