|
Piscataway Tribe
The Piscataway or Piscatawa , are an Indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands. They spoke Algonquian Piscataway, a regional dialect similar to Nanticoke. The neighboring Haudenosaunee, called them the Conoy, with whom they partly merged with after a massive decline of population and rise in colonial violence following two centuries of interactions with European settlers. Two major groups that represent Piscataway descendants received state recognition as Native American tribes from Maryland in 2012: the Piscataway Indian Nation and Piscataway Conoy Tribe. Within the latter group was included the Piscataway Conoy Confederacy and Sub-Tribes and the Cedarville Band of Piscataway Indians. All these groups descend from the Western Bank of the Chesapeake, spanning across Maryland, Virginia, D.C, Pennsylvania, and West Virginia, and are primarily located in Southern Maryland. None are federally recognized despite over a half-century tribal movement in being recognized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piscataway Indian Nation
The Piscataway Indian Nation ( or ,), also called Piscataway Indian Nation Inc. is a state-recognized tribe in Maryland who identify as descendants of the historic Piscataway people. At the time of European encounter, the Piscataway was one of the most populous and powerful Native polities of the Chesapeake Bay region, with a territory on the north side of the Potomac River. By the early seventeenth century, the Piscataway had come to exercise hegemony over other Algonquian-speaking Native American groups on the north bank of the river. The Piscataway nation declined dramatically before the nineteenth century, under the influence of colonization, infectious disease, and intertribal and colonial warfare. The Piscataway Indian Nation organized out of a 20th-century revival of its people and culture. Its members are committed to Indigenous and human rights. It is one of three contemporary organized groups of self-identified Piscataway descendants. On January 12, 2012, Maryland Gov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Recognition
Diplomatic recognition in international law is a unilateral declarative political act of a state that acknowledges an act or status of another state or government in control of a state (may be also a recognized state). Recognition can be accorded either on a '' de facto'' or ''de jure'' basis. Partial recognition can occur if many sovereign states refuse to recognize an entity as a peer. Recognition can be a declaration to that effect by the recognizing government or may be implied from an act of recognition, such as entering into a treaty with the other state or making a state visit. Recognition may, but need not, have domestic and international legal consequences. If sufficient countries recognize a particular entity as a state, that state may have a right to membership in international organizations, while treaties may require all existing member countries unanimously agreeing to the admission of a new member. A vote by a country in the United Nations in favour of the member ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assateague People
The Assateague (meaning: "swifly moving water") were an Algonquian people speaking the Nanticoke language who historically lived on the Atlantic coast side of the Delmarva Peninsula (known during the colonial period as the Eastern Shores of Maryland and Virginia, and the Lower Counties of Pennsylvania). While there are living people who may have distant heritage from this tribe, the tribe itself no longer exists as a culturally intact tribal community. Culture The Indigenous Assateague culture was based on the maritime and forest resources of the Chincoteague Bay watershed and, among other things, involved the manufacture and trade of shell beads. Historically, the Assateague practiced excarnation as part of their funerary rites. This involved the eventual storing of ancestors' bones on shelves in a log structure. Periodically, the remains were collected and buried in a common grave or ossuary. Several ossuaries have been discovered on the Eastern Shore of Maryland. Histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pamunkey
The Pamunkey Indian Tribe is a federally recognized tribe of Pamunkey people in Virginia. They control the Pamunkey Indian Reservation in King William County, Virginia. Historically, they spoke the Pamunkey language. They are one of 11 Native American tribes in Virginia and an Indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands. The tribe became the Commonwealth of Virginia's first federally recognized tribe receiving its status in January 2016. The historical Pamunkey people were part of the Powhatan paramountcy, made up of Algonquian-speaking nations. The Powhatan paramount chiefdom was made up of over 30 nations, estimated to total about 10,000 to 15,000 people at the time the English arrived in 1607.Rountree, Helen C. and E. Randolph Turner III. ''Before and After Jamestown: Virginia's Powhatans and Their Predecessors''. Gainesville: University Press of Florida, 2002. The Pamunkey nation comprised about one-tenth to one-fifteenth of the total. They numbered about 1,000 per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doeg People
The Doeg (also called Dogue, Taux, Tauxenent) were a Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Native American people who lived in Virginia. They spoke an Algonquian languages, Algonquian language and may have been a branch of the Nanticoke Indian Tribe, Nanticoke tribe, historically based on the Eastern Shore of Maryland. The Nanticoke considered the Algonquian Lenape as "grandfathers". The Doeg are known for a raid in July 1675 that contributed to colonists' uprising in Bacon's Rebellion. Background The Doeg (or Dogue) tribe of Virginia were part of the coastal Algonquian languages, Algonquian language family. They probably spoke Piscataway language, Piscataway or a dialect similar to Nanticoke language, Nanticoke. According to one account, the Doeg had been based in what is now King George County, Virginia, King George County, but about 50 years before the founding of Jamestown, Virginia, Jamestown (ca. 1557), they split into three sections, with groups going to Caroline County, V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choptico
The Chaptico, also known as the Cecomocomoco, were a group of Native Americans who lived along the Southwestern shore of the Chesapeake Bay in what is today St. Mary's County, Maryland. They were loosely dominated by the Patuxent in the pre-colonial time. While little is known about their culture, the Chaptico spoke an Algonquian language that was possibly similar to their Patuxent neighbors, who they absorbed in the 1690s. Sources *''Maryland: A Colonial History'' p. 22. *Maryland.gov See also *Chaptico, Maryland Chaptico is an unincorporated community in St. Mary's County, Maryland, United States. It lies on Chaptico Run, which forms a bay as it enters the Wicomico River. History ''Chaptico'' may be Algonquian for "big-broad-river-it-is" and related ..., a present-day community in the area References Eastern Algonquian peoples Extinct Native American tribes Native American tribes in Maryland {{NorthAm-native-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nacotchtank
The Nacotchtank, also Anacostine, were an Algonquian Indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands. During the 17th century, the Nacotchtank resided within the present-day borders of Washington, D.C., along the intersection of the Potomac and Anacostia rivers. The Nacotchtank spoke Piscataway, a variant of the Algonquian subfamily spoken by many tribes along the coast of the Atlantic Ocean. This was due to close association and tribute with the nearby Piscataway chiefdom, whose ''tayac'' (grand chief) ruled over a loose confederacy of tribes in Southern Maryland from the village of Moyaone to the south. As the neighboring Maryland colony sought land for tobacco plantations, the Nacotchtank were encroached upon and forcibly removed. They were last recorded in the late 1600s to have taken refuge on nearby Theodore Roosevelt Island located in the Potomac River. Over time, the small population that was left behind after battle and disease was absorbed into the Piscataway. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
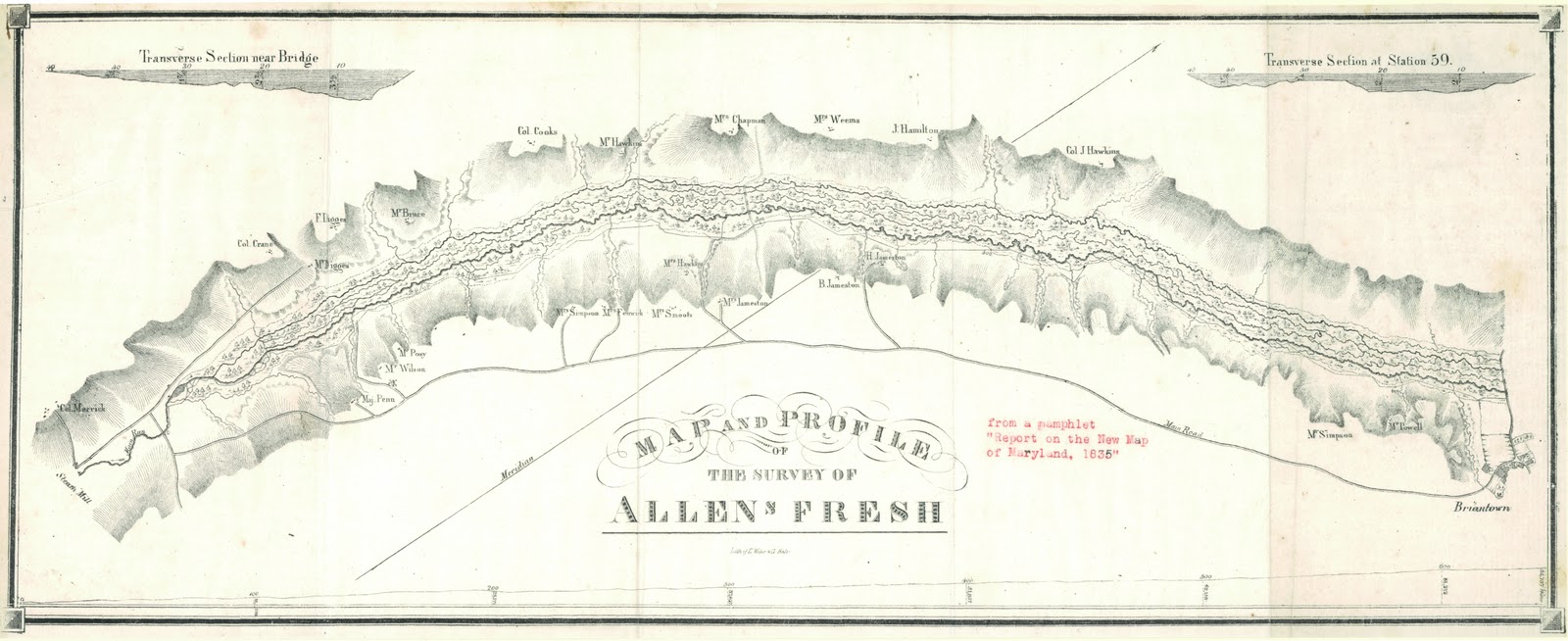
Zekiah Swamp
Zekiah Swamp is part of the Potomac River basin in Charles County, Maryland in the United States. The swamp is of braided stream stretching the length of Charles County and is a tributary of the Potomac River. It sits at an elevation of and of its southern end is protected as the Zekiah Swamp Natural Environment Area. The Maryland Department of Natural Resources has the authority to purchase an additional for the park. Charles County has moved to protect an additional of the wetland. The headwaters of the swamp are protected as part of Cedarville State Forest. It was first accurately surveyed by John Henry Alexander, Maryland's official cartographer, in 1835, as "Allen's Fresh". History Maryland was formed as an English colony in 1634. One of the original Thirteen Colonies, the Province of Maryland was established by Cecilius Calvert, 2nd Baron Baltimore as a haven for Roman Catholic Englishmen. Much of Zekiah Swamp is now thickly wooded and very swampy, but during the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port Tobacco, Maryland
Port Tobacco, officially Port Tobacco Village, is a town in Charles County, Maryland, Charles County, Maryland, United States. The population was 13 at the 2010 census, making Port Tobacco the smallest incorporated town in Maryland. Overview This was historically the territory of Algonquian languages, Algonquian-speaking peoples, especially the Potapoco and the more dominant Piscataway tribe, Piscataway. Settled by the England, English in the 17th century and established in 1727, the town on the Port Tobacco River soon became the second largest in Maryland. The first county seat of Charles County, it was a seaport with access to the Chesapeake Bay and Atlantic Ocean. It declined rapidly after river traffic was cut off by silting and the town was bypassed by the railroad. The town incorporated in 1888, but in 1895 the county seat moved to nearby La Plata, Maryland, La Plata, which drew population away but left the town with its historic significance intact. "Today just 13 residents ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accokeek Tribe
The Accokeek were a group of Native Americans living in Southern Maryland at the time of English colonization. They lived along the Potomac River in present-day Prince George's County, Maryland. They were an Algonquian-language tribe and were related to the Piscataway, another Algonquian-language tribe. Accokeek, Maryland Accokeek (), "at the edge of the hill" in Algonquin, is a census-designated place (CDP) located in Prince George's County, Maryland, United States. The CDP is located on the Potomac River, borders Charles County and is approximately 17 miles ..., a small unincorporated town in Maryland, was named after the Accokeek tribe. Accokeek means "at the edge of the hill". Sources *''The prehistoric people of Accokeek Creek'', p. 25 References External linksThe First MarylandersDelaware CREP page Algonquian peoples Extinct Native American tribes Native American tribes in Maryland {{NorthAm-native-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accokeek Creek Site
Accokeek Creek Site, also known as Moyaone, is an archaeological site in Prince George's County, Maryland, located along the Potomac River across from Mount Vernon in today's Piscataway Park, which was inhabited intermittently since 2000 BC. Accokeek Creek Site was declared a National Historic Landmark in 1964. Description The National Park Service describes the site as "remarkable for its variety and concentration of human occupation sites. Accokeek included a palisaded village that was occupied from ca. A.D. 1300 to ca. 1630. The site has been used by archeologists to define a culture-history sequence in prehistoric archaeology for the Mid-Atlantic region." The site dates from the Late Archaic Period, ca. 3,000 BC, to the historic period. During the Middle Woodland Period, ca. AD 800, small horticultural villages were established. The village called Moyaone appeared during the late-16th and early-17th centuries. Moyaone, also named the Accokeek Creek site, is the sister site ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federally Recognized Tribes
This is a list of federally recognized tribes in the contiguous United States. There are also federally recognized Alaska Native tribes. , 574 Indian tribes are legally recognized by the Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA) of the United States.Federal Acknowledgment of the Pamunkey Indian Tribe Of these, 228 are located in Alaska, and 109 are located in California. Of the 574 federally recognized tribes, 346 are located in the contiguous United States. Description [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |